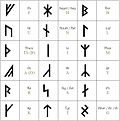
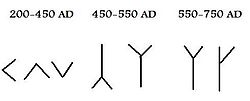
symbols instead of runes. The Elder Futhark (or Fuþark), also known as the Older Futhark, Old Futhark, or Germanic Futhark, is the oldest form of the runic...
33 KB (3,832 words) - 23:13, 5 August 2024
instead of runes. The Younger Futhark, also called Scandinavian runes, is a runic alphabet and a reduced form of the Elder Futhark, with only 16 characters...
14 KB (1,401 words) - 22:13, 14 October 2024
Algiz (redirect from Yr rune (Younger Futhark))
Elhaz) is the name conventionally given to the "z-rune" ᛉ of the Elder Futhark runic alphabet. Its transliteration is z, understood as a phoneme of the...
24 KB (2,886 words) - 20:10, 6 November 2024
Othala (section Elder Futhark o-rune)
and odal, is a rune that represents the o and œ phonemes in the Elder Futhark and the Anglo-Saxon Futhorc writing systems respectively. Its name is derived...
21 KB (2,266 words) - 12:42, 1 November 2024
Runic inscriptions (redirect from Alemannic Elder Futhark inscriptions)
The body of runic inscriptions falls into the three categories of Elder Futhark (some 350 items, dating to between the 2nd and 8th centuries AD), Anglo-Frisian...
22 KB (2,639 words) - 05:27, 4 February 2024
Elder Futhark, expanding to 28 characters in its older form and up to 34 characters in its younger form. In contemporary Scandinavia, the Elder Futhark developed...
36 KB (2,474 words) - 11:09, 1 November 2024
Jēran (section Elder Futhark)
Jeran, Jeraz, Yera) is the conventional name of the j-rune ᛃ of the Elder Futhark, from a reconstructed Common Germanic stem *jēra- meaning "harvest, (good)...
8 KB (869 words) - 18:00, 5 October 2024
Ansuz (rune) (section Development in Younger Futhark)
runes. Ansuz is the conventional name given to the a-rune of the Elder Futhark, ᚨ. The name is based on Proto-Germanic *ansuz, denoting a deity belonging...
5 KB (288 words) - 00:03, 21 July 2024
second rune in all runic alphabets (futharks), i.e. Germanic Elder Futhark, Anglo-Frisian Futhark and Norse Younger Futhark. It corresponds to the letter u...
14 KB (1,190 words) - 12:38, 30 October 2024
needed] Elder Futhark Sowilo rune, earlier ("Σ") variant. Elder Futhark Sowilo rune, later ("S") variant. Anglo-Saxon Sigel / Younger Futhark Sol rune Anglo-Saxon...
9 KB (854 words) - 03:07, 17 June 2024
reconstruct the Elder Futhark rune's Proto-Germanic name. Assuming that the Scandinavian name þurs is the most plausible reflex of the Elder Futhark name, a Common...
5 KB (436 words) - 08:01, 5 November 2024
Armanen Futharkh) are 18 pseudo-runes, inspired by the historic Younger Futhark runes, invented by Austrian mysticist and Germanic revivalist Guido von...
17 KB (1,925 words) - 11:48, 3 October 2024
at the end of an Elder Futhark inscription. From 500 AD, a Scandinavian C-bracteate (Seeland-II-C) features an Elder Futhark inscription ending with...
11 KB (963 words) - 04:57, 27 May 2024
Futhark is a multi-paradigm, high-level, functional, data parallel, array programming language. It is a dialect of the language ML, originally developed...
5 KB (452 words) - 23:36, 30 October 2024
in particular seem to have had magical significance in the early (Elder Futhark) period.[citation needed] The Sigrdrífumál instruction of "name Tyr twice"...
23 KB (3,004 words) - 17:03, 28 August 2024
marks, boxes, or other symbols instead of runes. The k-rune ᚲ (Younger Futhark ᚴ, Anglo-Saxon futhorc ᚳ) is called Kaun in both the Norwegian and Icelandic...
4 KB (209 words) - 06:13, 17 December 2023
Gothic alphabet 𐌳 d is called dags. This rune is also part of the Elder Futhark, with a reconstructed Proto-Germanic name *dagaz. Its "butterfly" shape...
3 KB (227 words) - 03:35, 30 July 2024
alphabet is 𐌲 g, called giba. The same rune also appears in the Elder Futhark, with a suggested Proto-Germanic name *gebô 'gift'. J. H. Looijenga speculates...
4 KB (373 words) - 16:51, 6 June 2023
(Old Norse fé; Old English feoh) represents the ⟨f⟩ sound in the Younger Futhark and Futhorc alphabets. Its name means '(mobile) wealth', cognate to English...
3 KB (192 words) - 14:31, 16 October 2024
as hægl, and, in the Younger Futhark, as ᚼ hagall. The corresponding Gothic letter is 𐌷 h, named hagl. The Elder Futhark letter has two variants, single-barred...
3 KB (188 words) - 21:22, 5 April 2024
slightly modified from Dickins (1915) It is not continued in the Younger Futhark, but in the Gothic alphabet, the letter 𐍅 w is called winja, allowing...
6 KB (537 words) - 10:19, 6 July 2024
accurately Ingvaeones, and is also the reconstructed name of the Elder Futhark rune ᛜ and Anglo-Saxon rune ᛝ, representing ŋ. Old Norse Yngvi as well...
12 KB (1,346 words) - 18:25, 9 August 2024
intended for the representation of text written in Elder Futhark, Anglo-Saxon runes, Younger Futhark (both in the long-branch and short-twig variants), Scandinavian...
30 KB (1,030 words) - 16:28, 26 July 2024
reconstructed Proto-Germanic name of the b rune ᛒ, meaning "birch". In the Younger Futhark it is called Bjarkan in the Icelandic and Norwegian rune poems. In the...
3 KB (127 words) - 08:57, 20 June 2023
In the Anglo-Saxon rune poem, it is called lagu "ocean". In the Younger Futhark, the rune is called lögr "waterfall" in Icelandic and logr "water" in Norse...
3 KB (173 words) - 19:43, 5 July 2024
of the Elder Futhark. It is derived from the reconstructed Proto-Germanic (or Common Germanic) word for 'man', *mannaz. The Younger Futhark equivalent ᛘ...
3 KB (167 words) - 22:53, 16 July 2024
reconstructed Proto-Germanic name of the i-rune ᛁ, meaning "ice". In the Younger Futhark, it is called íss in Old Norse. As a rune of the Anglo-Saxon futhorc, it...
2 KB (94 words) - 12:27, 13 April 2023
History of the Runic Script, Typology and Graphic Variation in the Older Futhark, Uppsala, ISBN 91-85352-20-9{{citation}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher...
4 KB (437 words) - 19:07, 23 June 2024
the sixth century onward. The letters of the Elder Futhark are arranged in an order called the futhark, so named after its first six characters. The alphabet...
163 KB (20,237 words) - 12:30, 30 October 2024