In medicine and psychology, clinical significance is the practical importance of a treatment effect—whether it has a real genuine, palpable, noticeable...
14 KB (1,684 words) - 15:03, 12 July 2024
statistical significance is not the same as research significance, theoretical significance, or practical significance. For example, the term clinical significance...
38 KB (4,059 words) - 02:19, 27 June 2024
Ectodysplasin A receptor (EDAR) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EDAR gene. EDAR is a cell surface receptor for ectodysplasin A which plays...
26 KB (2,676 words) - 02:12, 19 November 2024
Vulval vestibule (section Clinical significance)
The vulval vestibule (also known as the vulvar vestibule or vestibule of vagina) is the part of the vulva between the labia minora. At the innermost part...
4 KB (478 words) - 20:31, 22 September 2024
Uvula (section Clinical significance)
2004). "Why do we have a uvula?: literature review and a new theory". Clinical Otolaryngology and Allied Sciences. 29 (6): 689–93. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2273...
12 KB (1,322 words) - 00:45, 15 November 2024
Long bone (section Clinical significance)
The long bones are those that are longer than they are wide. They are one of five types of bones: long, short, flat, irregular and sesamoid. Long bones...
4 KB (471 words) - 03:40, 19 November 2024
Cecum (section Clinical significance)
The cecum or caecum is a pouch within the peritoneum that is considered to be the beginning of the large intestine. It is typically located on the right...
14 KB (1,530 words) - 23:57, 7 October 2024
Sigmoid colon (section Clinical significance)
The sigmoid colon (or pelvic colon) is the part of the large intestine that is closest to the rectum and anus. It forms a loop that averages about 35–40...
5 KB (557 words) - 18:41, 1 May 2024
Metatarsal bones (section Clinical significance)
The metatarsal bones or metatarsus (pl.: metatarsi) are a group of five long bones in the midfoot, located between the tarsal bones (which form the heel...
10 KB (792 words) - 13:48, 27 August 2024
Sarcoptes scabiei (section Clinical significance)
Sarcoptes scabiei (/sɑːrˈkɒptiːz skeɪˈbiːaɪ/ Traditional English pronunciation of Latin) or the itch mite is a parasitic mite found in all parts of the...
9 KB (1,214 words) - 22:45, 1 October 2024
Integumentary system (section Clinical significance)
The integumentary system is the set of organs forming the outermost layer of an animal's body. It comprises the skin and its appendages, which act as a...
12 KB (1,355 words) - 20:21, 11 October 2024
Circle of Willis (section Clinical significance)
The circle of Willis (also called Willis' circle, loop of Willis, cerebral arterial circle, and Willis polygon) is a circulatory anastomosis that supplies...
10 KB (1,054 words) - 22:14, 17 November 2024
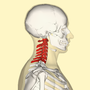
Cervical vertebrae (section Clinical significance)
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (sg.: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and...
19 KB (2,179 words) - 20:47, 4 November 2023
Hamstring (section Clinical significance)
A hamstring (/ˈhæmstrɪŋ/) is any one of the three posterior thigh muscles in human anatomy between the hip and the knee: from medial to lateral, the semimembranosus...
10 KB (1,010 words) - 22:02, 12 November 2024
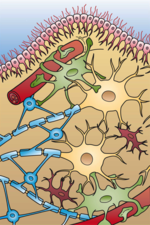
Glia (section Clinical significance)
Look up glia in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. Glia, also called glial cells (gliocytes) or neuroglia, are non-neuronal cells in the central nervous...
37 KB (3,809 words) - 06:55, 20 November 2024
Femur (section Clinical significance)
The femur (/ˈfiːmər/; pl.: femurs or femora /ˈfɛmərə/), or thigh bone, is the only bone in the thigh — the region of the lower limb between the hip and...
23 KB (2,450 words) - 16:11, 21 November 2024
Carpal tunnel (section Clinical significance)
In the human body, the carpal tunnel or carpal canal is a flattened body cavity on the flexor (palmar/volar) side of the wrist, bounded by the carpal bones...
8 KB (799 words) - 17:46, 29 October 2024
Coronary arteries (section Clinical significance)
J, Das R (January 2022). "A study of coronary dominance and its clinical significance". Folia Morphologica. 82 (1): 102–107. doi:10.5603/FM.a2022.0005...
11 KB (1,262 words) - 13:01, 1 October 2024
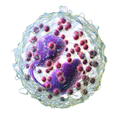
Eosinophil (section Clinical significance)
effectiveness of specific anti-inflammatory drugs. Despite their increasing use in clinical practice, data on "normal" blood eosinophil counts remain insufficient...
29 KB (3,166 words) - 00:19, 9 September 2024
Perineum (section Clinical significance)
disruption of which leads to hypospadias and cryptorchidism". Journal of Clinical Investigation, 13 March 2008. Sleep J, Grant A, Garcia J, Elbourne D, Spencer...
15 KB (1,543 words) - 02:03, 19 October 2024
Ascending aorta (section Clinical significance)
The ascending aorta (AAo) is a portion of the aorta commencing at the upper part of the base of the left ventricle, on a level with the lower border of...
8 KB (855 words) - 12:57, 17 October 2024
Calcium phosphate (section Clinical significance)
The term calcium phosphate refers to a family of materials and minerals containing calcium ions (Ca2+) together with inorganic phosphate anions. Some so-called...
7 KB (605 words) - 17:35, 11 September 2024
Alanine transaminase (section Clinical significance)
transaminase) level, and their ratio (AST/ALT ratio) are routinely measured clinically as biomarkers for liver health. The half-life of ALT in the circulation...
13 KB (1,370 words) - 19:23, 21 September 2024
Foot (section Clinical significance)
The foot (pl.: feet) is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion...
28 KB (3,446 words) - 14:44, 21 November 2024
QRS complex (section Clinical significance)
2010. Compendium for interpretation of ECG at Uppsala Institution for Clinical Physiology. Year 2010 "Complementary and Alternative Medicine Index (CAM)"...
18 KB (1,923 words) - 08:38, 31 August 2024
Urinary meatus (section Clinical significance)
ISSN 0018-506X. PMC 3894744. PMID 21195073. Gyftopoulos, K; Matkaris, M (2019). "Clinical implications of the anatomical position of the urethra meatus in women...
6 KB (639 words) - 07:52, 14 November 2024
Gyrus (section Clinical significance)
In neuroanatomy, a gyrus (pl.: gyri) is a ridge on the cerebral cortex. It is generally surrounded by one or more sulci (depressions or furrows; sg.: sulcus)...
8 KB (845 words) - 17:38, 26 April 2024
Septum pellucidum (section Clinical significance)
The septum pellucidum (Latin for "translucent wall") is a thin, triangular, vertical double membrane separating the anterior horns of the left and right...
5 KB (508 words) - 05:16, 26 February 2024
The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that play a role in the process of human reproduction. These organs are located on the...
26 KB (2,956 words) - 06:58, 14 November 2024
Spermatic cord (section Clinical significance)
The spermatic cord is the cord-like structure in males formed by the vas deferens (ductus deferens) and surrounding tissue that runs from the deep inguinal...
5 KB (502 words) - 02:27, 20 May 2024