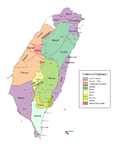
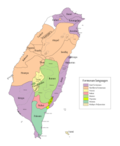
Saisiyat (sometimes spelled Saisiat) is the language of the Saisiyat, a Taiwanese indigenous people. It is a Formosan language of the Austronesian family...
11 KB (642 words) - 04:56, 13 December 2022
highlands of Miaoli), each with its own dialect. Their language is also known as Saisiyat. Saisiyat are sometimes rendered as Saiset, Seisirat, Saisett,...
5 KB (525 words) - 18:40, 16 February 2024
Saisiyat may refer to: Saisiyat people, of Taiwan Saisiyat language, their Austronesian language This disambiguation page lists articles associated with...
185 bytes (44 words) - 09:02, 20 August 2023
language; old Favorlang language: Taokas and Poavosa dialects Papora-Hoanya language: Papora, Hoanya dialects Northwest Formosan Saisiyat language:...
93 KB (7,234 words) - 08:04, 24 July 2024
languages, Pazeh does not distinguish between common nouns and personal names, whereas Saisiyat does (Li 2000). Although closely related to Saisiyat,...
19 KB (1,823 words) - 16:17, 23 July 2024
Formosan languages, such as Thao, Saisiyat, and Pazih, possibly from influence from Chinese. Li (1998) lists the word orders of several Formosan languages. Rukai:...
26 KB (1,532 words) - 06:27, 24 July 2024
Typhoons in the Philippines (category Articles containing Saisiyat-language text)
Cognates in other Austronesian languages include Sama baliw ('wind'), Amis faliyos or farios ('typhoon'); Saisiyat balosh ('typhoon'), Babuza bayus...
24 KB (3,210 words) - 23:44, 15 July 2024
Hsinchu County (category Articles containing Chinese-language text)
of the Han Chinese, the Hsinchu area was home to the indigenous Taokas, Saisiyat, and Atayal. After the Spanish occupied northern Taiwan, Catholic missionaries...
18 KB (1,154 words) - 01:29, 17 June 2024
An endangered language is a language that it is at risk of falling out of use, generally because it has few surviving speakers. If it loses all of its...
22 KB (118 words) - 13:57, 23 July 2024
(Papora, Hoanya, Babuza, and Taokas), and the Northwest Formosan languages (Pazeh and Saisiyat; Li places Western Plains with this grouping). The Northern...
5 KB (467 words) - 05:25, 7 October 2023
An endangered language is a language that is at risk of falling out of use, generally because it has few surviving speakers. If it loses all of its native...
71 KB (417 words) - 01:05, 1 May 2024
pages of Tsuchida (1985). Li (2008) follows Tsuchida in linking Kulon with Saisiyat, while Blust (1999) proposes it was more closely related to Pazeh. "Táiwān...
3 KB (196 words) - 02:24, 11 June 2024
citrus species from Taiwan. It is endangered in the wild. In the Saisiyat language it is called Katayoe'. The Japanese named it the Nansho Daidai sour...
2 KB (164 words) - 10:47, 3 May 2024
Kutai is a Malayic language spoken by 300,000 to 500,000 people. It is the native language of the Kutai people (Indonesian: Suku Kutai, Kutai: Urang Kutai)[what...
3 KB (285 words) - 18:40, 23 July 2023
indoˈnesija]) is the official and national language of Indonesia. It is a standardized variety of Malay, an Austronesian language that has been used as a lingua franca...
170 KB (14,543 words) - 13:45, 20 July 2024
Malay: Bahasa Melayu, Jawi: بهاس ملايو) is an Austronesian language that is an official language of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, and Singapore, and that...
58 KB (4,633 words) - 17:34, 24 July 2024
The languages of Taiwan consist of several varieties of languages under the families of Austronesian languages and Sino-Tibetan languages. The Formosan...
46 KB (4,315 words) - 15:14, 17 July 2024
tə-GAH-log; [tɐˈɣaː.loɡ]; Baybayin: ᜆᜄᜎᜓᜄ᜔) is an Austronesian language spoken as a first language by the ethnic Tagalog people, who make up a quarter of the...
115 KB (8,207 words) - 16:56, 4 July 2024
Caledonian languages also known as Kanak languages form a branch of the Southern Oceanic languages. Their speakers are known as Kanaks. One language is extinct...
9 KB (226 words) - 04:04, 21 December 2023
Chamorro: Finuʼ Chamorro (CNMI), Finoʼ CHamoru (Guam)) is an Austronesian language spoken by about 58,000 people, numbering about 25,800 on Guam and about...
44 KB (3,623 words) - 22:39, 23 July 2024
or True Motu to distinguish it from Hiri Motu) is a Central Papuan Tip language that is spoken by the Motuans, an indigenous ethnic group of Papua New...
6 KB (520 words) - 18:57, 21 July 2024
Borneo languages Central Sarawak languages Kayan–Murik languages Land Dayak languages Malayo–Chamic Chamic languages Malayic languages Rejang language Sundanese...
18 KB (1,524 words) - 09:18, 13 June 2024
Pascuan (/ˈpæskjuən/) or Pascuense, is an Eastern Polynesian language of the Austronesian language family. It is spoken on Easter Island, also known as Rapa...
52 KB (6,520 words) - 23:16, 28 May 2024
Teor and Kur are two Austronesian language varieties of the Central–Eastern Malayo-Polynesian branch spoken near Kei Island, Indonesia. They are reportedly...
1,019 bytes (44 words) - 21:10, 15 April 2023
The Bisayan languages or Visayan languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages spoken in the Philippines. They are most closely related to Tagalog...
27 KB (954 words) - 02:32, 24 June 2024
pronounced [ʔoːˈlɛlo həˈvɐjʔi]) is a Polynesian language and critically endangered language of the Austronesian language family that takes its name from Hawaiʻi...
69 KB (7,685 words) - 18:20, 16 July 2024
Soʼa is a language of central Flores, in East Nusa Tenggara Province, Indonesia. It forms a dialect cluster with Ngadha. Soʼa at Ethnologue (18th ed.,...
1,007 bytes (31 words) - 17:53, 28 November 2021
ancestor of the Malayo-Polynesian languages, which is by far the largest branch (by current speakers) of the Austronesian language family. Proto-Malayo-Polynesian...
22 KB (671 words) - 06:07, 25 March 2024
Museum of Saisiyat Folklore (traditional Chinese: 賽夏族民俗文物館; simplified Chinese: 赛夏族民俗文物馆; pinyin: Sàixiàzú Mínsú Wénwùguǎn) is a museum of Saisiyat people...
4 KB (197 words) - 02:25, 9 December 2022
approximately 450 Oceanic languages are a branch of the Austronesian languages. The area occupied by speakers of these languages includes Polynesia, as well...
14 KB (1,230 words) - 04:23, 25 March 2024