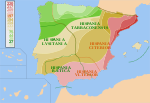
Hispania Baetica, often abbreviated Baetica, was one of three Roman provinces created in Hispania (the Iberian Peninsula) on 27 BC. Baetica was bordered...
16 KB (1,482 words) - 09:19, 25 August 2024
Ulterior was divided into two new provinces, Baetica and Lusitania, while Hispania Citerior was renamed Hispania Tarraconensis. Subsequently, the western...
44 KB (5,247 words) - 13:26, 23 September 2024
peninsula. Hispania Ulterior was divided into Baetica (modern Andalusia) and Lusitania (modern Portugal, Extremadura, and part of Castilla-León). Hispania Citerior...
8 KB (797 words) - 13:37, 30 August 2024
Southern Spain, the region now called Andalusia, was the province of Hispania Baetica. On the Atlantic west lay the province of Lusitania, partially coincident...
38 KB (3,152 words) - 13:10, 21 September 2024
north-western Hispania. Augustus also renamed Hispania Ulterior as Hispania Baetica and created a third province, Hispania Lusitania. Hispania is the Latin...
4 KB (336 words) - 13:41, 30 August 2024
Vandals (redirect from Vandal kingdom (Hispania Baetica))
the Romans, as foederati, in Asturia (Northwest) and the Silingi in Hispania Baetica (South), while the Alans got lands in Lusitania (West) and the region...
69 KB (7,655 words) - 07:01, 25 August 2024
History of Andalusia (category Hispania Baetica)
became fully integrated into the Roman world as the prosperous province of Baetica, which contributed emperors like Trajan and Hadrian to the Roman Empire...
70 KB (8,328 words) - 13:17, 6 September 2024
characteristic of Magna Graecia and Sicily, Egypt, Northwest Africa and Hispania Baetica. The latifundia were the closest approximation to industrialised agriculture...
10 KB (1,403 words) - 06:16, 7 September 2024
Córdoba, Spain (category Hispania Baetica)
became the capital of Baetica, with a forum and numerous temples, and was the main center of Roman intellectual life in Hispania Ulterior. The Roman philosopher...
114 KB (10,059 words) - 03:39, 25 September 2024
Italica (Spanish: Itálica) was an ancient Roman city in Hispania; its site is close to the town of Santiponce in the province of Seville, Spain. It was...
17 KB (1,912 words) - 16:51, 17 September 2024
Vettones) Calontienses Caluri Coerenses Today's Western Andalusia (Hispania Baetica), Baetis (Guadalquivir) river valley and basin, Marianus Mons (Sierra...
95 KB (10,152 words) - 12:50, 3 September 2024
Hadrian (category Romans from Hispania)
Italica, close to modern Seville in Spain, an Italic settlement in Hispania Baetica; his branch of the Aelia gens, the Aeli Hadriani, came from the town...
139 KB (17,460 words) - 16:45, 28 September 2024
names Hispania Citerior and Hispania Ulterior for 'near' and 'far' Hispania. At the time Hispania was made up of three Roman provinces: Hispania Baetica, Hispania...
127 KB (14,024 words) - 20:50, 25 September 2024
belladonna), its specific name derives from that of the Roman province of Hispania Baetica, while its common name refers to the Spanish region of Andalucía –...
45 KB (5,847 words) - 22:00, 5 May 2024
coastal Greek emporia from the Ligurian coast of Gaul to the coast of Hispania Baetica, and perhaps an impetus for Roman penetration of these coastal regions...
22 KB (2,300 words) - 14:54, 8 September 2024
Synod of Elvira (category 4th century in Hispania)
was an ecclesiastical synod held at Elvira in the Roman province of Hispania Baetica, now Granada in southern Spain. Its date has not been exactly determined...
17 KB (2,222 words) - 08:20, 26 August 2024
Visigothic Kingdom (redirect from Visigothic Hispania)
to the clergy's support of the Suebi. Theodoric took control over Hispania Baetica, Carthaginiensis and southern Lusitania. In 461, the Goths received...
65 KB (5,812 words) - 15:07, 22 September 2024
– Hispania". Library of Congress Country Series. Retrieved 2008-08-09. The Roman provinces of Hispania included Provincia Hispania Ulterior Baetica (Hispania...
191 KB (21,270 words) - 18:32, 29 September 2024
follows: Provincia Hispania Ulterior Baetica (Hispania Baetica), whose capital is Corduba (presently Córdoba); Provincia Hispania Ulterior Lusitania,...
27 KB (3,366 words) - 18:00, 26 December 2023
Lusitania (redirect from Hispania Lusitania)
BC or 16–13 BC) into the eastern and northern Hispania Tarraconensis, the southwestern Hispania Baetica and the western Provincia Lusitana. Originally...
35 KB (3,110 words) - 18:08, 26 September 2024
Seneca the Younger (category Romans from Hispania)
dramatic art." Seneca was born in Córdoba in the Roman province of Baetica in Hispania. His branch of the Annaea gens consisted of Italic colonists, of...
59 KB (6,842 words) - 22:18, 17 September 2024
Fidentia or simply Ulia was a Roman municipium in the province of Hispania Baetica. The site is the location of the current city of Montemayor, Córdoba...
1 KB (128 words) - 15:38, 8 August 2024
Roman rule, there were successive conquests of the Roman province of Hispania Baetica by the Germanic Vandals, Suebi and Visigoths during the 5th and 6th...
153 KB (15,343 words) - 10:15, 25 September 2024
Trajan (category Romans from Hispania)
Andalusian province of Seville in southern Spain, an Italic settlement in Hispania Baetica; his gens Ulpia came from the town of Tuder in the Umbria region of...
142 KB (18,741 words) - 19:46, 25 September 2024
Carmona, known as Carmo during Roman rule, was part of the province of Hispania Baetica. In the first century, agriculturalist Columella wrote of the production...
6 KB (559 words) - 10:51, 23 September 2024
present-day Santiponce (Seville), Spain–, in the Roman province of Hispania Baetica. Built during the reign of emperor Hadrian (who was born in Italica)...
6 KB (538 words) - 14:33, 3 July 2024
Ancient Rome and wine (section Hispania)
regions of Catalonia, the Rioja, the Ribera del Duero, and Galicia) and Hispania Baetica (which includes modern Andalusia) Montilla-Moriles winemaking region...
71 KB (9,506 words) - 13:25, 1 September 2024
444 the Spanish provinces of Lusitania and Hispania Baetica had been lost, and Roman authority in Hispania Tarraconensis was challenged by continued Bagaudic...
30 KB (3,281 words) - 08:32, 3 September 2024
the Romans as Baetis), in what was to become the Roman Province of Hispania Baetica (modern south of Spain). Strabo considers them to have been the successors...
4 KB (399 words) - 07:14, 3 May 2024
some Alans), who then resided in the Roman province of Hispania Baetica in southern Hispania. The Vandals had suffered greatly from attacks from the...
26 KB (3,192 words) - 10:11, 21 September 2024