epoch. The Paleolithic was characterized by climate oscillations between ice ages and small interglacials, producing heavy changes in Iberia's orography...
31 KB (3,578 words) - 22:53, 17 August 2024
produced significant changes in Iberia's orography. The first and biggest period in Iberia's prehistory is the Paleolithic, which starts c. 1.3 Ma and ends...
58 KB (6,893 words) - 20:12, 12 October 2024
Paleolithic Europe, or Old Stone Age Europe, encompasses the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age in Europe from the arrival of the first archaic humans, about...
22 KB (2,237 words) - 06:36, 13 September 2024
Iberian Peninsula (redirect from Iberia)
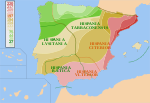
The Iberian Peninsula (IPA: /aɪˈbɪəriən/), also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in south-western Europe. Mostly separated from the rest of the European...
127 KB (14,020 words) - 16:14, 3 November 2024
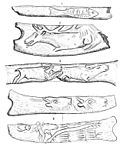
The art of the Upper Paleolithic represents the oldest form of prehistoric art. Figurative art is present in Europe and Southeast Asia, beginning around...
29 KB (3,175 words) - 18:13, 17 October 2024
The Upper Paleolithic (or Upper Palaeolithic) is the third and last subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. Very broadly, it dates to between...
45 KB (4,699 words) - 21:10, 21 October 2024
Hispania (redirect from Roman Iberia)
Homo heidelbergensis and Homo antecessor. In the Paleolithic period, the Neanderthals entered Iberia and eventually took refuge from the advancing migrations...
45 KB (5,276 words) - 05:32, 25 October 2024
Timeline of Iberian prehistory (section Paleolithic)
c. 1.5 to 1.8 million years Before Present (BP) Paleolithic – Tools used by hominids at Orce in the province of Granada c. 1 million years BP – Tools...
6 KB (678 words) - 13:01, 3 September 2024
to Europe before the start of written records, beginning in the Lower Paleolithic. As history progresses, considerable regional unevenness in cultural...
84 KB (8,820 words) - 13:23, 2 November 2024
Prehistory (section Paleolithic)
Armenia Paleolithic Europe Neolithic Europe Bronze Age Europe Iron Age Europe Atlantic fringe Prehistoric Britain Prehistoric Ireland Prehistoric Iberia Prehistoric...
56 KB (5,895 words) - 17:42, 3 November 2024
Solutrean (category Upper Paleolithic cultures of Europe)
industry is a relatively advanced flint tool-making style of the Upper Paleolithic of the Final Gravettian, from around 22,000 to 17,000 BP. Solutrean sites...
15 KB (1,468 words) - 14:38, 1 September 2024
Prehistoric warfare (redirect from Paleolithic warfare)
the current scientific community. Kelly believes that this period of "Paleolithic warlessness" persisted until well after the appearance of Homo sapiens...
35 KB (4,134 words) - 21:29, 29 October 2024
been ambitiously applied to popularized accounts of the Paleolithic inhabitants of Atlantic Iberia. The expulsion of the Oestrimni, from Ora Maritima: The...
3 KB (221 words) - 09:42, 26 February 2022
discovered in 1951. It shows traces of human occupation from the Middle Paleolithic. It contains cave art, most notably a total of 71 hand stencils, enumerated...
4 KB (509 words) - 05:41, 15 January 2024
and are dated as far back as around 50,000 years ago (Art of the Upper Paleolithic). Together with religion and other cultural universals of contemporary...
19 KB (1,965 words) - 22:14, 16 July 2024
Lagar Velho 1 (category Upper Paleolithic Europe)
anatomically modern human parent. In 1998, this discovery of an early Upper Paleolithic human burial at Abrigo do Lagar Velho by the team led by prehistoric...
4 KB (446 words) - 08:41, 27 May 2024
Cave painting (category Art of the Upper Paleolithic)
humans. The oldest known are more than 40,000 years old (art of the Upper Paleolithic) and found in the caves in the district of Maros (Sulawesi, Indonesia)...
67 KB (7,400 words) - 04:03, 22 October 2024
Prehistoric West Africa (redirect from West African Lower Paleolithic)
(Middle Pleistocene). At Ounjougou, in Mali, a yet-to-be-dated Lower Paleolithic economy (e.g., pebble cores, pebble tools, polyhedrons, spheroids, sub-spheroids)...
128 KB (14,386 words) - 07:59, 1 November 2024
Magdalenian (category Upper Paleolithic cultures of Europe)
(also Madelenian; French: Magdalénien) are later cultures of the Upper Paleolithic and Mesolithic in western Europe. They date from around 17,000 to 12...
26 KB (2,528 words) - 15:47, 6 November 2024
Prehistoric Georgia (redirect from Paleolithic Georgia)
presence of early humans outside the African continent. Later Lower Paleolithic Acheulian sites have been discovered in the highlands of Georgia, particularly...
12 KB (1,481 words) - 11:31, 19 August 2024
Neanderthal extinction (category Upper Paleolithic)
dating of the Middle-to-Upper Paleolithic transition in Murcia (Spain) supports late Neandertal persistence in Iberia". Heliyon. 3 (11): e00435. Bibcode:2017Heliy...
46 KB (5,133 words) - 12:45, 5 November 2024
Hemisphere. The Roman Republic conquered Iberia during the 2nd and 1st centuries BC. Hispania, the name given to Iberia by the Romans as a province of their...
83 KB (6,750 words) - 18:57, 12 October 2024
of Iberia." This indicates Basques were isolated from admixture with outside groups since at least 1000BC or 3000 years before the present. In Iberia, these...
47 KB (5,347 words) - 05:35, 4 November 2024
widely dispersed throughout Western Europe, being present in many regions of Iberia and stretching eastward to the Danubian plains, and northward to the islands...
165 KB (19,249 words) - 16:30, 4 November 2024
early people changed dramatically from the Upper Paleolithic to the Neolithic era. In the Paleolithic, people did not normally live in permanent constructions...
79 KB (8,074 words) - 20:51, 2 November 2024
classical era saw the emergence of several kingdoms, such as Colchis and Iberia, that formed the nucleus of the modern Georgian state. In the early fourth...
231 KB (21,754 words) - 00:56, 1 November 2024
during the early Upper Paleolithic. Its various subclades (labelled U1–U9, diverging over the course of the Upper Paleolithic) are found widely distributed...
86 KB (9,284 words) - 21:55, 24 September 2024
Prehistory of France (redirect from Paleolithic France)
first megaliths were erected in the early 5th millennium BC. The lower paleolithic period began with the first human occupation of the region. Stone tools...
58 KB (5,495 words) - 07:54, 14 October 2024
the Lapa do Picareiro also indicate human occupation during the Upper Paleolithic, Mesolithic, and Iron Age, including materials from the proto-Solutrean...
3 KB (309 words) - 01:01, 3 September 2024