Stone Age (subdivided into the Paleolithic, Mesolithic and Neolithic) and Bronze Age. These concepts originated for describing Iron Age Europe and the...
68 KB (6,697 words) - 12:21, 8 August 2024
In Europe, the Iron Age is the last stage of the prehistoric period and the first of the protohistoric periods, which initially meant descriptions of a...
32 KB (4,196 words) - 12:54, 8 July 2024
British Iron Age is a conventional name used in the archaeology of Great Britain, referring to the prehistoric and protohistoric phases of the Iron Age culture...
37 KB (4,443 words) - 01:05, 17 July 2024
cultural contact with the Central European La Tène culture (Celts), contributing to the development of the Iron Age by the 4th century BC, presumably...
23 KB (2,449 words) - 12:31, 17 July 2024
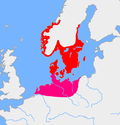
Iron Age Scandinavia (or Nordic Iron Age) was the Iron Age, as it unfolded in Scandinavia. It was preceded by the Nordic Bronze Age. The 6th and 5th centuries...
9 KB (725 words) - 17:07, 11 September 2023
subcontinent, the Iron Age succeeded Bronze Age India and partly corresponds with the megalithic cultures of India. Other Iron Age archaeological cultures...
6 KB (787 words) - 14:04, 12 August 2024
Ferrous metallurgy (redirect from Iron Age metallurgy)
wrought iron (worked iron) was known by the 1st millennium BC, and its spread defined the Iron Age. During the medieval period, smiths in Europe found a...
68 KB (8,412 words) - 11:09, 31 July 2024
Swords made of iron (as opposed to bronze) appear from the Early Iron Age (c. 12th century BC),[citation needed] but do not become widespread before the...
11 KB (1,456 words) - 00:51, 20 January 2024
Northern Europe, the Germanic Iron Age is taken to last until the beginning of the Viking Age, c. AD 800. The term "Iron Age" is mostly limited to Europe, the...
16 KB (267 words) - 00:33, 16 April 2024
some frequency on artefacts dated to the Germanic Iron Age, i.e. the Migration period to Viking Age period in Scandinavia, including the Vendel era in...
7 KB (803 words) - 19:29, 18 September 2023
periods in a few regions) into three time-periods: the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age, although the concept may also refer to other tripartite...
88 KB (11,477 words) - 20:45, 27 July 2024
Prehistoric religion (redirect from Bronze and Iron Age religion)
through shared religious elements between early Indo-European language speakers. Bronze Age and Iron Age religions are understood in part through archaeological...
164 KB (19,603 words) - 14:20, 22 May 2024
The stone circles of the Iron Age (c. 500 BC – c. 400 AD) were a characteristic burial custom of southern Scandinavia and Southwestern Finland, especially...
4 KB (457 words) - 13:55, 8 November 2023
The Bronze and Iron Age cultures in Poland are known mainly from archeological research. Early Bronze Age cultures in Poland began around 2400–2300 BCE...
41 KB (5,495 words) - 21:18, 22 June 2024
Age succeeds the Neolithic and Copper Age and is followed by the Iron Age. It starts with the Aegean Bronze Age in 3200 BC and spans the entire 2nd millennium...
26 KB (2,919 words) - 00:38, 12 August 2024
Hillfort (redirect from Iron Age Hill Towns)
elevation for defensive advantage. They are typical of the late European Bronze Age and Iron Age. Some were used in the post-Roman period. The fortification...
35 KB (4,113 words) - 01:17, 9 August 2024
Prehistory (redirect from Prehistoric age)
prehistory during the following Iron Age. The three-age division of prehistory into Stone Age, Bronze Age, and Iron Age remains in use for much of Eurasia...
55 KB (5,873 words) - 22:30, 27 July 2024
civilization. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of the three-age system, between the Stone and Iron Ages. Worldwide, the Bronze Age generally followed...
107 KB (12,210 words) - 22:15, 12 August 2024
reduced iron (DRI), also called sponge iron, is produced from the direct reduction of iron ore (in the form of lumps, pellets, or fines) into iron by a reducing...
10 KB (1,354 words) - 04:29, 10 August 2024
Ancient history (redirect from Ancient age)
period 3000 BC – AD 500. The three-age system periodizes ancient history into the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age, with recorded history generally...
98 KB (11,795 words) - 08:18, 13 August 2024
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period (also spelt mediaeval or mediæval) lasted from approximately 500 to 1500 AD. It is the second...
172 KB (20,119 words) - 13:59, 10 August 2024
eds., The Bronze Age: Iron Age Transition in Europe (Oxford) 1989, and T.A. Wertime and J.D. Muhly, The Coming of the Age of Iron (New Haven) 1980. Palmer...
68 KB (8,879 words) - 19:02, 7 August 2024
Chalcolithic (redirect from Chalcolithic Age)
from Copper Age to Bronze Age in Europe occurred between the late 5th and the late 3rd millennium BC. In the Ancient Near East the Copper Age covered about...
30 KB (3,329 words) - 09:16, 4 August 2024
Bloomery (redirect from Iron bloom)
smelting iron from its oxides. The bloomery was the earliest form of smelter capable of smelting iron. Bloomeries produce a porous mass of iron and slag...
25 KB (3,200 words) - 00:27, 1 July 2024
Interreg Danube Transnational Programme of the European Union. In the Iron-Age-Danube project the early Iron Age landscapes in the Danube river basin are explored...
3 KB (341 words) - 11:13, 7 January 2022
Neolithic (redirect from Neolithic Age)
New Stone Age (from Greek νέος néos 'new' and λίθος líthos 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Europe, Asia and...
77 KB (7,916 words) - 22:32, 7 August 2024
Roman Iron Age weapon deposits are intentional burials of large quantities of weapons from the Roman Iron Age of Scandinavia. The weapon deposits were...
7 KB (880 words) - 15:03, 20 July 2024
Empire. The early Celtic culture dominate Central Europe while Northern Europe is in the Pre-Roman Iron Age. In East Africa, the Nubian Empire and Aksum arise...
27 KB (1,651 words) - 19:50, 16 July 2024
Triskelion (section Neolithic to Iron Age)
human limbs. It occurs in artifacts of the European Neolithic and Bronze Ages with continuation into the Iron Age – especially in the context of the La Tène...
21 KB (2,228 words) - 23:37, 10 August 2024
Upper Paleolithic (redirect from Reindeer Age)
Palaeolithic) is the third and last subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. Very broadly, it dates to between 50,000 and 12,000 years ago (the beginning...
45 KB (4,690 words) - 21:15, 3 August 2024