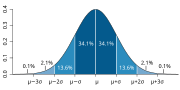
Intuitively, an algorithmically random sequence (or random sequence) is a sequence of binary digits that appears random to any algorithm running on a (prefix-free...
33 KB (4,875 words) - 16:37, 11 May 2024
Pseudorandom number generator (redirect from Pseudo-random number generator)
random bit generator (DRBG), is an algorithm for generating a sequence of numbers whose properties approximate the properties of sequences of random numbers...
26 KB (3,303 words) - 08:49, 21 October 2024
needed] Algorithmically random sequence Quasi-random sequence Random number generation Random sequence Random variable Random variate Random real Richard...
4 KB (386 words) - 02:59, 14 October 2024
example, it is an algorithmically random sequence and thus its binary digits are evenly distributed (in fact it is normal). Algorithmic information theory...
22 KB (2,582 words) - 21:36, 25 May 2024
Chaitin's constant (category Algorithmic information theory)
enumerated. A real number is random if the binary sequence representing the real number is an algorithmically random sequence. Calude, Hertling, Khoussainov...
17 KB (2,387 words) - 20:33, 27 September 2024
concept of a random sequence is essential in probability theory and statistics. The concept generally relies on the notion of a sequence of random variables...
9 KB (1,191 words) - 00:02, 21 August 2024
NIST Statistical Test Suite Randomness Statistical randomness Algorithmically random sequence Seven states of randomness Wald–Wolfowitz runs test Wolfram...
9 KB (1,112 words) - 18:41, 18 March 2024
Pseudorandomness (redirect from Pseudo-random sequence)
A pseudorandom sequence of numbers is one that appears to be statistically random, despite having been produced by a completely deterministic and repeatable...
7 KB (865 words) - 12:05, 1 October 2024
Random number generation is a process by which, often by means of a random number generator (RNG), a sequence of numbers or symbols that cannot be reasonably...
36 KB (4,419 words) - 15:23, 28 October 2024
Fisher–Yates shuffle (redirect from Algorithm P)
next element in the shuffled sequence by randomly drawing an element from the list until no elements remain. The algorithm produces an unbiased permutation:...
39 KB (4,792 words) - 21:43, 24 October 2024
values of a low-discrepancy sequence are neither random nor pseudorandom, but such sequences share some properties of random variables and in certain applications...
25 KB (4,259 words) - 22:43, 18 October 2024
In common usage, randomness is the apparent or actual lack of definite pattern or predictability in information. A random sequence of events, symbols...
34 KB (4,301 words) - 12:36, 17 June 2024
will produce the same sequence of numbers. For a seed to be used in a pseudorandom number generator, it does not need to be random. Because of the nature...
2 KB (245 words) - 17:34, 23 September 2024
difficult to predict and exhibits statistical behavior similar to a truly random sequence. PRBS generators are used in telecommunication, such as in analog-to-information...
8 KB (1,064 words) - 16:26, 5 February 2024
Kolmogorov complexity (redirect from Kolmogorov randomness)
randomness for infinite sequences from a finite alphabet. These algorithmically random sequences can be defined in three equivalent ways. One way uses an effective...
55 KB (7,273 words) - 22:06, 22 August 2024
optimization algorithm Odds algorithm (Bruss algorithm): Finds the optimal strategy to predict a last specific event in a random sequence event Random Search...
71 KB (7,829 words) - 19:14, 31 October 2024
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm (/ˈælɡərɪðəm/ ) is a finite sequence of mathematically rigorous instructions, typically used to solve...
58 KB (6,735 words) - 18:51, 30 October 2024
approach to the definition of an algorithmically random sequence which is alternative to the concept of Martin-Löf randomness. Schnorr was a professor of mathematics...
3 KB (181 words) - 21:40, 24 March 2022
training set.: 587–588 The first algorithm for random decision forests was created in 1995 by Tin Kam Ho using the random subspace method, which, in Ho's...
46 KB (6,483 words) - 22:02, 2 October 2024
Reservoir sampling (category Randomized algorithms)
Reservoir sampling is a family of randomized algorithms for choosing a simple random sample, without replacement, of k items from a population of unknown...
21 KB (3,514 words) - 00:25, 14 October 2024
theory, there exist several different notions of convergence of sequences of random variables, including convergence in probability, convergence in distribution...
41 KB (5,280 words) - 21:51, 25 September 2024
some algorithms are designed for sequential access, the highest-performing algorithms assume data is stored in a data structure which allows random access...
68 KB (6,408 words) - 17:30, 26 September 2024
The Logic of Scientific Discovery (1934), calling them "shortest random-like sequences". Taking A = {0, 1}, there are two distinct B(2, 3): 00010111 and...
32 KB (3,515 words) - 19:08, 29 October 2024
A maze-solving algorithm is an automated method for solving a maze. The random mouse, wall follower, Pledge, and Trémaux's algorithms are designed to be...
20 KB (2,874 words) - 05:39, 23 July 2024
passing through the same sequence of states. Deterministic algorithms are by far the most studied and familiar kind of algorithm, as well as one of the...
9 KB (965 words) - 21:18, 20 August 2024
invariant to the model of computation being used. An algorithmically random sequence is an infinite sequence of characters, all of whose prefixes (except possibly...
27 KB (2,874 words) - 01:32, 5 October 2024
is, appear to be random for many purposes. They were first introduced in 1960 and are an example of a quasi-random number sequence. They generalize the...
7 KB (738 words) - 15:53, 4 April 2024
in games of chance and in randomized algorithms in coding theory, cryptography, and simulation. A good example of a random permutation is the fair shuffling...
7 KB (835 words) - 18:28, 23 September 2024
physics, the Metropolis–Hastings algorithm is a Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) method for obtaining a sequence of random samples from a probability distribution...
30 KB (4,535 words) - 20:02, 13 June 2024
Cycle detection (redirect from Floyd's cycle-finding algorithm.)
science, cycle detection or cycle finding is the algorithmic problem of finding a cycle in a sequence of iterated function values. For any function f that...
31 KB (4,183 words) - 21:18, 20 August 2024