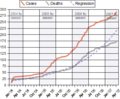
for human mortality from H5N1 is the case-fatality rate (CFR); the ratio of the number of confirmed human deaths resulting from infection of H5N1 to the...
61 KB (7,991 words) - 12:46, 29 December 2024
Transmission and infection of H5N1 from infected avian sources to humans has been a concern since the first documented case of human infection in 1997, due to...
38 KB (4,450 words) - 14:11, 2 August 2024
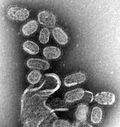
Influenza A virus subtype H5N1 (A/H5N1) is a subtype of the influenza A virus, which causes the disease avian influenza (often referred to as "bird flu")...
71 KB (8,315 words) - 22:41, 7 January 2025
poultry against the avian H5N1 influenza epizootic is widespread in certain countries. Some vaccines also exist for use in humans, and others are in testing...
21 KB (1,817 words) - 07:49, 8 January 2025
Since 2020, outbreaks of avian influenza subtype H5N1 have been occurring, with cases reported from every continent except Australia as of January 2025...
70 KB (6,596 words) - 01:42, 7 January 2025
genetic level from a highly pathogenic, emergent strain of H5N1, which was able to achieve hitherto unprecedented global spread in 2008. The H5N1 strain is...
44 KB (5,383 words) - 20:24, 21 December 2024
species have been shown to contract and spread Influenza A virus subtype H5N1, from waterfowl to poultry and birds of prey, mammalian infections have been...
13 KB (738 words) - 09:22, 17 November 2024
PMC 9584108. PMID 21881144. "Cumulative number of confirmed human cases for avian influenza A(H5N1) reported to WHO, 2003-2021". World Health Organization...
42 KB (2,182 words) - 16:19, 11 December 2024
The first known transmission of A/H5N1 to a human occurred in Hong Kong in 1997, when there was an outbreak of 18 human cases resulting in 6 deaths. It...
64 KB (7,173 words) - 09:50, 8 January 2025
pathogenic) H5N1 in birds is considered a significant pandemic threat. While prior H5N1 strains have been known, they were significantly different from the current...
7 KB (858 words) - 05:24, 24 December 2024
pathogenic) H5N1 in birds is considered a significant pandemic threat. While prior H5N1 strains have been known, they were significantly different from the 2006...
80 KB (9,192 words) - 20:28, 2 October 2024
H5N1 clinical trials are clinical trials concerning H5N1 vaccines, which are intended to provide immunization to influenza A virus subtype H5N1. They...
22 KB (2,944 words) - 01:13, 2 April 2024
pathogenic) H5N1 in birds is considered a significant pandemic threat. While prior H5N1 strains have been known, they were significantly different from the current...
14 KB (1,635 words) - 19:40, 7 October 2024
The genetic structure of H5N1, a highly pathogenic avian influenza virus (influenza A virus subtype H5N1), is characterized by a segmented RNA genome...
28 KB (3,756 words) - 16:53, 25 December 2024
pathogenic) H5N1 in birds is considered a significant pandemic threat. While prior H5N1 strains have been known, they were significantly different from the current...
19 KB (2,451 words) - 20:28, 2 October 2024
Influenza pandemic (category Influenza A virus subtype H5N1)
produced mild illness.) When it first killed humans in Asia in the 1990s, a deadly avian strain of H5N1 posed a great risk for a new influenza pandemic;...
111 KB (12,786 words) - 20:27, 19 December 2024
Influenza A virus (category Use dmy dates from May 2024)
populations worldwide, H5N1 and H7N9. Both of these have potential to devastate poultry stocks, and both have jumped to humans with relatively high case...
60 KB (6,050 words) - 22:43, 7 January 2025
Respiratory tract infection (category Short description is different from Wikidata)
respiratory tracts, but more dangerous strains such as the highly pernicious H5N1 tend to bind to receptors deep in the lungs. Pulmonary Function Testing (PFT)...
20 KB (1,918 words) - 17:17, 26 August 2024
for government preparation for an H5N1 pandemic The social impact of H5N1 is the effect or influence of H5N1 in human society.[citation needed] On November...
20 KB (2,407 words) - 14:04, 2 August 2024
Pandemic H1N1/09 virus (category Articles containing potentially dated statements from September 2009)
on genetic material." The H5N1 virus is mostly limited to birds, but in rare cases when it infects humans it has a mortality rate of between 60% and 70%...
62 KB (6,709 words) - 07:06, 14 August 2024
Water bird (category Articles with dead external links from November 2022)
DEV, and the mortality rate of this disease can reach up to 100%, especially in young birds. Avian influenza caused by infection with H5N1, a highly pathogenic...
14 KB (1,560 words) - 20:04, 11 October 2024
Fujian flu (redirect from A/Fujian (H5N1))
subtype H5N1 and Influenza A virus subtype H3N2 for details about the causative agents. Fujian flu refers to flu caused by either a Fujian human flu strain...
34 KB (4,276 words) - 18:26, 21 December 2024
Oseltamivir (category Short description is different from Wikidata)
October 2005). "Oseltamivir-resistant H5N1 virus isolated from Vietnamese girl". University of Minnesota. Archived from the original on 14 December 2014....
63 KB (5,827 words) - 04:34, 19 December 2024
Spanish flu (category Use dmy dates from December 2021)
first attempts to reduce mortality to combat superinfecting bacteria: an opinion from a virologist and a military historian". Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics...
239 KB (26,849 words) - 19:06, 14 December 2024
Influenza A virus subtype H3N2 (category Short description is different from Wikidata)
Pigs can carry human influenza viruses, which can combine (i.e. exchange homologous genome subunits by genetic reassortment) with H5N1, passing genes...
16 KB (1,651 words) - 20:44, 20 August 2024
Antigenic shift (category Use dmy dates from April 2017)
that combine their antigens; for example, H3N2 and H5N1 can form H5N2 this way. Because the human immune system has difficulty recognizing the new influenza...
8 KB (910 words) - 16:57, 11 July 2024
subtype H5N1", is the causative agent of H5N1 flu. HPAI A(H5N1) is considered an avian disease, although there is some evidence of limited human-to-human transmission...
20 KB (2,017 words) - 19:30, 26 September 2024
Orthomyxoviridae (category Short description is different from Wikidata)
confirmed human deaths, are: H1N1 caused "Spanish flu" in 1918 and "Swine flu" in 2009. H2N2 caused "Asian Flu". H3N2 caused "Hong Kong Flu". H5N1, "avian"...
39 KB (4,238 words) - 21:59, 1 December 2024
Hong Kong flu (category Wikipedia articles needing page number citations from November 2024)
while all-cause excess mortality was 47,000. Pandemic influenza was not detected in Italy until the last week of February 1969, from a case in Genova. The...
90 KB (11,009 words) - 08:45, 21 December 2024