Inspired by—but distinct from—the Hamiltonian of classical mechanics, the Hamiltonian of optimal control theory was developed by Lev Pontryagin as part...
22 KB (3,975 words) - 08:46, 9 August 2024
Molecular Hamiltonian, the Hamiltonian operator representing the energy of the electrons and nuclei in a molecule Hamiltonian (control theory), a function...
1 KB (207 words) - 13:25, 12 October 2024
it is of fundamental importance in most formulations of quantum theory. The Hamiltonian is named after William Rowan Hamilton, who developed a revolutionary...
27 KB (4,903 words) - 04:26, 29 August 2024
Optimal control theory is a branch of control theory that deals with finding a control for a dynamical system over a period of time such that an objective...
32 KB (4,711 words) - 04:55, 19 August 2024
equation in control theory Hamilton–Jacobi–Einstein equation In both mathematics and physics (specifically mathematical physics): the term Hamiltonian refers...
3 KB (296 words) - 18:15, 13 October 2022
The Hamiltonian constraint arises from any theory that admits a Hamiltonian formulation and is reparametrisation-invariant. The Hamiltonian constraint...
20 KB (3,745 words) - 20:35, 7 August 2023
In control theory, a bang–bang controller (hysteresis, 2 step or on–off controller), is a feedback controller that switches abruptly between two states...
7 KB (784 words) - 09:17, 29 July 2024
(generalized) momenta. Both theories provide interpretations of classical mechanics and describe the same physical phenomena. Hamiltonian mechanics has a close...
52 KB (9,287 words) - 18:23, 1 November 2024
of time Time translation symmetry Hamiltonian system Propagator Time evolution operator Hamiltonian (control theory) Lecture 1 | Quantum Entanglements...
8 KB (1,014 words) - 09:11, 19 July 2024
the Seiberg–Witten gauge theory which reduces SU(2) to U(1) in N = 2, d = 4 gauge theory. The Hamiltonian version of the theory has been developed by Floer...
27 KB (3,775 words) - 11:40, 24 July 2024
perturbation theory, the perturbation Hamiltonian is static (i.e., possesses no time dependence). Time-independent perturbation theory was presented...
70 KB (15,969 words) - 10:32, 26 October 2024
Loop quantum gravity (redirect from Quantum loop theory)
defined an anomaly-free Hamiltonian operator and showed the existence of a mathematically consistent background-independent theory. The covariant, or "spin...
118 KB (16,621 words) - 18:43, 23 October 2024
Stochastic control or stochastic optimal control is a sub field of control theory that deals with the existence of uncertainty either in observations or...
12 KB (1,683 words) - 09:57, 3 March 2023
In physics, a gauge theory is a type of field theory in which the Lagrangian, and hence the dynamics of the system itself, do not change under local transformations...
47 KB (6,766 words) - 07:11, 30 October 2024
Pontryagin's maximum principle (category Optimal control)
milestone in optimal control theory, the significance of the maximum principle lies in the fact that maximizing the Hamiltonian is much easier than the...
12 KB (1,645 words) - 17:18, 24 November 2023
Møller–Plesset perturbation theory uses the difference between the Hartree–Fock Hamiltonian and the exact non-relativistic Hamiltonian as the perturbation. The...
22 KB (2,948 words) - 08:45, 18 October 2024
Interaction picture (redirect from Free Hamiltonian)
time-independent Hamiltonian HS, where H0,S is the free Hamiltonian, Duck, Ian; Sudarshan, E.C.G. (1998). "Chapter 6: Dirac's Invention of Quantum Field Theory". Pauli...
16 KB (2,285 words) - 01:30, 30 August 2024
Hamilton–Jacobi–Bellman equation (redirect from Hamiltonian-Jacobi-Bellman equation)
optimal control by taking the maximizer (or minimizer) of the Hamiltonian involved in the HJB equation. The equation is a result of the theory of dynamic...
14 KB (2,050 words) - 17:50, 26 April 2024
Probability theory or probability calculus is the branch of mathematics concerned with probability. Although there are several different probability interpretations...
25 KB (3,593 words) - 14:59, 31 October 2024
Analytical mechanics (section Hamiltonian field theory)
and corresponding generalized velocities in configuration space) and Hamiltonian mechanics (using coordinates and corresponding momenta in phase space)...
40 KB (5,758 words) - 22:46, 21 September 2024
that includes every vertex of the graph without repeats is known as a Hamiltonian path. Two paths are vertex-independent (alternatively, internally disjoint...
10 KB (1,175 words) - 17:28, 18 October 2024
field theory Classical unified field theories Variational methods in general relativity Higgs field (classical) Lagrangian (field theory) Hamiltonian field...
27 KB (3,848 words) - 21:31, 6 November 2024
Chaos theory is an interdisciplinary area of scientific study and branch of mathematics. It focuses on underlying patterns and deterministic laws of dynamical...
121 KB (13,853 words) - 21:57, 6 November 2024
}}e^{-ip_{\mu }(x^{\mu }-y^{\mu })}.} In an interacting theory, where the Lagrangian or Hamiltonian contains terms L I ( t ) {\displaystyle L_{I}(t)} or...
106 KB (14,793 words) - 16:44, 27 October 2024
Classical mechanics (redirect from Newtonian theory)
(generalized) momenta. Both theories provide interpretations of classical mechanics and describe the same physical phenomena. Hamiltonian mechanics has a close...
52 KB (5,830 words) - 08:18, 13 September 2024
Coding theory is the study of the properties of codes and their respective fitness for specific applications. Codes are used for data compression, cryptography...
27 KB (3,549 words) - 20:59, 5 November 2024
In physics, string theory is a theoretical framework in which the point-like particles of particle physics are replaced by one-dimensional objects called...
123 KB (15,355 words) - 01:55, 7 October 2024
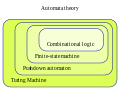
Automata theory is the study of abstract machines and automata, as well as the computational problems that can be solved using them. It is a theory in theoretical...
32 KB (3,843 words) - 13:32, 25 October 2024
A conformal field theory (CFT) is a quantum field theory that is invariant under conformal transformations. In two dimensions, there is an infinite-dimensional...
40 KB (6,808 words) - 05:16, 9 August 2024
Renormalization group (redirect from History of renormalization group theory)
physics of the system will be described by a certain formula, say the Hamiltonian H(T, J). Now proceed to divide the solid into blocks of 2×2 squares;...
49 KB (6,981 words) - 12:41, 7 September 2024