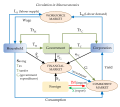
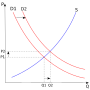
Classical economics, also known as the classical school of economics, or classical political economy, is a school of thought in political economy that...
24 KB (3,089 words) - 16:08, 22 November 2024
New classical macroeconomics, sometimes simply called new classical economics, is a school of thought in macroeconomics that builds its analysis entirely...
14 KB (1,629 words) - 18:16, 22 November 2024
distinguishing factors between neoclassical economics and other earlier economic theories, such as Classical and Marxian, which use the labor theory of...
53 KB (6,460 words) - 00:02, 17 July 2024
literature; classical economics, neoclassical economics, Keynesian economics, the neoclassical synthesis, monetarism, new classical economics, New Keynesian...
175 KB (17,852 words) - 19:40, 17 November 2024
classical theory of the interest rate. In regards to employment, the condition referred to by Keynes as the "first postulate of classical economics"...
107 KB (13,226 words) - 22:17, 11 November 2024
Classical liberalism is a political tradition and a branch of liberalism that advocates free market and laissez-faire economics and civil liberties under...
80 KB (9,026 words) - 01:54, 12 November 2024
Look up classical or classically in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. Classical may refer to: Classical antiquity, a period of history from roughly the...
3 KB (484 words) - 12:56, 25 July 2024
Schools of economic thought (redirect from Schools of Economics)
(beginning with Adam Smith and classical economics in the late 18th century, and Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels' Marxian economics in the mid 19th century)...
46 KB (5,301 words) - 14:51, 22 November 2024
Macroeconomics (redirect from Macro-economics)
Macroeconomics is a branch of economics that deals with the performance, structure, behavior, and decision-making of an economy as a whole. This includes...
57 KB (6,821 words) - 06:19, 22 November 2024
factors of production". This classification originated during the classical economics period and has remained the dominant method for classification. Capital...
23 KB (3,079 words) - 15:54, 26 September 2024
is no market to set a price then there is no economic value. In classical economics, the value of an object or condition is the amount of discomfort/labor...
23 KB (3,012 words) - 04:18, 18 October 2024
In macroeconomics, the classical dichotomy is the idea, attributed to classical and pre-Keynesian economics, that real and nominal variables can be analyzed...
4 KB (478 words) - 04:25, 15 November 2023
Marxian economics, or the Marxian school of economics, is a heterodox school of political economic thought. Its foundations can be traced back to Karl...
53 KB (6,512 words) - 10:43, 10 September 2024
on Austrian Economics. New York: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-12283-2. OCLC 70769328. Raico, Ralph (2011). "Austrian Economics and Classical Liberalism"...
59 KB (6,268 words) - 20:04, 29 October 2024
countries and over time. Prior to the development and prevalence of classical economics, the dominant school in Europe was mercantilism, which was rather...
19 KB (1,955 words) - 00:28, 5 November 2024
Agricultural economics Attention economics Behavioral economics Classical economics Comparative economic systems Contract theory Cultural economics Demographic...
24 KB (2,176 words) - 04:53, 17 October 2024
Factors of production (redirect from Resource (economics))
capital. Materials and energy are considered secondary factors in classical economics because they are obtained from land, labour, and capital. The primary...
24 KB (3,100 words) - 03:14, 21 September 2024
from each other. Specifically, new Keynesian economics was developed as a response to new classical economics, electing to incorporate the insight of rational...
48 KB (5,164 words) - 00:23, 13 November 2024
Goods (economics) Income distribution Income Distribution of wealth Wealth concentration Wealth Classical economics: value theory Marxian economics: Marx's...
14 KB (1,268 words) - 10:25, 13 July 2024
currency leads to inflation. He also played a part in the emergence of classical economics, which meant he fought for free trade and free competition without...
14 KB (1,873 words) - 06:30, 11 January 2024
Liberalism (section Keynesian economics)
contributed to classical liberalism include John Locke, Jean-Baptiste Say, Thomas Malthus, and David Ricardo. It drew on classical economics, especially...
153 KB (17,584 words) - 00:21, 21 November 2024
Inframarginal analysis (category Theory of value (economics))
Inframarginal analysis is an analytical method in the study of classical economics. Xiaokai Yang created the super marginal analysis method and revived...
17 KB (2,426 words) - 07:38, 11 November 2024
process, nor do they become a whole component in the product. Under classical economics, materials and energy are categorised as secondary factors as they...
45 KB (6,224 words) - 18:53, 29 October 2024
Inflation (redirect from Inflation (economics))
In economics, inflation is a general increase in the prices of goods and services in an economy. This is usually measured using a consumer price index...
122 KB (14,086 words) - 15:21, 22 November 2024
The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money (category Keynesian economics)
booms and crises. The General Theory is a sustained attack on the classical economics orthodoxy of its time. It introduced the concepts of the consumption...
65 KB (9,292 words) - 11:18, 17 November 2024
American individualist anarchist Benjamin Tucker, who connected the classical economics of Adam Smith and the Ricardian socialists as well as that of Pierre-Joseph...
142 KB (18,315 words) - 01:18, 21 November 2024
Neoclassical synthesis (redirect from Neo-Keynesian economics)
neoclassical–Keynesian synthesis is an academic movement and paradigm in economics that worked towards reconciling the macroeconomic thought of John Maynard...
37 KB (4,760 words) - 14:57, 31 October 2024
or satisfaction with life, was seen as unmeasurable in classical and neo-classical economics. Van Praag was the first person who organized large surveys...
68 KB (7,591 words) - 11:29, 27 October 2024
the decisive factor. The failure is characteristic of classical economics and bourgeoisie economics, inadequate at explaining the true movement of economic...
82 KB (10,653 words) - 19:11, 12 November 2024
Economic rent (redirect from Economic rent (economics))
a factor of production or resource, supply of which is fixed. In classical economics, economic rent is any payment made (including imputed value) or benefit...
24 KB (2,845 words) - 17:58, 20 August 2024