The Villanovan culture (c. 900–700 BCE), regarded as the earliest phase of the Etruscan civilization, was the earliest Iron Age culture of Italy. It directly...
18 KB (1,531 words) - 15:23, 22 November 2024
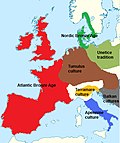
The Proto-Villanovan culture was a late Bronze Age culture that appeared in Italy in the first half of the 12th century BC and lasted until the 10th century...
6 KB (609 words) - 19:35, 17 October 2024
Tuscany (category Villanovan culture)
peoples of the so-called Proto-Villanovan culture (c. 1100 – c. 900 BC) part of the central European Urnfield culture system. Following this, at the beginning...
56 KB (5,565 words) - 15:22, 28 January 2025
of the Roman Kingdom. Latial culture is identified by their hut-shaped burial urns. Urns of the Proto-Villanovan culture are plain and biconical, and...
12 KB (1,474 words) - 20:14, 3 January 2025
Etruscan civilization (redirect from Etruscan culture)
earliest evidence of a culture that is identifiably Etruscan dates from about 900 BC. This is the period of the Iron Age Villanovan culture, considered to be...
108 KB (11,981 words) - 17:39, 4 February 2025
Prehistoric Italy (section Proto-Villanovan culture)
in the Proto-Villanovan culture. Pianello di Genga is an exception to the small cemeteries characterized for the Protov-Villanovan culture. More than 500...
34 KB (3,952 words) - 12:04, 20 January 2025
Italic peoples (redirect from Italic culture)
collapse. The Proto-Villanovan culture dominated the peninsula and replaced the preceding Apennine culture. The Proto-Villanovans practiced cremation...
25 KB (2,731 words) - 13:38, 8 January 2025
peninsula by the later Proto-Villanovan culture (1200–900 BC), and perhaps by the contemporary but more northerly Terramare culture (1700–1150 BC). Some of...
11 KB (1,253 words) - 21:24, 17 January 2025
Terramare culture was a dominant component of the Proto-Villanovan culture—especially in its northern and Campanian phases and the Terramare culture has been...
17 KB (1,874 words) - 19:13, 15 January 2025
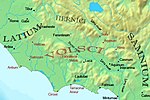
hypotheses. The first is the autochthonous development in situ out of the Villanovan culture, as claimed by the Greek historian Dionysius of Halicarnassus who...
82 KB (10,476 words) - 20:50, 5 January 2025
peoples of the so-called of the Proto-Villanovan culture (c. 1100-900 BC) part of the central European Urnfield culture system. Following this, at the beginning...
19 KB (2,278 words) - 22:55, 1 November 2024
Latins (Italic tribe) (category Latial culture)
(1200–900 BC). The material culture of the Latins, known as the Latial culture, was a distinctive subset of the proto-Villanovan culture that appeared in parts...
62 KB (7,879 words) - 11:22, 2 February 2025
first attestations of an Etruscan religion can be traced back to the Villanovan culture. Greek traders brought their religion and hero figures with them to...
29 KB (3,308 words) - 10:11, 25 January 2025
archaeology to explore. The Este culture existed next to the Villanovan Culture in the Bologna area and the Golasecca culture in the western Po Valley. It...
8 KB (772 words) - 09:22, 20 December 2024
Central Europe the Urnfield culture had already given way to the Hallstatt culture. In north Italy the Villanovan culture is regarded as the start of...
32 KB (4,196 words) - 18:09, 28 January 2025
Etruria (category Villanovan culture)
identified as Etruscans. Their complex culture centered on numerous city-states that arose during the Villanovan period in the ninth century BC, and they...
11 KB (970 words) - 11:00, 2 January 2025
area was home to the Apennine and Proto-Villanovan cultures before the advent of the more regional Latial culture. Archaeological evidence suggests that...
43 KB (5,475 words) - 12:19, 4 December 2024
the Lusatian culture is found. In Italy the late Bronze Age Canegrate and Proto-Villanovan cultures and the early Iron Age Villanovan culture show similarities...
105 KB (11,167 words) - 05:50, 5 February 2025
The Bell Beaker culture, also known as the Bell Beaker complex or Bell Beaker phenomenon, is an archaeological culture named after the inverted-bell beaker...
171 KB (19,849 words) - 20:18, 25 January 2025
c. 1100 BC—Late Minoan culture ends. c. 1100 BC—Greek Dark Ages begin. c. 1100 BC—Beginning of the proto-Villanovan culture in northern Italy. c. 1100...
2 KB (169 words) - 17:46, 18 July 2024
Lydia (section Culture and society)
earliest phase, the Villanovan culture, emerged around 900 BC, which itself developed from the previous Proto-Villanovan culture of Italy in the late...
70 KB (7,556 words) - 14:30, 24 January 2025
Culture, India are 2,900 years old: The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) c. 900 BC — the Villanovan culture emerges in northern Italy (Villanovan...
2 KB (273 words) - 01:13, 6 July 2024
Tyrrhenians (category Villanovan culture)
12th century BC invasion from the Aegean and Anatolia imposing itself over the Villanovan culture, with some scholars claiming a relationship or at least evidence of...
12 KB (1,437 words) - 01:25, 9 October 2024
Proto-Villanovan culture Polada culture Castelluccio Culture Thapsos Culture Terramare culture Castellieri culture Luco-Meluno culture Scamozzina culture Hallstatt...
23 KB (1,885 words) - 14:22, 4 December 2024
BC, a fourth wave, the Proto-Villanovan culture, brought iron-working to the Italian peninsula. Proto-Villanovan culture may have been part of the central...
179 KB (20,752 words) - 00:56, 24 January 2025
Hallstatt culture. Archeologists see an obvious connection to the Pomeranian culture of the same age. The relation to the Etruscan Villanovan culture, which...
2 KB (173 words) - 02:14, 4 November 2024
Iron Age: either by autochthonous development in situ out of the Villanovan culture of Etruria in northern and central Italy, or via an eastern (Anatolian...
20 KB (2,158 words) - 09:05, 12 October 2024
The Karasuk culture (Russian: Карасукская культура, romanized: Karasukskaya kul'tura) describes a group of late Bronze Age societies who ranged from the...
31 KB (3,322 words) - 08:30, 26 January 2025
producing areas elsewhere. Bronze Age cultures were the first to develop writing. According to archaeological evidence, cultures in Mesopotamia, which used cuneiform...
103 KB (11,939 words) - 05:43, 1 February 2025
Bronze Age disintegrated, transforming into the small isolated village cultures of the Greek Dark Ages, which lasted from c. 1100 to c. 750 BC, and were...
70 KB (9,066 words) - 02:23, 20 January 2025