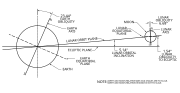
the Earth's orbit of the maximum tilt of the Earth's axis, toward the Sun or away from the Sun) and the equinoxes (the two points in the Earth's orbit where...
17 KB (1,874 words) - 21:16, 6 November 2024
the Earth's surface is much less than the Earth's radius. However, an object in orbit is in a permanent free fall around Earth, because in orbit the gravitational...
19 KB (2,126 words) - 18:36, 21 November 2024
Earth orbit may refer to: Earth's orbit, the orbit of the Earth around the Sun Low Earth orbit, an orbit around the Earth Geocentric orbit, an orbit around...
266 bytes (68 words) - 03:27, 12 August 2024
above Earth's equator, 42,164 km (26,199 mi) in radius from Earth's center, and following the direction of Earth's rotation. An object in such an orbit has...
49 KB (4,882 words) - 17:29, 19 November 2024
geosynchronous orbit, in which a satellite takes 24 hours to circle the Earth, the same period as the Earth’s own rotation. All satellites in MEO have an orbital period...
10 KB (1,037 words) - 23:27, 10 October 2024
A geosynchronous orbit (sometimes abbreviated GSO) is an Earth-centered orbit with an orbital period that matches Earth's rotation on its axis, 23 hours...
33 KB (3,226 words) - 04:30, 12 November 2024
synodic month). Earth and the Moon orbit about their barycentre (common centre of mass), which lies about 4,670 km (2,900 miles) from Earth's centre (about...
37 KB (4,642 words) - 18:48, 20 November 2024
high Earth orbit is a geocentric orbit with an apogee farther than that of the geosynchronous orbit, which is 35,786 km (22,236 mi) away from Earth. In...
7 KB (602 words) - 22:39, 24 September 2024
the orbit is not fixed in space relative to the distant stars, but rotates slowly about the Earth's axis. Typical Sun-synchronous orbits around Earth are...
14 KB (1,657 words) - 07:15, 21 October 2024
Lagrange point (redirect from Lagrange orbit)
opposite side of Earth from the Sun, the orbital period of an object would normally be greater than Earth's. The extra pull of Earth's gravity decreases...
51 KB (5,703 words) - 01:24, 30 October 2024
water. Almost all of Earth's water is contained in its global ocean, covering 70.8% of Earth's crust. The remaining 29.2% of Earth's crust is land, most...
218 KB (19,311 words) - 18:44, 20 November 2024
Earth's Moon. Areocentric orbit (named after Ares): An orbit around the planet Mars, such as that of its moons or artificial satellites. For orbits centered...
31 KB (3,455 words) - 19:37, 27 October 2024
the Sun (passing Earth's orbit), and roughly 1 km/s at aphelion 35 AU (5.2 billion km) from the Sun. Objects passing Earth's orbit going faster than...
11 KB (1,410 words) - 01:29, 7 October 2024
times when it is far from making a close approach of Earth. If an NEO's orbit crosses the Earth's orbit, and the object is larger than 140 meters (460 ft)...
148 KB (15,529 words) - 02:09, 13 November 2024
A geocentric orbit, Earth-centered orbit, or Earth orbit involves any object orbiting Earth, such as the Moon or artificial satellites. In 1997, NASA estimated...
17 KB (1,997 words) - 14:43, 5 September 2024
{1+e}{1-e}}} For Earth, orbital eccentricity e ≈ 0.01671, apoapsis is aphelion and periapsis is perihelion, relative to the Sun. For Earth's annual orbit path, the...
25 KB (2,767 words) - 19:34, 21 October 2024
with an orbital period of 12 hours." Both geosynchronous orbit (GSO) and geostationary orbit (GEO) are orbits around Earth matching Earth's sidereal...
57 KB (8,123 words) - 14:46, 21 November 2024
geostationary [Earth] orbit (GEO) exhibit a 53-year cycle of orbital inclination due to the interaction of the Earth's tilt with the lunar orbit. The orbital inclination...
8 KB (1,003 words) - 02:20, 12 October 2024
transfer orbit (GTO) or geosynchronous transfer orbit is a highly elliptical type of geocentric orbit, usually with a perigee as low as low Earth orbit (LEO)...
13 KB (1,801 words) - 19:57, 9 August 2024
Axial tilt (redirect from Earth's inclination)
the Earth's orbital axis is the line perpendicular to the imaginary plane through which the Earth moves as it revolves around the Sun; the Earth's obliquity...
33 KB (3,103 words) - 21:08, 4 October 2024
the plane in which the Earth orbits the Sun. This reference plane is most practical for Earth-based observers. Therefore, Earth's inclination is, by definition...
11 KB (1,465 words) - 15:40, 23 October 2023
Satellite (redirect from Earth satellite)
exploration outside of Earth, and space stations are in essence crewed satellites. The first artificial satellite launched into the Earth's orbit was the Soviet...
61 KB (6,356 words) - 10:15, 21 November 2024
take advantage of the Earth's rotational velocity. Depending on the location of the launch site and the inclination of the polar orbit, the launch vehicle...
3 KB (416 words) - 15:33, 8 January 2024
to Earth and the Sun) differs from the tropical period owing to Earth's motion around the Sun. For example, the synodic period of the Moon's orbit as...
17 KB (2,059 words) - 22:31, 24 October 2024
to raise a satellite's orbit from low Earth orbit to geostationary orbit. In the idealized case, the initial and target orbits are both circular and coplanar...
27 KB (3,626 words) - 18:17, 19 September 2024
Spaceflight (redirect from Difference between sub-orbital and orbital spaceflights)
spacecraft such as satellites in orbit around Earth, but also includes space probes for flights beyond Earth orbit. Such spaceflights operate either...
60 KB (6,987 words) - 18:44, 15 November 2024
Orbital forcing is the effect on climate of slow changes in the tilt of the Earth's axis and shape of the Earth's orbit around the Sun (see Milankovitch...
11 KB (1,159 words) - 04:49, 20 June 2024
orbit. Low Earth orbit A low Earth orbit (LEO) typically is a circular orbit about 160 to 2,000 kilometres (99 to 1,243 mi) above the Earth's surface and...
50 KB (5,949 words) - 15:01, 26 October 2024
Earth's rotation or Earth's spin is the rotation of planet Earth around its own axis, as well as changes in the orientation of the rotation axis in space...
43 KB (4,885 words) - 16:45, 12 November 2024
Apsis (category Orbits)
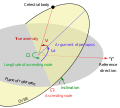
solar orbit. The Moon's two apsides are the farthest point, apogee, and the nearest point, perigee, of its orbit around the host Earth. Earth's two apsides...
42 KB (3,906 words) - 14:59, 3 November 2024