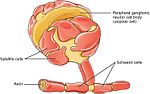
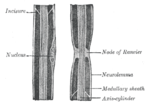
Schwann cells or neurolemmocytes (named after German physiologist Theodor Schwann) are the principal glia of the peripheral nervous system (PNS). Glial...
19 KB (2,450 words) - 00:59, 1 November 2024
considered to be the extension of cell theory to animals. Other contributions include the discovery of Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system,...
43 KB (4,434 words) - 09:12, 13 September 2024
Schwannoma (redirect from Schwann cell tumor)
(or neurilemmoma) is a usually benign nerve sheath tumor composed of Schwann cells, which normally produce the insulating myelin sheath covering peripheral...
10 KB (1,075 words) - 18:42, 9 September 2024
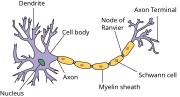
Dendrite Soma Axon Axon hillock Nucleus Node of Ranvier Axon terminal Schwann cell Myelin sheath Many vertebrate axons are surrounded by a myelin sheath...
24 KB (3,285 words) - 18:14, 29 May 2024
terminal Schwann cells, present at neuromuscular junctions, the Schwann cells of Remak fibers (also called Remak Schwann cells) and the Schwann cells associated...
2 KB (277 words) - 21:52, 7 April 2024
Neurilemma (redirect from Nucleated sheath of Schwann)
known as neurolemma, sheath of Schwann, or Schwann's sheath) is the outermost nucleated cytoplasmic layer of Schwann cells (also called neurilemmocytes)...
2 KB (186 words) - 20:34, 24 September 2022
Glia (redirect from Spider cell)
glial cells include oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, ependymal cells and microglia, and in the peripheral nervous system they include Schwann cells and satellite...
37 KB (3,800 words) - 03:06, 23 September 2024
Neurofibroma (section Schwann cells)
regulating the RAS-mediated cell growth signaling pathway. In contrast to schwannomas, another type of tumor arising from Schwann cells, neurofibromas incorporate...
30 KB (3,257 words) - 16:53, 28 October 2024
Perisynaptic schwann cells (also known as Terminal schwann cells or Teloglia) are neuroglia found at the Neuromuscular junction (NMJ) with known functions...
16 KB (2,255 words) - 01:58, 20 July 2023
Nerve injury (section Role of Schwann cells)
that essentially prepares the distal stump for reinnervation. Schwann cells are glial cells in the peripheral nervous system that support neurons by forming...
34 KB (4,113 words) - 01:03, 12 July 2024
macrophages. The macrophages, accompanied by Schwann cells, serve to clear the debris from the degeneration. Schwann cells respond to loss of axons by extrusion...
41 KB (5,083 words) - 00:04, 7 August 2024
Schwann may refer to: The Schwann cell Henry Schwann, English cricketer Theodor Schwann, a German physiologist, histologist and cytologist Schwann Records...
439 bytes (79 words) - 10:38, 17 April 2020
Oligodendrocyte (redirect from Oligodendroglial cell)
system (CNS) of jawed vertebrates. Their function is similar to that of Schwann cells, which perform the same task in the peripheral nervous system (PNS)...
27 KB (2,759 words) - 16:23, 27 October 2024
Soma (biology) (redirect from Cell body)
terminal Schwann cell Myelin sheath In cellular neuroscience, the soma (pl.: somata or somas; from Greek σῶμα (sôma) 'body'), neurocyton, or cell body is...
7 KB (817 words) - 05:35, 30 October 2024
neurolemmocytes (Schwann cells), which only myelinate a section of one axon. In the CNS, axons carry electrical signals from one nerve cell body to another...
33 KB (4,052 words) - 12:44, 23 September 2024
Matthias Jakob Schleiden and Theodor Schwann, states that all organisms are composed of one or more cells, that cells are the fundamental unit of structure...
60 KB (6,271 words) - 04:42, 20 August 2024
Nerve guidance conduit (section Schwann cells)
on Schwann cells. Lavdas et al. (2006) investigated whether sustained expression of PSA on Schwann cells enhances their migration. Schwann cells were...
106 KB (14,549 words) - 22:54, 1 July 2024
School of Medicine. In particular, she focused on researching Schwann cells, which are cells that wrap around the axon of neurons to form the myelin sheath...
14 KB (1,501 words) - 17:28, 25 June 2024
Mesaxon (category Glial cells)
membranes of a Schwann cell. It marks the point of edge-to-edge contact by the Schwann cell encircling the axon. A single Schwann cell of the peripheral...
2 KB (225 words) - 17:43, 28 November 2023
Theodor Schwann in 1838, who viewed live cells in plant and animal tissue, respectively. 19 years later, Rudolf Virchow further contributed to the cell theory...
41 KB (5,252 words) - 05:01, 2 November 2024
defined as the differentiation of oligodendrocyte progenitor cells (OPCs) or Schwann cell progenitors into their mature counterparts, followed by myelin...
17 KB (2,145 words) - 20:22, 23 November 2023
Theodor Schwann both also studied cells of both animal and plants. What they discovered were significant differences between the two types of cells. This...
26 KB (3,347 words) - 22:27, 9 September 2024
Neuron (redirect from Nerve cell)
Dendrite Soma Axon Axon hillock Nucleus Node of Ranvier Axon terminal Schwann cell Myelin sheath Neurons are highly specialized for the processing and transmission...
79 KB (9,153 words) - 06:43, 7 November 2024
formed by two types of glial cells: Schwann cells and oligodendrocytes. In the peripheral nervous system Schwann cells form the myelin sheath of a myelinated...
59 KB (6,983 words) - 23:19, 1 November 2024
medullary segments) are small pockets of cytoplasm left behind during the Schwann cell myelination process. They are histological evidence of the small amount...
2 KB (292 words) - 01:31, 20 July 2023
myelination is needed. The way in which the Schwann cells and oligodendrocytes myelinate nerves differ. A Schwann cell usually myelinates a single axon, completely...
34 KB (3,645 words) - 12:08, 24 October 2024
Anti-MAG peripheral neuropathy (category Glial cells)
Specifically, antibodies against myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG) damage Schwann cells. While the disorder occurs in only 10% of those afflicted with peripheral...
17 KB (2,039 words) - 18:54, 12 November 2023
Lactotroph Ameloblast Neuron Glia Schwann cell Satellite glial cell Chromaffin cell Glomus cell Melanocyte Nevus cell Merkel cell Odontoblast Cementoblast Corneal...
5 KB (366 words) - 04:28, 18 September 2024
Synaptogenesis (section Origin and movement of cells)
observation. The synapse itself is composed of three cells: the motor neuron, the myofiber, and the Schwann cell. In a normally functioning synapse, a signal...
26 KB (3,488 words) - 05:24, 13 March 2024
influenced by a number of factors in the PNS system. Some factors include Schwann cell characteristics, neurotrophic factors, and nerve branch size. These factors...
19 KB (2,307 words) - 15:46, 26 June 2024