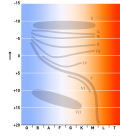
In astronomy, the main sequence is a classification of stars which appear on plots of stellar color versus brightness as a continuous and distinctive...
61 KB (6,817 words) - 10:25, 18 July 2024
Red dwarf (redirect from M-type main sequence)
A red dwarf is the smallest kind of star on the main sequence. Red dwarfs are by far the most common type of fusing star in the Milky Way, at least in...
36 KB (4,249 words) - 12:06, 3 July 2024
A G-type main-sequence star (spectral type: G-V), also often, and imprecisely, called a yellow dwarf, or G star, is a main-sequence star (luminosity class...
12 KB (1,178 words) - 21:29, 20 July 2024
A K-type main-sequence star, also referred to as a K-type dwarf, or orange dwarf, is a main-sequence (hydrogen-burning) star of spectral type K and luminosity...
13 KB (1,420 words) - 11:27, 21 July 2024
A pre-main-sequence star (also known as a PMS star and PMS object) is a star in the stage when it has not yet reached the main sequence. Earlier in its...
4 KB (481 words) - 21:34, 25 September 2023
Hertzsprung–Russell diagram where it leaves the main sequence after its main fuel is exhausted – the main sequence turnoff. By plotting the turnoff points of...
2 KB (249 words) - 22:16, 10 December 2023
Star (section Main sequence)
cores. Such stars are said to be on the main sequence and are called dwarf stars. Starting at zero-age main sequence, the proportion of helium in a star's...
146 KB (16,331 words) - 03:00, 17 July 2024
An A-type main-sequence star (AV) or A dwarf star is a main-sequence (hydrogen burning) star of spectral type A and luminosity class V (five). These stars...
12 KB (1,063 words) - 11:20, 21 July 2024
supergiant Hypergiants absolute magni- tude (MV) An O-type main-sequence star (O V) is a main-sequence (core hydrogen-burning) star of spectral type O and luminosity...
12 KB (1,301 words) - 01:29, 4 July 2024
supergiant Hypergiants absolute magni- tude (MV) A B-type main-sequence star (B V) is a main-sequence (hydrogen-burning) star of spectral type B and luminosity...
12 KB (1,369 words) - 11:26, 21 July 2024
An F-type main-sequence star (F V) is a main-sequence, hydrogen-fusing star of spectral type F and luminosity class V. These stars have from 1.0 to 1...
11 KB (1,249 words) - 19:36, 24 March 2024
belonging to K-type stars. Yellow dwarfs comprise the G-type stars of the main sequence, with masses between 0.9 and 1.1 M☉ and surface temperatures between...
35 KB (3,485 words) - 23:02, 3 May 2024
Stellar classification (redirect from Blue-white main sequence star)
class III for regular giants, class IV for subgiants, class V for main-sequence stars, class sd (or VI) for subdwarfs, and class D (or VII) for white...
104 KB (11,345 words) - 23:50, 20 July 2024
settle down into a state of equilibrium, becoming what is known as a main-sequence star. Nuclear fusion powers a star for most of its existence. Initially...
49 KB (6,421 words) - 16:30, 19 July 2024
Hertzsprung–Russell diagram (redirect from Main line stars)
diagram along the line called the main sequence. During the stage of their lives in which stars are found on the main sequence line, they are fusing hydrogen...
23 KB (2,771 words) - 01:42, 18 July 2024
Main Sequence (foaled 13 February 2009) is a Kentucky-bred Thoroughbred racehorse. In his first three seasons he raced in Europe winning his first four...
18 KB (2,241 words) - 01:57, 23 March 2023
Convection zone (section Main sequence stars)
solar granulation. Low-mass main-sequence stars, such as red dwarfs below 0.35 solar masses, as well as pre-main sequence stars on the Hayashi track,...
7 KB (821 words) - 17:12, 2 June 2024
Sun (category G-type main-sequence stars)
elements, including oxygen, carbon, neon, and iron. The Sun is a G-type main-sequence star (G2V), informally called a yellow dwarf, though its light is actually...
169 KB (18,725 words) - 20:56, 22 July 2024
type O B A F G K M L T Brown dwarfs White dwarfs Red dwarfs Subdwarfs Main sequence ("dwarfs") Subgiants Giants Red giants Blue giants Bright giants Supergiants...
26 KB (3,358 words) - 23:26, 22 July 2024
energy from its outer photosphere. Astronomers classify it as a G-type main-sequence star. The largest objects that orbit the Sun are the eight planets....
220 KB (21,680 words) - 09:05, 22 July 2024
The habitability of F-type main-sequence star (or yellow-white dwarf) systems is disputed due to the shorter lifetimes (3-8 Gyrs as opposed to 9-15 Gyrs...
12 KB (1,471 words) - 19:39, 23 February 2024
amplitude ranges, the main sequence can best be modeled by an inverse power law function. The high peak velocities and the main sequence relationship can also...
29 KB (3,820 words) - 19:43, 6 July 2024
as the main sequence. Main-sequence stars derive energy from the fusion of hydrogen into helium in their cores. The Sun remains a main-sequence star today...
112 KB (13,426 words) - 05:47, 18 July 2024
the system boundary from actors to systems. A system sequence diagram should be done for the main success scenario of the use case, and frequent or complex...
7 KB (909 words) - 04:54, 11 June 2024
type O B A F G K M L T Brown dwarfs White dwarfs Red dwarfs Subdwarfs Main sequence ("dwarfs") Subgiants Giants Red giants Blue giants Bright giants Supergiants...
39 KB (5,371 words) - 18:49, 20 July 2024
black holes or neutron stars. Most of these stars are young massive main sequence, giant, or supergiant stars, but also some central stars of planetary...
30 KB (3,350 words) - 09:26, 22 April 2024
chromospheric lines. T Tauri stars are pre-main-sequence stars in the process of contracting to the main sequence along the Hayashi track, a luminosity–temperature...
9 KB (928 words) - 20:03, 20 March 2024
Stellar core (section Main sequence)
extremely hot, dense region at the center of a star. For an ordinary main sequence star, the core region is the volume where the temperature and pressure...
15 KB (1,845 words) - 05:26, 29 January 2024
type O B A F G K M L T Brown dwarfs White dwarfs Red dwarfs Subdwarfs Main sequence ("dwarfs") Subgiants Giants Red giants Blue giants Bright giants Supergiants...
11 KB (1,543 words) - 20:53, 2 September 2023
infalling gas is depleted, leaving a pre-main-sequence star, which contracts to later become a main-sequence star at the onset of hydrogen fusion producing...
11 KB (1,238 words) - 17:40, 18 June 2024