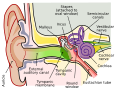
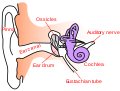
middle ear is the portion of the ear medial to the eardrum, and distal to the oval window of the cochlea (of the inner ear). The mammalian middle ear...
20 KB (2,590 words) - 19:40, 29 July 2024
Middle ear barotrauma (MEBT), also known to underwater divers as ear squeeze and reverse ear squeeze, is an injury caused by a difference in pressure between...
20 KB (2,227 words) - 09:30, 13 August 2024
parts: the outer ear, the middle ear and the inner ear. The outer ear consists of the pinna and the ear canal. Since the outer ear is the only visible...
60 KB (6,966 words) - 08:25, 19 August 2024
Cholesteatoma (redirect from Cholesteatoma, middle ear)
expanding growth consisting of keratinizing squamous epithelium in the middle ear and/or mastoid process. Cholesteatomas are not cancerous as the name may...
27 KB (3,194 words) - 19:24, 29 July 2024
Otorhinolaryngology (redirect from Ear nose and throat)
ear or ear canal inflammation Exostoses or Surfer's ear are bony growths in the outer ear canal Middle ear and mastoid diseases Otitis media – middle...
15 KB (1,242 words) - 11:16, 25 August 2024
The ear canal (external acoustic meatus, external auditory meatus, EAM) is a pathway running from the outer ear to the middle ear. The adult human ear canal...
5 KB (535 words) - 21:52, 3 May 2024
Barotrauma (redirect from Ear fear)
and decompression events. Barotrauma generally manifests as sinus or middle ear effects, lung overpressure injuries and injuries resulting from external...
77 KB (8,034 words) - 14:33, 7 August 2024
Middle ear implants work by improving the conduction of sound vibrations from the middle ear to the inner ear. There are two types of middle ear devices:...
9 KB (1,204 words) - 22:21, 25 May 2024
Eustachian tube (redirect from Middle ear inflation)
tetrapods, both the middle ear and the ear canal are normally filled with air. Unlike the air of the ear canal, however, the air of the middle ear is not in direct...
22 KB (2,610 words) - 21:51, 3 May 2024
Otitis media (redirect from Middle ear infection)
diseases of the middle ear. One of the two main types is acute otitis media (AOM), an infection of rapid onset that usually presents with ear pain. In young...
70 KB (7,273 words) - 06:58, 21 August 2024
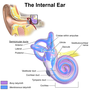
The inner ear (internal ear, auris interna) is the innermost part of the vertebrate ear. In vertebrates, the inner ear is mainly responsible for sound...
21 KB (2,852 words) - 20:25, 4 June 2024
Otitis (redirect from Ear infection)
is a general term for inflammation in ear or ear infection, inner ear infection, middle ear infection of the ear, in both humans and other animals. When...
6 KB (491 words) - 17:15, 27 August 2024
Hearing (section Middle ear)
system: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear. The outer ear includes the pinna, the visible part of the ear, as well as the ear canal, which terminates...
22 KB (2,638 words) - 22:09, 18 August 2024
Conductive hearing loss (section Middle ear)
waves anywhere along the pathway through the outer ear, tympanic membrane (eardrum), or middle ear (ossicles). If a conductive hearing loss occurs in...
12 KB (1,385 words) - 01:15, 13 August 2023
Tensor tympani muscle (category Ear)
The tensor tympani is a muscle within the middle ear, located in the bony canal above the bony part of the auditory tube, and connects to the malleus bone...
10 KB (1,276 words) - 05:29, 25 June 2024
Ear pain, also known as earache or otalgia, is pain in the ear. Primary ear pain is pain that originates from the ear. Secondary ear pain is a type of...
41 KB (3,953 words) - 20:12, 12 July 2024
Ossicles (redirect from Middle ear bone complex)
bones in either middle ear that are among the smallest bones in the human body. They serve to transmit sound vibrations sent from the ear drum to the fluid-filled...
11 KB (1,349 words) - 19:05, 30 May 2024
process that resulted in the formation of the bones of the mammalian middle ear. These bones, or ossicles, are a defining characteristic of all mammals...
40 KB (4,252 words) - 07:09, 9 August 2024
Acoustic reflex (redirect from Middle-ear-muscle reflex)
(also known as the stapedius reflex, stapedial reflex, auditory reflex, middle-ear-muscle reflex (MEM reflex, MEMR), attenuation reflex, cochleostapedial...
15 KB (1,760 words) - 05:02, 8 March 2024
Oral skills (section Middle ear)
injury. The middle ear is a cavity that is filled with air. The tympanic membrane separates the middle ear from the external ear. The middle ear is joined...
17 KB (2,332 words) - 18:58, 28 October 2023
The outer ear, external ear, or auris externa is the external part of the ear, which consists of the auricle (also pinna) and the ear canal. It gathers...
11 KB (1,238 words) - 01:40, 5 August 2024
Ear clearing, clearing the ears or equalization is any of various maneuvers to equalize the pressure in the middle ear with the outside pressure, by letting...
14 KB (1,696 words) - 19:40, 28 June 2024
Evolution of mammals (redirect from Evolution of the mammalian middle ear and jaw)
Other important research characteristics include the evolution of the middle ear bones, erect limb posture, a bony secondary palate, fur, hair, and warm-bloodedness...
141 KB (15,179 words) - 04:35, 13 August 2024
Otomycosis (redirect from Singapore ear)
Otomycosis is a fungal ear infection, a superficial mycotic infection of the outer ear canal caused by micro-organisms called fungi which are related...
6 KB (597 words) - 16:28, 29 May 2024
Human embryonic development (section Middle ear)
third to the eighth week the face and neck develop. The inner ear, middle ear and outer ear have distinct embryological origins. At about 22 days into development...
43 KB (5,259 words) - 16:16, 15 August 2024
Auditory system (section Middle ear)
vibrations to the eardrum, increasing the sound pressure in the middle frequency range. The middle-ear ossicles further amplify the vibration pressure roughly...
38 KB (4,516 words) - 14:47, 19 April 2024
Tinnitus (redirect from Ear ringing)
the middle ear. Spontaneous otoacoustic emissions (SOAEs)—faint high-frequency tones that are produced in the inner ear and can be measured in the ear canal...
80 KB (8,317 words) - 12:14, 26 August 2024
Tympanic membrane retraction (category Diseases of middle ear and mastoid)
maneuver increases middle ear pressure and can push a retracted eardrum out of the middle ear if it is not adherent to middle ear structures. Hearing...
15 KB (1,827 words) - 22:47, 12 January 2024
Audiology (redirect from Ear doctor)
where the lesion causing the hearing loss is found (outer ear, middle ear, inner ear, auditory nerve and/or central nervous system). If an audiologist...
17 KB (1,965 words) - 15:57, 26 August 2024