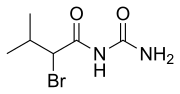
Hyperchloremia is an electrolyte disturbance in which there is an elevated level of chloride ions in the blood. The normal serum range for chloride is...
20 KB (2,332 words) - 15:36, 2 November 2023
Electrolyte imbalance (section Hyperchloremia)
acidosis. Patients are usually asymptomatic with mild hyperchloremia. Symptoms associated with hyperchloremia are usually caused by the underlying cause of this...
34 KB (3,856 words) - 19:48, 18 July 2024
hypoventilation. It can be associated with chronic respiratory acidosis. Hyperchloremia (having too much chloride) usually does not produce symptoms. When symptoms...
117 KB (13,028 words) - 14:07, 11 August 2024
available nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs presenting an indefinite hyperchloremia] (pdf). Nihon Ronen Igakkai Zasshi. Japanese Journal of Geriatrics (in...
6 KB (305 words) - 18:13, 7 May 2021
Normal anion gap metabolic acidosis/acidemia Hypokalemia, Hypocalcemia, Hyperchloremia Urinary stone formation (related to alkaline urine, hypercalciuria,...
19 KB (2,073 words) - 05:58, 19 July 2024
bionumbers.org. Retrieved 24 March 2017. Nagami, Glenn T. (1 July 2016). "Hyperchloremia – Why and how". Nefrología (English Edition). 36 (4): 347–353. doi:10...
18 KB (1,796 words) - 04:15, 9 May 2024
children) and osteomalacia (in adults) Growth failure Acidosis Hypokalemia Hyperchloremia Other features of the generalized proximal tubular dysfunction of the...
12 KB (1,203 words) - 05:48, 21 January 2024
salt (sodium chloride) is the main dietary source. hypochloremia / hyperchloremia Sodium 1500 2300; NE A systemic electrolyte and is essential in coregulating...
37 KB (3,052 words) - 11:48, 23 July 2024
Hyperlipoproteinemia Hyperreninemia and hyperaldosteronism Guanidine compounds Hyperchloremia Hyperglucagonemia Hyporeninemia "Middle molecules" Hypocalcemia Hypoaldosteronism...
33 KB (3,274 words) - 05:34, 21 July 2024
17 Chlorine 1.5×10−3 0.095 0.024 Yes (e.g. Cl-transporting ATPase) Hyperchloremia 17 12 Magnesium 500×10−6 0.019 0.0070 Yes (e.g. binding to ATP and other...
37 KB (2,512 words) - 19:22, 10 August 2024
duodenum Spironolactone High ostomy output Hyperparathyroidism – can cause hyperchloremia and increase renal bicarbonate loss, which may result in a normal anion...
4 KB (351 words) - 04:36, 2 August 2022
(Cl) 95, 98, 100 105, 106, 110 mmol/L or mEq/L See hypochloremia or hyperchloremia 340 370 mg/dL Ionized calcium (Ca) 1.03, 1.10 1.23, 1.30 mmol/L See...
108 KB (6,105 words) - 10:44, 2 July 2024
causes hypophosphatemia, leading to muscle weakness and sometimes coma. Hyperchloremia also occurs. Kidney dysfunction also causes gout, a form of arthritis...
22 KB (2,624 words) - 21:06, 29 June 2024
electrical equilibrium, if [Cl−] goes up, [HCO−3] must come down. Hence, hyperchloremia always causes a metabolic acidosis as [HCO−3] must fall; alternatively...
7 KB (1,010 words) - 05:09, 19 July 2024
hyperparathyroidism.[citation needed] Hyperparathyroidism can cause hyperchloremia and increase renal bicarbonate loss, which may result in a normal anion...
53 KB (5,244 words) - 01:40, 17 May 2024
hypertension until later in life. They also commonly experience both hyperchloremia and metabolic acidosis together, a condition called hyperchloremic metabolic...
19 KB (1,660 words) - 02:14, 9 June 2024
proper diagnosis. Laboratory findings can include metabolic acidosis, hyperchloremia, hypercalcemia, and elevated urinary pH. Specifically, the urine will...
6 KB (620 words) - 22:49, 18 April 2022