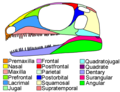
Diapsids ("two arches") are a clade of sauropsids, distinguished from more primitive eureptiles by the presence of two holes, known as temporal fenestrae...
29 KB (1,776 words) - 08:48, 9 October 2024
synapsids (mammals and their extinct relatives) there is one, and most diapsids (including birds, crocodilians, squamates, and tuataras), have two. Turtles...
48 KB (3,794 words) - 19:35, 7 October 2024
though not diapsids in a purely anatomical sense, qualify as members of the clade Diapsida due to their likely diapsid ancestry. Some diapsids, particularly...
6 KB (602 words) - 10:54, 27 January 2024
thus defining Reptilia as a more restricted crown group encompassing diapsids and parareptiles (apart from mesosaurs, which he considered to be the most...
30 KB (2,759 words) - 09:34, 12 October 2024
Archosauria (lit. 'ruling reptiles') or archosaurs (/ˈɑːrkəˌsɔːr/) is a clade of diapsid sauropsid tetrapods, with birds and crocodilians being the only extant...
59 KB (5,566 words) - 06:56, 24 August 2024
as diapsids, dinosaurs ancestrally had two pairs of Infratemporal fenestrae (openings in the skull behind the eyes), and as members of the diapsid group...
283 KB (28,268 words) - 18:06, 12 October 2024
reassignment of synapsids as non-reptiles, and classification of turtles as diapsids. Gauthier 1994 and Laurin and Reisz 1995's definition of Sauropsida defined...
138 KB (14,814 words) - 04:05, 4 October 2024
goniatites), and orthoceridans all abundant. Crown reptiles arise from earlier diapsids, and split into the ancestors of lepidosaurs, kuehneosaurids, choristoderes...
174 KB (9,789 words) - 10:34, 9 October 2024
Araeoscelida is a clade of extinct amniotes (traditionally classified as diapsid reptiles) superficially resembling lizards, extending from the Late Carboniferous...
11 KB (986 words) - 16:30, 21 June 2024
"anapsid" clade. Analysis of fossil data has shown that turtles are likely diapsid reptiles, most closely related either to the archosaurs (crocodiles, bird...
20 KB (1,491 words) - 15:13, 11 August 2024
Petrolacosaurus ("rock lake lizard") is an extinct genus of diapsid reptile from the late Carboniferous period. It was a small, 40-centimetre (16 in)...
13 KB (1,536 words) - 23:53, 21 February 2024
for theropod dinosaurs, is rare among vertebrates in general, and modern diapsid carnivores (including lizards, crocodiles, and birds) rarely cooperate...
132 KB (14,954 words) - 18:53, 28 September 2024
modern paleontologists believe that the Testudines are descended from diapsid reptiles that lost their temporal fenestrae. More recent morphological...
15 KB (1,607 words) - 00:12, 25 June 2024
found turtles to either be descendants of parareptiles, early-diverging diapsids outside of Sauria, or close relatives of lepidosaurs within the clade Ankylopoda...
12 KB (946 words) - 19:52, 6 July 2024
Drepanosaur (section Drepanosaurs as basal diapsids)
archosauromorphs, lepidosauromorphs related to kuehneosaurids, non-saurian diapsids related to weigeltisaurids, or (most recently) basal neodiapsids. When...
24 KB (2,559 words) - 23:52, 24 July 2024
Archosauromorpha (Greek for "ruling lizard forms") is a clade of diapsid reptiles containing all reptiles more closely related to archosaurs (such as...
32 KB (3,105 words) - 19:19, 21 September 2024
synapsid amniotes were dominant during the late Paleozoic, the Permian, while diapsid amniotes became dominant during the Mesozoic. In the sea, the teleosts...
78 KB (7,094 words) - 19:34, 7 October 2024
bones at the back of the skull. While all but the earliest eureptiles were diapsids, with two openings at the back of the skull, parareptiles were generally...
35 KB (2,809 words) - 18:03, 19 April 2024
Scotia, and possibly New Brunswick. Petrolacosaurus, the earliest known diapsid reptile, lived during the late Carboniferous. Archaeothyris is the oldest...
114 KB (11,979 words) - 20:55, 8 October 2024
Captorhinidae and Protorothyrididae (extinct) Diapsids...
234 KB (22,713 words) - 19:23, 14 September 2024
Avemetatarsalia (meaning "bird metatarsals") is a clade of diapsid reptiles containing all archosaurs more closely related to birds than to crocodilians...
22 KB (2,099 words) - 18:50, 6 July 2024
Sauria is the clade of diapsids containing the most recent common ancestor of Archosauria (which includes crocodilians and birds) and Lepidosauria (which...
23 KB (1,193 words) - 00:05, 4 October 2024
ISSN 0311-5518. S2CID 131795055. Rieppel, Olivier; DeBraga, M. (1996). "Turtles as Diapsid Reptiles" (PDF). Nature. 384 (6608): 453–455. Bibcode:1996Natur.384..453R...
126 KB (13,111 words) - 12:38, 22 August 2024
Color. New York: Sterling Publishers. ISBN 0-8069-6460-X. Sanchez A. "Diapsids III: Snakes". Father Sanchez's Web Site of West Indian Natural History...
151 KB (15,113 words) - 04:40, 28 September 2024
attachment sites for jaw muscles. A similar development took place in the diapsids, which evolved two rather than one opening behind each eye. Originally...
57 KB (5,746 words) - 21:05, 25 September 2024
archosaurs continued to dominate aquatic environments, while non-archosaurian diapsids continued to dominate marine environments. The Temnospondyl lineage of...
147 KB (15,027 words) - 23:14, 10 October 2024
mammals) and the diapsids (the line leading to crocodiles, birds and other dinosaurs, tuatara, lizards, and snakes). The synapsids and the diapsids diverged about...
569 KB (54,489 words) - 20:40, 11 October 2024
America. Towards the end of the era, large, sophisticated synapsids and diapsids were dominant and the first modern plants (conifers) appeared. The Paleozoic...
34 KB (3,642 words) - 18:52, 20 August 2024
located higher on the skull. The function of the holes in both synapsids and diapsids was to lighten the skull and give room for the jaw muscles to move, allowing...
30 KB (3,190 words) - 14:03, 10 September 2024
19th century paleontologist Gideon Mantell who viewed it as dominated by diapsids such as Iguanodon, Megalosaurus, Plesiosaurus, and Pterodactylus. The current...
41 KB (4,325 words) - 04:33, 24 August 2024