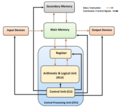
A CPU cache is a hardware cache used by the central processing unit (CPU) of a computer to reduce the average cost (time or energy) to access data from...
96 KB (13,298 words) - 19:32, 31 October 2024
When the cache client (a CPU, web browser, operating system) needs to access data presumed to exist in the backing store, it first checks the cache. If an...
31 KB (4,229 words) - 14:09, 13 November 2024
Central processing unit (redirect from Cpu)
components. Modern CPUs devote a lot of semiconductor area to caches and instruction-level parallelism to increase performance and to CPU modes to support...
100 KB (11,315 words) - 15:32, 24 November 2024
requested data is cached in high-speed access memory stores, allowing swifter access by central processing unit (CPU) cores. Cache hierarchy is a form...
24 KB (3,175 words) - 05:25, 6 November 2024
address-translation cache. It is a part of the chip's memory-management unit (MMU). A TLB may reside between the CPU and the CPU cache, between CPU cache and the...
24 KB (3,328 words) - 21:20, 14 August 2024
science, cache coloring (also known as page coloring) is the process of attempting to allocate free pages that are contiguous from the CPU cache's point...
4 KB (404 words) - 20:50, 28 July 2023
In computing, cache replacement policies (also known as cache replacement algorithms or cache algorithms) are optimizing instructions or algorithms which...
40 KB (5,213 words) - 04:39, 21 October 2024
List of Intel Core processors (redirect from Core 2 cpus)
L1 cache: 64 KB (32 KB data + 32 KB instructions) per core. L2 cache: 256 KB per core. In addition to the Smart Cache (L3 cache), Haswell-H CPUs also...
479 KB (14,101 words) - 15:26, 25 November 2024
Cache placement policies are policies that determine where a particular memory block can be placed when it goes into a CPU cache. A block of memory cannot...
16 KB (2,176 words) - 04:22, 12 November 2024
List of AMD Ryzen processors (redirect from List of AMD Ryzen CPUs)
the CPUs support DDR4-2933 in dual-channel mode. L1 cache: 96 KB (32 KB data + 64 KB instruction) per core. L2 cache: 512 KB per core. All the CPUs support...
7 KB (6,422 words) - 16:38, 19 November 2024
very fast memory known as a CPU cache which holds recently accessed data. As long as the data that the CPU needs is in the cache, the performance is much...
14 KB (1,849 words) - 10:42, 22 September 2024
and hardware complexity Within the L1 cache of the NetBurst CPUs, Intel incorporated its execution trace cache. It stores decoded micro-operations, so...
10 KB (1,250 words) - 17:33, 8 June 2024
is a program optimization approach motivated by efficient usage of the CPU cache, often used in video game development. The approach is to focus on the...
5 KB (581 words) - 01:27, 3 November 2024
Direct memory access (section Cache coherency)
problems. Imagine a CPU equipped with a cache and an external memory that can be accessed directly by devices using DMA. When the CPU accesses location...
28 KB (3,914 words) - 19:57, 18 November 2024
Overhead (computing) (section CPU caches)
function calls. In a CPU cache, the "cache size" (or capacity) refers to how much data a cache stores. For instance, a "4 KB cache" is a cache that holds 4 KB...
7 KB (822 words) - 01:36, 3 November 2024
Athlon's CPU cache consisted of the typical two levels. Athlon was the first x86 processor with a 128 KB split level-1 cache; a 2-way associative cache separated...
50 KB (5,116 words) - 01:52, 17 September 2024
Computer architecture (redirect from CPU architecture)
particular processor will implement the ISA. The size of a computer's CPU cache for instance, is an issue that generally has nothing to do with the ISA...
26 KB (3,176 words) - 05:34, 4 November 2024
CPUID (redirect from CPU flag (x86))
49h indicates a level-3 cache on GenuineIntel Family 0Fh Model 6 (Pentium 4 based Xeon) CPUs, and a level-2 cache on other CPUs. Intel's CPUID documentation...
222 KB (12,429 words) - 04:24, 14 November 2024
List of Intel processors (redirect from Intel CPUs)
16 KB L1 cache 256 KB integrated L2 cache 60 MHz system bus clock rate Variants 150 MHz 0.35 μm process technology, (two die, a 0.35 μm CPU with 0.6 μm...
178 KB (13,538 words) - 02:19, 24 November 2024
Glossary of computer hardware terms (redirect from Cache way)
component compromises the way another component works. cache A small and fast buffer memory between the CPU and the main memory. Reduces access time for frequently...
39 KB (4,596 words) - 08:07, 3 October 2024
CoreWare CW33300-based core MIPS R3000A-compatible 32-bit RISC CPU MIPS R3051 with 5 KB L1 cache, running at 33.8688 MHz. The microprocessor was manufactured...
11 KB (1,034 words) - 20:31, 6 October 2024
Meltdown (security vulnerability) (redirect from Rogue data cache load)
on Security and Privacy warned against a covert timing channel in the CPU cache and translation lookaside buffer (TLB). This analysis was performed under...
87 KB (8,241 words) - 01:50, 18 November 2024
bus, was a computer bus used on early Intel platforms to connect the CPU to CPU cache memory, usually off-die L2. If a design utilizes a back-side bus along...
4 KB (404 words) - 15:33, 3 December 2023
with newer computers cache is built into either the CPU or the motherboard. COASt modules decoupled the motherboard from its cache, allowing varying configurations...
4 KB (564 words) - 15:43, 6 July 2022
primary storage and static random-access memory (SRAM) used mainly for CPU cache. Most semiconductor memory is organized into memory cells each storing...
29 KB (3,284 words) - 18:37, 1 October 2024
NetBurst (redirect from Execution trace cache)
competitor processor, Athlon. Within the L1 cache of the CPU, Intel incorporated its Execution Trace Cache. It stores decoded micro-operations, so that...
16 KB (1,648 words) - 12:59, 15 September 2024
frequency as well as the potentially present CPU cache. It is not usable for performance comparisons among different CPUs. In 1993, Lars Wirzenius posted a Usenet...
10 KB (1,009 words) - 04:54, 25 November 2024
are stored in the same memory system and (without the complexity of a CPU cache) must be accessed in turn. The physical separation of instruction and...
12 KB (1,650 words) - 10:34, 22 September 2024
In CPU design, the use of a sum-addressed decoder (SAD) or sum-addressed memory (SAM) decoder is a method of reducing the latency of the CPU cache access...
13 KB (2,076 words) - 21:31, 12 April 2023