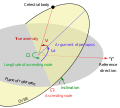
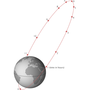
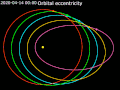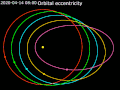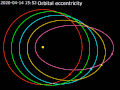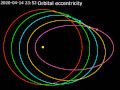
occupy an inclined orbit around Earth if the orbit exhibits an angle other than 0° to the equatorial plane. This angle is called the orbit's inclination...
3 KB (338 words) - 20:20, 12 June 2024
equatorial orbit, non-inclined orbit that is coplanar with the equator of Earth. List of orbits Geostationary orbit (GEO) Celestial equator Orbital inclination...
5 KB (689 words) - 02:48, 9 August 2023
Syncom 2 was successfully placed into a geosynchronous orbit in 1963. Although its inclined orbit still required moving antennas, it was able to relay TV...
33 KB (3,183 words) - 15:36, 22 August 2024
An orbital node is either of the two points where an orbit intersects a plane of reference to which it is inclined. A non-inclined orbit, which is contained...
9 KB (951 words) - 03:10, 24 October 2024
Non-inclined orbit: An orbit whose inclination is equal to zero with respect to some plane of reference. Ecliptic orbit: A non-inclined orbit with respect...
31 KB (3,455 words) - 19:37, 27 October 2024
above Earth's surface. The remaining four satellites are in inclined geosynchronous orbit (GSO). Two of them cross the equator at 55° E and two at 111...
56 KB (4,682 words) - 15:20, 11 October 2024
than 2,000 km (1,200 mi). Inclined orbit An orbit whose inclination in reference to the equatorial plane is not 0. Polar orbit A satellite that passes above...
17 KB (1,997 words) - 14:43, 5 September 2024
satellites that are not in geostationary orbit are sometimes referred to as being in an inclined geostationary orbit (IGSO). Some of these satellites are...
67 KB (729 words) - 09:39, 30 October 2024
Pluto (redirect from Hadeocentric orbit)
Moon, and one-third its volume. Pluto has a moderately eccentric and inclined orbit, ranging from 30 to 49 astronomical units (4.5 to 7.3 billion kilometres;...
165 KB (14,274 words) - 05:51, 2 November 2024
elliptical orbit (HEO) is an elliptic orbit with high eccentricity, usually referring to one around Earth. Examples of inclined HEO orbits include Molniya...
3 KB (307 words) - 19:21, 6 July 2024
Syncom 2 was successfully placed into a geosynchronous orbit in 1963. Although its inclined orbit still required moving antennas, it was able to relay TV...
49 KB (4,861 words) - 12:14, 29 October 2024
Planets beyond Neptune (section Sedna's orbit)
highly inclined orbit at some 1,500 AU. In 2016, further work showed this unknown distant planet is likely to be on an inclined, eccentric orbit that goes...
76 KB (9,335 words) - 20:04, 24 October 2024
altitude of the orbit (see Technical details) such that Earth's equatorial bulge, which perturbs inclined orbits, causes the orbital plane of the spacecraft...
14 KB (1,657 words) - 07:15, 21 October 2024
geostationary orbit. The more general case, when the orbit is inclined to Earth's equator or is non-circular is called a geosynchronous orbit. The corresponding...
5 KB (574 words) - 11:41, 22 September 2024
Planet Nine (section Orbit)
be in a distant (a ≈ 1500 AU), eccentric (e ≈ 0.4), and steeply inclined (i ≈ 40°) orbit. Like Planet Nine it would cause the perihelia of objects with...
178 KB (18,988 words) - 15:51, 31 October 2024
Gonggong (dwarf planet) (section Orbit)
of the scattered disc beyond Neptune. It has a highly eccentric and inclined orbit during which it ranges from 34–101 astronomical units (5.1–15.1 billion...
75 KB (6,133 words) - 05:55, 2 November 2024
Moons of Saturn (section Orbital groups)
prograde orbits not greatly inclined to Saturn's equatorial plane, with the exception of Iapetus which has a prograde but highly inclined orbit, an unusual...
169 KB (10,469 words) - 06:35, 20 October 2024
asteroid Pallas is inclined at 34°. In 1966, Peter Goldreich published a classic paper on the evolution of the Moon's orbit and on the orbits of other moons...
11 KB (1,465 words) - 15:40, 23 October 2023
In celestial mechanics, an orbit (also known as orbital revolution) is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star...
57 KB (8,167 words) - 12:48, 16 October 2024
Earth orbits the Sun at an average distance of 149.60 million km (92.96 million mi), or 8.317 light-minutes, in a counterclockwise direction as viewed...
17 KB (1,874 words) - 04:15, 29 October 2024
passes directly over the pole). Because of Earth's equatorial bulge, an orbit inclined at a slight angle is subject to a torque, which causes precession. An...
3 KB (416 words) - 15:33, 8 January 2024
Iapetus (moon) (category Moons with a prograde orbit)
has the most inclined orbital plane of the regular satellites; only the irregular outer satellites like Phoebe have more inclined orbits. Because of this...
42 KB (4,219 words) - 00:00, 31 October 2024
A medium Earth orbit (MEO) is an Earth-centered orbit with an altitude above a low Earth orbit (LEO) and below a high Earth orbit (HEO) – between 2,000...
10 KB (1,037 words) - 23:27, 10 October 2024
necessarily inclined over the equator, can only view these regions from a low angle, hampering performance. In practice, a satellite in a Molniya orbit serves...
28 KB (3,119 words) - 03:30, 2 October 2024
An orbital spaceflight (or orbital flight) is a spaceflight in which a spacecraft is placed on a trajectory where it could remain in space for at least...
13 KB (1,399 words) - 09:38, 6 October 2024
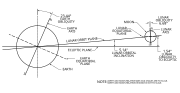
its orbit is closer to the ecliptic plane instead of its primary's (in this case, Earth's) equatorial plane. The Moon's orbital plane is inclined by about...
37 KB (4,642 words) - 12:31, 11 October 2024
elliptic orbit or elliptical orbit is a Kepler orbit with an eccentricity of less than 1; this includes the special case of a circular orbit, with eccentricity...
19 KB (2,744 words) - 21:11, 2 October 2024
transfer orbit (GTO) or geosynchronous transfer orbit is a highly elliptical type of geocentric orbit, usually with a perigee as low as low Earth orbit (LEO)...
13 KB (1,801 words) - 19:57, 9 August 2024