In Euclidean geometry, a plane is a flat two-dimensional surface that extends indefinitely. Euclidean planes often arise as subspaces of three-dimensional...
17 KB (2,819 words) - 16:27, 10 June 2025
the three-dimensional Euclidean space, that is, the Euclidean space of dimension three, which models physical space. More general three-dimensional spaces...
34 KB (4,825 words) - 21:40, 24 June 2025
the three-dimensional space of Euclidean geometry, but in modern mathematics there are Euclidean spaces of any positive integer dimension n, which are...
47 KB (6,967 words) - 08:16, 28 June 2025
In mathematics, a Euclidean plane is a Euclidean space of dimension two, denoted E 2 {\displaystyle {\textbf {E}}^{2}} or E 2 {\displaystyle \mathbb {E}...
16 KB (1,967 words) - 02:25, 31 May 2025
two coordinates or they can move in two independent directions. Common two-dimensional spaces are often called planes, or, more generally, surfaces. These...
7 KB (803 words) - 22:02, 19 August 2024
In mathematics, the group of rotations about a fixed point in four-dimensional Euclidean space is denoted SO(4). The name comes from the fact that it is...
37 KB (5,718 words) - 03:50, 1 March 2025
Four-dimensional space (4D) is the mathematical extension of the concept of three-dimensional space (3D). Three-dimensional space is the simplest possible...
45 KB (5,284 words) - 21:23, 27 June 2025
is six-dimensional Euclidean space, in which 6-polytopes and the 5-sphere are constructed. Six-dimensional elliptical space and hyperbolic spaces are also...
14 KB (2,020 words) - 08:13, 22 November 2024
indefinitely extended in a two-dimensional plane that are both perpendicular to a third line (in the same plane): In Euclidean geometry, the lines remain...
45 KB (6,066 words) - 03:48, 14 May 2025
in the Euclidean plane The distance from a point to a plane in three-dimensional Euclidean space The distance between two lines in three-dimensional Euclidean...
26 KB (3,288 words) - 16:41, 30 April 2025
the physical world. However, the three-dimensional "space part" of the Minkowski space remains the space of Euclidean geometry. This is not the case with...
60 KB (7,199 words) - 23:16, 13 June 2025
dimension) and three-dimensional space. When working exclusively in two-dimensional Euclidean space, the definite article is used, so the Euclidean plane...
7 KB (1,672 words) - 16:13, 9 June 2025
In mathematics, a Euclidean group is the group of (Euclidean) isometries of a Euclidean space E n {\displaystyle \mathbb {E} ^{n}} ; that is, the transformations...
16 KB (2,147 words) - 02:29, 16 December 2024
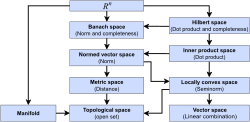
In mathematics, an affine space is a geometric structure that generalizes some of the properties of Euclidean spaces in such a way that these are independent...
48 KB (7,537 words) - 05:07, 13 April 2025
A two-dimensional Euclidean space is a two-dimensional space on the plane. The inside of a cube, a cylinder or a sphere is three-dimensional (3D) because...
35 KB (3,933 words) - 07:35, 25 June 2025
Honeycomb (geometry) (redirect from Three-dimensional Euclidean tesselation)
be cell-transitive or isochoric. In the 3-dimensional euclidean space, a cell of such a honeycomb is said to be a space-filling polyhedron. A necessary...
14 KB (1,321 words) - 13:44, 6 May 2025
a Euclidean space of dimension n, En (Euclidean line, E; Euclidean plane, E2; Euclidean three-dimensional space, E3) form a real coordinate space of...
31 KB (4,248 words) - 16:09, 26 June 2025
projective space may thus be viewed as the extension of a Euclidean space, or, more generally, an affine space with points at infinity, in such a way...
37 KB (5,670 words) - 20:15, 2 March 2025
Hyperbolic geometry (redirect from Gauss-Bolyai-Lobachevsky space)
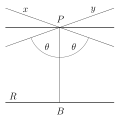
geometry. The parallel postulate of Euclidean geometry is replaced with: For any given line R and point P not on R, in the plane containing both line R and point...
56 KB (6,970 words) - 13:36, 7 May 2025
In mathematics, a zero-dimensional topological space (or nildimensional space) is a topological space that has dimension zero with respect to one of several...
4 KB (397 words) - 00:57, 17 August 2024
that exist in five-dimensional space. Four-dimensional space — a foundational step to understanding five-dimensional extensions. 5D Euclidean geometry designated...
9 KB (811 words) - 11:44, 30 June 2025
interval in spacetime between events. Minkowski space differs from four-dimensional Euclidean space insofar as it treats time differently from the three spatial...
79 KB (10,493 words) - 03:35, 7 June 2025
one-dimensional space, regardless of the dimension of the ambient space in which the line or curve is embedded. Examples include the circle on a plane, or...
3 KB (398 words) - 23:21, 25 December 2024
Elliptic geometry (redirect from Elliptic space)
"elliptic space" to refer specifically to 3-dimensional elliptic geometry. This is in contrast to the previous section, which was about 2-dimensional elliptic...
18 KB (2,656 words) - 19:30, 16 May 2025
the points of a three-dimensional Euclidean space are uniquely determined by Euclid's axioms, and all three-dimensional Euclidean spaces are considered...
69 KB (9,328 words) - 07:59, 25 June 2025
called 7-dimensional space. Often such a space is studied as a vector space, without any notion of distance. Seven-dimensional Euclidean space is seven-dimensional...
5 KB (499 words) - 00:42, 11 December 2024
3-manifold (redirect from Three-dimensional manifold)
In mathematics, a 3-manifold is a topological space that locally looks like a three-dimensional Euclidean space. A 3-manifold can be thought of as a possible...
45 KB (5,821 words) - 09:01, 24 May 2025
Solid geometry (redirect from Three-dimensional geometry)
the geometry of three-dimensional Euclidean space (3D space). A solid figure is the region of 3D space bounded by a two-dimensional closed surface; for...
9 KB (387 words) - 12:38, 17 June 2025
called 8-dimensional space. Often such spaces are studied as vector spaces, without any notion of distance. Eight-dimensional Euclidean space is eight-dimensional...
7 KB (718 words) - 02:17, 21 May 2025
Space is a three-dimensional continuum containing positions and directions. In classical physics, physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions...
35 KB (4,436 words) - 02:25, 31 March 2025