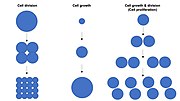
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle in which...
41 KB (4,735 words) - 04:03, 18 November 2024
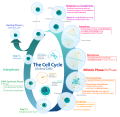
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the sequential series of events that take place in a cell that causes it to divide into two daughter cells. These...
78 KB (9,093 words) - 03:11, 11 November 2024
cell divisions occur repeatedly without cell growth. Conversely, some cells can grow without cell division or without any progression of the cell cycle...
37 KB (4,869 words) - 09:19, 17 May 2024
An asymmetric cell division produces two daughter cells with different cellular fates. This is in contrast to symmetric cell divisions which give rise...
30 KB (3,691 words) - 02:37, 10 June 2024
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all forms of life. Every cell consists of cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane; many cells contain...
60 KB (6,269 words) - 17:14, 21 November 2024
multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can change into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely...
98 KB (11,480 words) - 15:46, 20 November 2024
increase in cell number and is therefore a rapid mechanism of tissue growth. Cell proliferation requires both cell growth and cell division to occur at...
5 KB (646 words) - 20:04, 5 January 2024
Mitosis (redirect from Mitotic cell division)
part of the cell cycle in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division by mitosis is an equational division which gives...
71 KB (7,317 words) - 22:13, 2 November 2024
come from the division of pre-existing cells. Viruses are not considered in cell biology – they lack the characteristics of a living cell and instead are...
41 KB (5,252 words) - 05:01, 2 November 2024
method of cell division involving the formation of a cell plate or phragmoplast that separates the new daughter cells. Plant cells have cell walls composed...
19 KB (2,224 words) - 04:45, 3 January 2024
Meristem (redirect from Meristematic cell)
cell biology, the meristem is a type of tissue found in plants. It consists of undifferentiated cells (meristematic cells) capable of cell division....
37 KB (4,544 words) - 19:45, 9 November 2024
Epidermis (redirect from Epidermal cell)
epithelium, the epidermis is maintained by cell division within the stratum basale. Differentiating cells delaminate from the basement membrane and are...
28 KB (3,056 words) - 06:49, 2 November 2024
Cleavage (embryo) (redirect from Eight-cell stage)
cleavage is the division of cells in the early development of the embryo, following fertilization. The zygotes of many species undergo rapid cell cycles with...
26 KB (2,959 words) - 13:44, 3 November 2024
Hayflick limit (section The belief in cell immortality)
number of times a normal somatic, differentiated human cell population will divide before cell division stops. The concept of the Hayflick limit was advanced...
16 KB (1,838 words) - 14:45, 6 August 2024
Cancer cells are cells that divide continually, forming solid tumors or flooding the blood or lymph with abnormal cells. Cell division is a normal process...
16 KB (1,727 words) - 14:31, 8 November 2024
Epithelium (redirect from Epithelial cell)
there are too few of the cells, the stretch that they experience rapidly activates cell division. Alternatively, when too many cells accumulate, crowding...
32 KB (2,908 words) - 21:06, 1 November 2024
Carcinogenesis (section Cancer cell biology)
the cellular, genetic, and epigenetic levels and abnormal cell division. Cell division is a physiological process that occurs in almost all tissues and...
115 KB (13,952 words) - 04:56, 2 November 2024
Meiosis (redirect from Reduction division)
reductional division) is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, the sperm or egg cells. It...
64 KB (7,478 words) - 23:27, 22 August 2024
Caenorhabditis elegans (redirect from P4 cell)
daughter cells of the first cell division are called the AB cell (containing PAR-6 and PAR-3) and the P1 cell (containing PAR-1 and PAR-2). A second cell division...
94 KB (10,755 words) - 04:06, 19 November 2024
non-differentiated somatic cells form the germ line and, in Cnidaria, differentiated somatic cells are the source of the germline. Mitotic cell division is only seen...
15 KB (1,793 words) - 21:51, 3 September 2024
Divisome (section DNA replication and cell division)
responsible for cell division, constriction of inner and outer membranes during division, and peptidoglycan (PG) synthesis at the division site. The divisome...
12 KB (1,477 words) - 08:32, 3 December 2023
studying the regulation of the cell cycle, asymmetric cell division, and cellular differentiation. Caulobacter daughter cells have two very different forms...
26 KB (3,357 words) - 22:10, 2 December 2023
Mitochondrion (redirect from Cell powerhouse)
A mitochondrion (pl. mitochondria) is an organelle found in the cells of most eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double...
167 KB (18,357 words) - 17:01, 19 November 2024
Adult stem cells are undifferentiated cells, found throughout the body after development, that multiply by cell division to replenish dying cells and regenerate...
52 KB (5,961 words) - 10:24, 3 October 2024
Cellular differentiation (redirect from Cell differentiation)
differentiation, a precursor cell formerly capable of cell division permanently leaves the cell cycle, dismantles the cell cycle machinery and often expresses...
50 KB (6,030 words) - 16:44, 2 October 2024
Chromosome (section Metaphase chromatin and division)
microscope only during the metaphase of cell division, where all chromosomes are aligned in the center of the cell in their condensed form. Before this stage...
63 KB (6,554 words) - 11:15, 15 November 2024
(TSG), or anti-oncogene, is a gene that regulates a cell during cell division and replication. If the cell grows uncontrollably, it will result in cancer....
30 KB (3,409 words) - 03:26, 14 November 2024
Cell division orientation is the direction along which the new daughter cells are formed. Cell division orientation is important for morphogenesis, cell...
7 KB (733 words) - 03:10, 14 August 2023
means the non-specific use of intracellular poisons to inhibit mitosis (cell division) or to induce DNA damage (so that DNA repair can augment chemotherapy)...
155 KB (17,518 words) - 23:36, 26 October 2024
cell nucleus (from Latin nucleus or nuculeus 'kernel, seed'; pl.: nuclei) is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells usually...
87 KB (9,963 words) - 07:20, 9 October 2024