Compared to earlier and contemporary cultures the Vučedol culture exploited a diversity in food sources: the Vučedol people were hunters, fishermen and...
23 KB (2,210 words) - 01:12, 2 April 2025
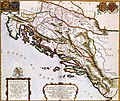
Danube, which also forms the border with Serbia. Vučedol became the eponym of the eneolithic Vučedol culture. It is estimated that the site had once been...
3 KB (301 words) - 14:53, 1 March 2024
Vučedol Culture Museum (Croatian: Muzej vučedolske kulture) is a museum of prehistoric culture in at Vučedol, near the city of Vukovar, Croatia. The museum...
5 KB (556 words) - 13:15, 20 October 2024
Vukovar (section Vučedol Culture Museum)
sites. The Vučedol culture, which developed in the Vučedol locality, is particularly significant for the Vukovar area. In 1938, the Vučedol dove was found...
100 KB (10,406 words) - 16:59, 14 April 2025
Bell Beaker culture complex as an amalgam of the Vučedol and Yamna culture, formed after the incursion of the Yamna people into the Vučedol milieu and...
183 KB (21,153 words) - 13:55, 15 April 2025
used, the Vučedol culture arose (c. 3000 BC – c. 2200 BC), named after the locality of Vučedol, on the bank of the Danube near Vukovar. Vučedol, near Vukovar...
10 KB (1,240 words) - 01:48, 7 April 2025
The Peiligang culture was a Neolithic culture in the Yi-Luo river basin (in modern Henan Province, China) that existed from about 7000 to 5000 BC. Over...
5 KB (466 words) - 22:07, 29 October 2023
reaching as far as the Adriatic coast. It was preceded by the Vučedol culture. The end of this culture is not clear. According to N. Tasic, its decline would...
5 KB (555 words) - 02:15, 1 November 2024
The Yamnaya culture or the Yamna culture, also known as the Pit Grave culture or Ochre Grave culture, is a late Copper Age to early Bronze Age archaeological...
69 KB (7,089 words) - 17:35, 15 April 2025
Romania belonging to the Wietenberg culture, a gold dagger from Mala Gruda in Montenegro belonging to the Vučedol culture, a gold dagger from Dabene in Bulgaria...
81 KB (8,469 words) - 10:03, 17 April 2025
Between 3000 BC and 2400 BC, Syrmia was at the centre of Indo-European Vučedol culture. Sirmium was conquered by Romans in the first century BC and became...
27 KB (2,872 words) - 01:34, 28 February 2025
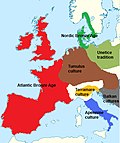
The Urnfield culture (c. 1300–750 BC) was a late Bronze Age culture of Central Europe, often divided into several local cultures within a broader Urnfield...
105 KB (11,179 words) - 18:27, 15 April 2025
Copper Age or Eneolithic findings are from Vučedol culture. Out of that culture, the Bronze Age Vinkovci culture (named after the city of Vinkovci) developed...
79 KB (8,000 words) - 19:55, 24 March 2025
Hunter-Gatherers. Ancient peoples of Italy Prehistoric Italy Terramare culture Vučedol culture Coles, John M.; Harding, A. F. (1979). The bronze age in Europe:...
11 KB (1,253 words) - 12:02, 10 March 2025
The Linear Pottery culture (LBK) is a major archaeological horizon of the European Neolithic period, flourishing c. 5500–4500 BC. Derived from the German...
79 KB (8,857 words) - 04:08, 3 April 2025
The first Indo-Europeans are thought to be members of eneolithic Vučedol culture. In the Bronze Age the area is thought to have been inhabited by Iron...
13 KB (1,235 words) - 23:25, 21 January 2025
The Tumulus culture (German: Hügelgräberkultur) was the dominant material culture in Central Europe during the Middle Bronze Age (c. 1600 to 1300 BC)...
27 KB (2,611 words) - 14:18, 15 April 2025
The Vinča culture [ʋîːnt͜ʃa], also known as Turdaș culture, Turdaș–Vinča culture or Vinča-Turdaș culture, is a Neolithic archaeological culture of Southeast...
36 KB (3,566 words) - 01:49, 3 April 2025
III - Kostolac-Vučedol A-B. During the evolution of the Coțofeni culture, there were clearly relationships with other neighbouring cultures. The influence...
8 KB (744 words) - 01:56, 3 April 2025
The Argaric culture, named from the type site El Argar near the town of Antas, in what is now the province of Almería in southeastern Spain, is an Early...
20 KB (2,113 words) - 01:18, 3 April 2025
Brak Tell Sabi Abyad Tell Arpachiyah Tepe Gawra Chagar Bazar The Halaf culture is a prehistoric period which lasted between about 6100 BC and 5100 BC...
11 KB (1,056 words) - 04:34, 17 June 2024
not biological. Prehistoric Europe Ezero culture Coțofeni culture Prehistory of Transylvania Vučedol culture Tünde Horváth, S. Éva Svingor, Mihály Molnár :...
14 KB (1,242 words) - 16:45, 2 April 2025
Al-Magar (category Neolithic cultures of Asia)
prehistoric culture of the Neolithic whose epicenter lay in modern-day southwestern Najd in Saudi Arabia. Al-Magar is possibly one of the first cultures in the...
5 KB (459 words) - 16:03, 11 December 2024
Hoti, Marina (December 1993). "Vučedol-Streimov vinograd: magijski ritual i dvojni grob vučedolske kulture" [Vučedol-Streim vineyard: the magical ritual...
22 KB (2,437 words) - 10:16, 6 September 2024
This is a list of Neolithic cultures of China that have been unearthed by archaeologists. They are sorted in chronological order from earliest to latest...
17 KB (606 words) - 13:07, 7 October 2024
describes the early Cetina culture as a "syncretistic Bell Beaker culture", splitting off from the dissolving variant of the Vučedol complex, and at the same...
18 KB (1,750 words) - 23:01, 14 January 2025
Terramare culture was a dominant component of the Proto-Villanovan culture—especially in its northern and Campanian phases and the Terramare culture has been...
17 KB (1,874 words) - 19:13, 15 January 2025
Nagyrév culture was a Bronze-Age culture that existed in what is now Nagyrév, Hungary. It existed alongside the Vatya culture and Hatvan cultures and was...
5 KB (481 words) - 11:24, 4 October 2024