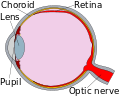
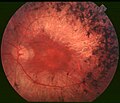
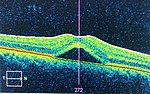
pigmented layer of retina or retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) is the pigmented cell layer just outside the neurosensory retina that nourishes retinal...
9 KB (1,181 words) - 23:04, 9 May 2024
Retina (redirect from Retinal pigments)
the vertebrate retinal pigment epithelium (RPE). Although their photoreceptors contain a protein, retinochrome, that recycles retinal and replicates one...
84 KB (9,299 words) - 13:58, 2 November 2024
sensory retina from the retinal pigment epithelium.[citation needed] Combined traction-rhegmatogenous A small number of retinal detachments result from...
18 KB (2,305 words) - 09:46, 28 September 2024
Congenital hypertrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium (CHRPE) is a harmless, pigmented fundus lesion that can be of various forms: solitary, grouped...
7 KB (752 words) - 07:41, 19 October 2024
Macular degeneration (redirect from Central retinal degeneration)
There are several functions of the retinal pigment epithelium. One of the main functions of the retinal pigment epithelium is to minimize oxidative stress...
92 KB (9,938 words) - 03:48, 9 November 2024
Retinitis pigmentosa (redirect from Retinal pigmentosa)
the development of (1) a mottled appearance of the retina and retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) that gives the same visual appearance of bone spicule patterns...
63 KB (6,334 words) - 13:01, 11 November 2024
Drusen (redirect from Retinal drusen)
extracellular material that build up between Bruch's membrane and the retinal pigment epithelium of the eye. The presence of a few small ("hard") drusen is normal...
10 KB (1,060 words) - 14:31, 18 February 2024
result in the progressive and irreversible loss of retinal tissue (photoreceptors, retinal pigment epithelium, choriocapillaris) which can lead to a loss of...
22 KB (2,654 words) - 18:25, 22 September 2024
epidermis and the retinal pigment epithelium. In healthy subjects, epidermal melanin is correlated with UV exposure, while retinal melanin has been found...
68 KB (7,185 words) - 18:38, 1 November 2024
neural retinal structures. Central progressive retinal atrophy (CPRA) is a different disease from PRA involving the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE),...
12 KB (1,586 words) - 03:34, 26 August 2024
Retinal pigment epithelium-specific 65 kDa protein (also known as RPE65) is a retinoid isomerohydrolase enzyme of the vertebrate visual cycle. RPE65 is...
24 KB (2,829 words) - 19:19, 23 May 2024
there are defects in the retinal pigment epithelium without accumulation of fluid below the retina, a pachychoroid pigment epitheliopathy (PPE) is present...
27 KB (2,993 words) - 01:46, 29 August 2024
Iris pigment epithelium Neuroepithelial cell Retinal pigment epithelium Skin cancer Sulcular epithelium List of distinct cell types in the adult human...
32 KB (2,908 words) - 21:06, 1 November 2024
the pigmented ciliary epithelium. The ciliary epithelia represent the anterior continuation of the multilayered retina, whose retinal pigmented epithelium...
2 KB (271 words) - 19:40, 15 January 2023
placed between the outer retinal layer and the retinal pigment epithelium. Epiretinal implants are placed on top of the retinal surface, above the nerve...
28 KB (3,215 words) - 10:31, 12 December 2023
Opsin (redirect from Visual pigment)
opsin groups of different species. RPE, retinal pigment epithelium; ipRGC, intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells; OPL, outer plexiform layer;...
83 KB (8,995 words) - 19:04, 16 October 2024
Fuchs spot (redirect from Forster-Fuchs' retinal spot)
described a pigmented lesion in 1901, and Forster, who described subretinal neovascularization in 1862. It occurs due to proliferation of retinal pigment epithelium...
3 KB (236 words) - 04:41, 19 March 2023
Visual cycle (section Retinal)
and 7 occur in retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cells. When a photon is absorbed, 11-cis-retinal is transformed to all-trans-retinal, and it moves to...
11 KB (1,373 words) - 00:19, 8 November 2023
and/or retinal pigment epithelium cells for this conversion. The two isoforms of melanopsin differ in their spectral sensitivity, for the 11-cis-retinal isoform...
26 KB (3,118 words) - 05:44, 25 July 2024
from the pigment cells that reside within the uvea and give color to the eye. These melanocytes are distinct from the retinal pigment epithelium cells underlying...
32 KB (3,519 words) - 15:49, 28 August 2024
occur in rod cell outer segments; Steps 1, 2, and 7 occur in retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cells. RPE65 isomerohydrolases are homologous with beta-carotene...
33 KB (3,318 words) - 20:15, 11 September 2024
This whitening is indicative of cell damage, which occurs in the retinal pigment epithelium and outer segment layer of photoreceptors. Damage to the outer...
6 KB (666 words) - 21:29, 16 August 2024
endothelium of capillaries of the retina and iris, ciliary epithelium and retinal pigment epithelium. It is a physical barrier between the local blood vessels...
3 KB (371 words) - 22:53, 18 March 2024
PEDF (redirect from Pigment epithelium-derived factor)
group was studying human retinal cell development by identifying secreted factors produced by the retinal pigmented epithelium (RPE), a layer of cells...
23 KB (2,742 words) - 21:03, 11 December 2023
Mendelian type X-linked recessive disorder wherein the retinal pigment epithelium lacks pigment while hair and skin appear normal. Since it is usually...
23 KB (2,871 words) - 18:02, 9 November 2024
of the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE), photoreceptors and the choroid. As of 2019, there is no treatment for choroideremia; however, retinal gene therapy...
28 KB (3,087 words) - 00:22, 15 August 2024
Maculopathy (redirect from Doyne honeycomb retinal dystrophy)
sight loss. It is characterised by changes in pigmentation in the Retinal Pigment Epithelium, the appearance of drusen on the retina of the eye and choroidal...
2 KB (190 words) - 22:57, 12 January 2024
Rhodopsin (redirect from Retinal rhodopsin)
Rhodopsin pigment must be regenerated for further phototransduction to occur. This means replacing all-trans-retinal with 11-cis-retinal and the decay...
39 KB (4,404 words) - 14:51, 9 November 2024
layer underneath the macula, the choroid, damage to the retinal pigment epithelium and the retinal photoreceptor cells ensues. This leads to impaired vision...
10 KB (1,020 words) - 01:12, 27 October 2024
affect vision, and there were no signs of reduced pigment on the retina or retinal pigment epithelium. TE1/TE1 or TE1/TE2: Yellow, amber, or bright orange...
6 KB (738 words) - 02:26, 1 December 2023