negligibly slow at NMR frequencies. Hence truly isolated nuclear spins would show negligible rates of T1 relaxation. However, a variety of relaxation mechanisms...
26 KB (3,756 words) - 18:52, 20 June 2024
related to Relaxation. In the sciences, the term is used in the following ways: Relaxation (physics), and more in particular: Relaxation (NMR), processes...
2 KB (263 words) - 01:36, 23 December 2024
in nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). It is characterized by the spin–spin relaxation time, known as T2, a time constant...
10 KB (1,094 words) - 18:04, 10 December 2024
with an exponential curve characterized by a time constant T1 (see Relaxation (NMR)).[citation needed] T1 weighted images can be obtained by setting short...
12 KB (1,602 words) - 18:13, 27 May 2024
Nuclear magnetic resonance (redirect from NMR)
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is a physical phenomenon in which nuclei in a strong constant magnetic field are disturbed by a weak oscillating magnetic...
93 KB (11,860 words) - 07:47, 4 January 2025
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (redirect from NMR Spectroscopy)
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, most commonly known as NMR spectroscopy or magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), is a spectroscopic technique...
54 KB (6,159 words) - 05:39, 28 November 2024
"thermal relaxation". In nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), various relaxations are the properties that it measures. In chemical kinetics, relaxation methods...
11 KB (1,537 words) - 03:42, 6 October 2024
Carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance (redirect from 13C NMR)
carbon-13 NMR spectroscopy or 13C NMR spectroscopy or sometimes simply referred to as carbon NMR) is the application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy...
17 KB (1,877 words) - 04:17, 9 June 2024
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins (redirect from Protein NMR)
spectroscopy of proteins (usually abbreviated protein NMR) is a field of structural biology in which NMR spectroscopy is used to obtain information about the...
43 KB (5,337 words) - 03:39, 27 October 2024
Nuclear Overhauser effect (section Relaxation)
etc.) to another via cross-relaxation. A phenomenological definition of the NOE in nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR) is the change in the integrated...
33 KB (4,634 words) - 03:41, 25 February 2024
Two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (redirect from 2D-NMR)
Magnetic Resonance (2D NMR) is an advanced spectroscopic technique that builds upon the capabilities of one-dimensional (1D) NMR by incorporating an additional...
29 KB (3,715 words) - 00:24, 25 November 2024
J-coupling (redirect from NMR coupling)
acids Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins Proton NMR Relaxation (NMR) Residual dipolar coupling Hahn, E. L.; Maxwell, D. E. (1952). "Spin...
20 KB (2,408 words) - 21:30, 13 November 2024
Chemical shift (redirect from Shielding (NMR))
In nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, the chemical shift is the resonant frequency of an atomic nucleus relative to a standard in a magnetic...
24 KB (2,808 words) - 16:27, 11 October 2024
Transverse relaxation optimized spectroscopy (TROSY) is an experiment in protein NMR spectroscopy that allows studies of large molecules or complexes...
2 KB (326 words) - 21:31, 18 July 2023
magnetic resonance (NMR) because of their prolonged relaxation times, both T1 (spin-lattice relaxation) or T2 (spin-spin relaxation). Damadian was the...
38 KB (4,579 words) - 01:51, 2 November 2024
leading to stronger NMR signal intensities. The larger γ and faster relaxation of electron spins also help shorten T1 relaxation times of nearby nuclei...
32 KB (4,201 words) - 03:44, 14 November 2024
the measurement of NMR relaxation of water in the arms of living human subjects. In 1968, Jackson and Langham published the first NMR signals from a living...
35 KB (3,747 words) - 01:55, 29 December 2024
Magnetic resonance imaging (redirect from NMR imaging)
application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) which can also be used for imaging in other NMR applications, such as NMR spectroscopy. MRI is widely used in...
92 KB (10,737 words) - 21:02, 30 December 2024
NMR signal i.e. the NMR spectrum. The duration of the NMR signal is ultimately limited by T2 relaxation, but mutual interference of the different NMR...
4 KB (405 words) - 01:13, 6 November 2024
Nuclear magnetic resonance in porous media (redirect from NMR in porous media)
volume. With respect to NMR excitations of nuclear states for hydrogen-containing molecules in these regions, different relaxation times for the induced...
19 KB (2,912 words) - 05:21, 2 July 2023
nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectrum. These peaks can occur in the NMR spectrum of any NMR active atom (e.g. 19F or 31P NMR) where those atoms adjoin...
8 KB (965 words) - 05:07, 28 July 2024
Alfred G. Redfield (section Early work on NMR resonance saturation in solids and Redfield relaxation theory)
biochemist. In 1955 he published the Redfield relaxation theory, effectively moving the practice of NMR or Nuclear magnetic resonance from the realm of...
33 KB (3,680 words) - 05:49, 9 December 2024
Proton nuclear magnetic resonance (redirect from H NMR)
nuclear magnetic resonance (proton NMR, hydrogen-1 NMR, or 1H NMR) is the application of nuclear magnetic resonance in NMR spectroscopy with respect to hydrogen-1...
21 KB (2,502 words) - 01:19, 5 October 2024
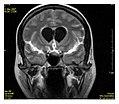
temporal lobes (Short arrow), and the substantia nigra (Long arrow). Relaxation (NMR) Bakshi R, Ariyaratana S, Benedict RH, Jacobs L (May 2001). "Fluid-attenuated...
4 KB (389 words) - 11:24, 17 October 2024
in NMR spectroscopy. There one replaces an atom lacking a nuclear spin (and so is NMR-silent) with an isotope having a spin I ≠ 0 (and so is NMR-active)...
3 KB (389 words) - 15:53, 2 February 2022
Chromium(III) acetylacetonate (section Use in NMR)
as Cr(acac)3. This purplish coordination complex is used in NMR spectroscopy as a relaxation agent because of its solubility in nonpolar organic solvents...
7 KB (580 words) - 13:32, 8 September 2023
hydrocarbon exploration. The most important mechanism affecting NMR relaxation is grain-surface relaxation. Molecules in fluids are in constant Brownian motion,...
2 KB (291 words) - 11:15, 26 January 2024
Paramagnetic nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (redirect from Paramagnetic NMR)
wide chemical shift range (often 200 ppm in 1H NMR). Since paramagnetism leads to shorter relaxation times (T1), the rate of spectral acquisition can...
7 KB (799 words) - 19:35, 27 January 2023
Solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance (redirect from Solid-State NMR)
magnetic resonance (ssNMR) is a spectroscopy technique used to characterize atomic-level structure and dynamics in solid materials. ssNMR spectra are broader...
50 KB (5,448 words) - 05:42, 16 December 2024
Low field nuclear magnetic resonance (redirect from Low field NMR)
Low field NMR spans a range of different nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) modalities, going from NMR conducted in permanent magnets, supporting magnetic...
3 KB (376 words) - 13:18, 13 August 2023