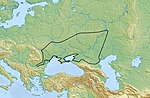
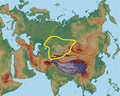
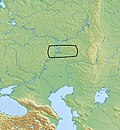
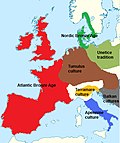
The Srubnaya culture (Russian: Срубная культура, romanized: Srubnaya kul'tura, Ukrainian: Зрубна культура, romanized: Zrubna kul'tura), also known as Timber-grave...
16 KB (1,630 words) - 04:49, 24 October 2024
Srubnaya culture. The Catacomb culture emerged on the southern part of the Pontic steppe in 2,500 BC, as a western descendant of the Yamnaya culture....
28 KB (3,353 words) - 14:11, 20 October 2024
These two cultures were followed by the Srubnaya culture (18th–12th century BC). Maps of the origins of Yamnaya culture Sredny Stog culture (c.4500-3500...
68 KB (7,046 words) - 22:53, 22 November 2024
a major role in the development of the Sintashta culture and Srubnaya culture. The Abashevo culture is believed to have formed on the northern Don in...
25 KB (2,936 words) - 00:38, 21 November 2024
culture, the Srubnaya culture, the Potapovka culture, and the Andronovo culture. These were found to harbor mixed ancestry from the Yamnaya culture and...
46 KB (4,908 words) - 14:33, 20 October 2024
culture, Sintashta culture and Srubnaya culture. The Poltavka culture emerged ca. 2800 BC, as an eastern successor of the Yamnaya culture. The western successor...
17 KB (2,143 words) - 18:43, 6 November 2024
populations. Andronovo skulls are similar to those of the Srubnaya culture and Sintashta culture, exhibiting features such as dolicocephaly. Through Iranian...
64 KB (7,134 words) - 04:43, 25 November 2024
Androphagi (section Society and culture)
of the Srubnaya culture containing a significant element originating from the Siberian Andronovo culture. The population of the Srubnaya culture was among...
19 KB (2,047 words) - 20:20, 28 October 2024
Lola culture came under increasing pressure from the Srubnaya culture, who were advancing from the Middle Volga region. By 1800 BC, the Lola culture had...
6 KB (614 words) - 17:20, 10 November 2024
Sintashta culture, its people are believed to have spoken a form of Proto-Indo-Iranian. It was directly ancestral to the Srubnaya culture, and probably...
16 KB (1,841 words) - 01:04, 6 November 2024
the Potapovka culture, the Andronovo culture and the Srubnaya culture to be closely related to the Corded Ware culture. These cultures were found to harbor...
78 KB (9,104 words) - 22:28, 16 November 2024
Greece Nordic Bronze Age Ottomany culture Srubnaya culture Terramare culture Urnfield culture Vatya culture Wietenberg culture Nora Kershaw Chadwick, J. X....
23 KB (2,077 words) - 14:03, 22 November 2024
The Karasuk culture (Russian: Карасукская культура, romanized: Karasukskaya kul'tura) describes a group of late Bronze Age societies who ranged from the...
31 KB (3,313 words) - 05:51, 25 November 2024
the population of the Srubnaya culture, to which the Scythians themselves initially belonged. The population of the Srubnaya culture was among the first...
95 KB (13,137 words) - 20:07, 13 October 2024
Bondarikha culture or Bondarikhinskaya culture was a Late Bronze Age (11th-9th centuries BCE) culture of modern-day Ukraine. It replaced the Srubnaya culture. It...
3 KB (283 words) - 21:27, 6 November 2024
Kurgan hypothesis (redirect from Kurgan culture)
prehistoric cultures, including the Yamnaya (or Pit Grave) culture and its predecessors. In the 2000s, David Anthony instead used the core Yamnaya culture and...
34 KB (3,818 words) - 02:41, 26 August 2024
The Apennine culture is a technology complex in central and southern Italy from the Italian Middle Bronze Age (15th–14th centuries BC). In the mid-20th...
11 KB (1,253 words) - 14:53, 15 November 2024
Sauromatian culture emerged during the 6th century BCE out of elements of the Bronze Age Srubnaya culture and the neighbouring Andronovo culture, combined...
56 KB (6,257 words) - 14:27, 2 November 2024
culture of the later (12th–10th centuries BCE) which replaced the Srubnaya culture on the steppes of Ukraine and Moldova. There are finds near the lower...
2 KB (173 words) - 11:19, 3 November 2024
Cycladic culture (also known as Cycladic civilisation) was a Bronze Age culture (c. 3100–c. 1000 BC) found throughout the islands of the Cyclades in the...
13 KB (1,529 words) - 07:51, 14 October 2024
Terramare culture was a dominant component of the Proto-Villanovan culture—especially in its northern and Campanian phases and the Terramare culture has been...
17 KB (1,874 words) - 13:12, 1 November 2024
Various cultures occupied the area during this period and contributed to monumental stone constructions, starting with the Afanasievo culture, and continuing...
81 KB (9,909 words) - 04:44, 25 November 2024
The Urnfield culture (c. 1300–750 BC) was a late Bronze Age culture of Central Europe, often divided into several local cultures within a broader Urnfield...
104 KB (11,112 words) - 21:57, 2 October 2024
Scytho-Siberian world (redirect from Scytho-Siberian culture)
between Srubnaya-Alakulskaya and the western Scythians." Gurkan, Cemal (8 January 2019). "On The Genetic Continuity of the Iron Age Pazyryk Culture: Geographic...
63 KB (7,324 words) - 15:23, 22 November 2024
The Wessex culture is the predominant prehistoric culture of central and southern Britain during the early Bronze Age, originally defined by the British...
6 KB (718 words) - 06:26, 21 March 2024
The Únětice culture, Aunjetitz culture or Unetician culture (Czech: Únětická kultura, German: Aunjetitzer Kultur, Polish: Kultura unietycka, Slovak: Únětická...
78 KB (8,275 words) - 17:04, 13 November 2024
of the succeeding Abashevo culture, Sintashta culture, Srubnaya culture and Andronovo culture. Skulls of the Yamnaya culture and their direct descendants...
24 KB (2,795 words) - 21:24, 31 October 2024
The Hallstatt culture was the predominant Western and Central European archaeological culture of the Late Bronze Age (Hallstatt A, Hallstatt B) from the...
77 KB (8,530 words) - 07:16, 15 November 2024
Indus Valley Civilisation (redirect from Indus Valley Culture)
and later cultures called Early Harappan and Late Harappan in the same area. The early Harappan cultures were populated from Neolithic cultures, the earliest...
191 KB (21,641 words) - 15:50, 25 November 2024
The Lusatian culture existed in the later Bronze Age and early Iron Age (1300–500 BC) in most of what is now Poland and parts of the Czech Republic, Slovakia...
14 KB (1,263 words) - 12:16, 13 September 2024