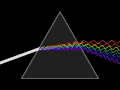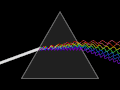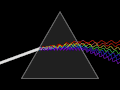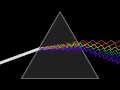
Crown glass article Applied photographic optics Book Book- The properties of optical glass Handbook of Ceramics, Glasses, and Diamonds Optical glass construction...
4 KB (393 words) - 19:50, 21 August 2024
Crown glass is either of two kinds of glass: Crown glass (window) was a type of hand-blown window glass. Crown glass (optics) is a type of optical glass...
198 bytes (64 words) - 04:13, 28 December 2019
potash lead glass that was the precursor to English lead crystal. Wikimedia Commons has media related to Flint glass. Crown glass (optics) Chromatic aberration...
2 KB (233 words) - 14:56, 19 August 2024
Gradient-index (GRIN) optics is the branch of optics covering optical effects produced by a gradient of the refractive index of a material. Such gradual...
14 KB (1,858 words) - 22:50, 7 December 2023
Then, by adding phosphates and fluorides, phosphate crowns and fluorine crowns were obtained. As optics became increasingly complex and diverse, manufacturers'...
70 KB (7,700 words) - 00:44, 26 October 2024
Optical fiber (redirect from Fiber optics)
Attenuation coefficients in fiber optics are usually expressed in units of dB/km. The medium is usually a fiber of silica glass that confines the incident light...
99 KB (12,099 words) - 04:54, 15 November 2024
Uranium glass is glass which has had uranium, usually in oxide diuranate form, added to a glass mix before melting for colouration. The proportion usually...
12 KB (1,363 words) - 23:34, 18 November 2024
tableware, and optics. Some common objects made of glass are named after the material, e.g. "glass", "glasses", "magnifying glass". Glass is most often...
89 KB (9,110 words) - 04:05, 23 November 2024
Fused quartz (redirect from Quartz glass)
photography, as the quartz glass can be transparent at much shorter wavelengths than lenses made with more common flint or crown glass formulas. Fused quartz...
21 KB (2,394 words) - 15:12, 19 August 2024
Glass microspheres are microscopic spheres of glass manufactured for a wide variety of uses in research, medicine, consumer goods and various industries...
9 KB (1,088 words) - 06:47, 13 July 2024
Borosilicate glass is a type of glass with silica and boron trioxide as the main glass-forming constituents. Borosilicate glasses are known for having...
30 KB (3,648 words) - 02:06, 1 September 2024
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments...
106 KB (12,873 words) - 20:20, 18 November 2024
Glass-ceramics are polycrystalline materials produced through controlled crystallization of base glass, producing a fine uniform dispersion of crystals...
27 KB (3,634 words) - 23:18, 26 June 2024
toughened glass is a type of safety glass processed by controlled thermal or chemical treatments to increase its strength compared with normal glass. Tempering...
20 KB (2,586 words) - 22:56, 19 November 2024
The glass–liquid transition, or glass transition, is the gradual and reversible transition in amorphous materials (or in amorphous regions within semicrystalline...
58 KB (6,792 words) - 08:56, 30 September 2024
Lead glass, commonly called crystal, is a variety of glass in which lead replaces the calcium content of a typical potash glass. Lead glass contains typically...
34 KB (4,076 words) - 23:23, 22 November 2024
Fluorite (redirect from Fluorite glass)
apochromatic lenses, and particularly valuable in photographic optics. Fluorite optics are also usable in the far-ultraviolet and mid-infrared ranges...
34 KB (3,738 words) - 14:08, 7 November 2024
Glass fiber (or glass fibre) is a material consisting of numerous extremely fine fibers of glass. Glassmakers throughout history have experimented with...
29 KB (3,633 words) - 16:50, 30 September 2024
frequency. Sometimes the term chromatic dispersion is used to refer to optics specifically, as opposed to wave propagation in general. A medium having...
33 KB (3,422 words) - 21:57, 23 November 2024
Ernst Abbe (category History of glass)
Abbe–Porro prism Aberration in optical systems Crown glass (optics) Dermatoscopy Diaphragm (optics) Calculation of glass properties Optical aberration Optical...
41 KB (3,391 words) - 03:49, 12 September 2024
McCamly (1949). Milk glass. Crown Publishers. p. 327. ISBN 9780517097403. Chiarenza, Frank; James Slater (2007). The Milk Glass Book. A Schiffer book...
6 KB (618 words) - 21:51, 31 August 2024
Zerodur (category Glass types)
in telescope optics, microlithography machines and inertial navigation systems. The main applications for Zerodur include telescope optics in astronomy...
12 KB (1,007 words) - 12:50, 28 October 2024
Borophosphosilicate glass, commonly known as BPSG, is a type of silicate glass that includes additives of both boron and phosphorus. Silicate glasses such...
2 KB (174 words) - 03:13, 31 July 2024
Cobalt glass—known as "smalt" when ground as a pigment—is a deep blue coloured glass prepared by including a cobalt compound, typically cobalt oxide or...
10 KB (1,124 words) - 21:48, 24 July 2024
Crossing (physics) Crosswind Crow instability Crowbar (circuit) Crown glass (optics) CryoEDM Cryocooler Cryoelectronics Cryogenic Dark Matter Search...
27 KB (2,788 words) - 23:35, 20 October 2024
Soda–lime glass, also called soda–lime–silica glass, is the transparent glass, used for windowpanes and glass containers (bottles and jars) for beverages...
11 KB (961 words) - 06:45, 23 November 2024
Phosphosilicate glass, commonly referred to by the acronym PSG, is a silicate glass commonly used in semiconductor device fabrication for intermetal layers...
2 KB (134 words) - 07:47, 27 September 2023
A glass electrode is a type of ion-selective electrode made of a doped glass membrane that is sensitive to a specific ion. The most common application...
19 KB (2,386 words) - 13:28, 11 September 2024
Fiberglass (redirect from Glass reinforced plastic)
plastic using glass fiber. The fibers may be randomly arranged, flattened into a sheet called a chopped strand mat, or woven into glass cloth. The plastic...
39 KB (4,795 words) - 01:53, 8 November 2024
When glass ionomer cements were first used, they were mainly used for the restoration of abrasion/erosion lesions and as a luting agent for crown and bridge...
42 KB (4,847 words) - 21:03, 15 March 2024