Chemical polarity (redirect from Polar bond)
containing polar bonds have no molecular polarity if the bond dipoles cancel each other out by symmetry. Polar molecules interact through dipole-dipole intermolecular...
24 KB (2,751 words) - 02:20, 28 September 2024
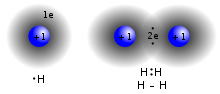
the bond. Two atoms with equal electronegativity will make nonpolar covalent bonds such as H–H. An unequal relationship creates a polar covalent bond such...
28 KB (3,673 words) - 05:58, 14 October 2024
in drawings, or modeled as sticks between spheres in models. In a polar covalent bond, one or more electrons are unequally shared between two nuclei. Covalent...
40 KB (4,872 words) - 13:33, 22 September 2024
coordinate covalent bond, also known as a dative bond, dipolar bond, or coordinate bond is a kind of two-center, two-electron covalent bond in which the two...
10 KB (1,313 words) - 13:10, 17 August 2024
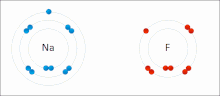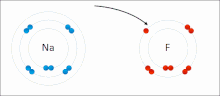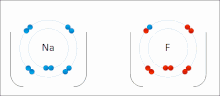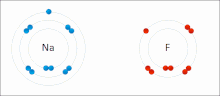
– that is, a bond in which there is a large difference in electronegativity between the two atoms, causing the bonding to be more polar (ionic) than in...
18 KB (2,338 words) - 02:36, 8 February 2024
this small difference in electronegativities, the C−H bond is generally regarded as being non-polar. In structural formulas of molecules, the hydrogen atoms...
6 KB (533 words) - 20:36, 1 October 2024
electronegative oxygen atom pulls electrons away from the carbon atom, forming a polar bond with greater electron density around the oxygen atom, giving it a partial...
6 KB (481 words) - 18:32, 18 September 2024
Haloalkane (redirect from Carbon-halogen bond)
reaction in which water breaks a bond, is a good example of the nucleophilic nature of haloalkanes. The polar bond attracts a hydroxide ion, OH− (NaOH(aq)...
20 KB (2,413 words) - 06:14, 8 September 2024
The carbon–fluorine bond is a polar covalent bond between carbon and fluorine that is a component of all organofluorine compounds. It is one of the strongest...
15 KB (1,701 words) - 19:03, 21 September 2024
Intermolecular force (redirect from Dipole-dipole bond)
a dipole moment. Ion–dipole bonding is stronger than hydrogen bonding. An ion–dipole force consists of an ion and a polar molecule interacting. They align...
28 KB (3,469 words) - 12:04, 9 October 2024
hydrogen bond acceptor (Ac). Such an interacting system is generally denoted Dn−H···Ac, where the solid line denotes a polar covalent bond, and the dotted...
46 KB (5,459 words) - 23:38, 3 October 2024
Solvent (redirect from Polar solvent)
parameters, separates the cohesive energy density into dispersion, polar, and hydrogen bonding contributions. Solvents with a dielectric constant (more accurately...
45 KB (3,709 words) - 21:17, 6 September 2024
Inductive effect (category Chemical bonding)
addition of the individual bond dipole moments results in a net dipole moment for the molecule. A polar bond is a covalent bond in which there is a separation...
10 KB (1,258 words) - 17:02, 2 October 2024
The polar bear (Ursus maritimus) is a large bear native to the Arctic and nearby areas. It is closely related to the brown bear, and the two species can...
96 KB (12,428 words) - 18:23, 15 October 2024
hydrogen bonding, although they can be proton acceptors. Many solvents, including chlorocarbons and hydrocarbons, are classifiable as aprotic, but polar aprotic...
3 KB (140 words) - 17:22, 13 October 2023
electrophilic group such as the carbon atom that is present within the polar bond of a carbonyl group. A prominent organomagnesium reagent beyond Grignard...
78 KB (8,533 words) - 23:46, 27 September 2024
of this moderately large difference in electronegativities, the Si−O bond is polar but not fully ionic. Carbon has an electronegativity of 2.55 so carbon–oxygen...
11 KB (1,124 words) - 12:41, 22 September 2024
Non-covalent interaction (redirect from Non-covalent bond)
In chemistry, a non-covalent interaction differs from a covalent bond in that it does not involve the sharing of electrons, but rather involves more dispersed...
27 KB (3,307 words) - 20:40, 5 October 2024
Look up polar in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. Polar may refer to: Polar may refer to: Geographical pole, either of two fixed points on the surface...
3 KB (427 words) - 13:20, 18 June 2024
A carbon–oxygen bond is a polar covalent bond between atoms of carbon and oxygen.: 16–22 Carbon–oxygen bonds are found in many inorganic compounds such...
10 KB (1,026 words) - 08:23, 5 October 2024
Grignard reaction (category Carbon-carbon bond forming reactions)
acts as a nucleophile and attacks the electrophilic carbon atom in the polar bond of a carbonyl group. The addition of the Grignard reagent to the carbonyl...
12 KB (1,095 words) - 14:22, 26 September 2024
Intramolecular force (category Chemical bonding)
covalent. The polarity of a covalent bond is determined by the electronegativities of each atom and thus a polar covalent bond has a dipole moment pointing from...
7 KB (795 words) - 01:57, 17 October 2024
with each other and are strongly polar. This polarity allows it to dissociate ions in salts and bond to other polar substances such as alcohols and acids...
89 KB (9,582 words) - 03:21, 30 September 2024
metallic bonding is neither intra- nor inter-molecular. 'Nonmolecular' would perhaps be a better term. Metallic bonding is mostly non-polar, because even...
24 KB (3,401 words) - 20:25, 18 January 2024
Lewis structure (category Chemical bonding)
upon its electron dot structure, assuming exclusive covalency or non-polar bonding. It has uses in determining possible electron re-configuration when...
16 KB (2,140 words) - 19:28, 3 October 2024
Alkene (redirect from Carbon-carbon double bond)
distinguished by the position and conformation of the double bond. Alkenes are generally colorless non-polar compounds, somewhat similar to alkanes but more reactive...
48 KB (5,122 words) - 13:15, 16 October 2024
Bent's rule (category Chemical bonding)
atom A and shortens the adjacent A--Y bond. Bonds between elements of disparate electronegativities will be polar and the electron density in such bonds...
38 KB (4,250 words) - 13:50, 4 October 2024
In chemistry, bond cleavage, or bond fission, is the splitting of chemical bonds. This can be generally referred to as dissociation when a molecule is...
6 KB (696 words) - 03:07, 24 August 2023
influenced by the degree and the period of heating dissolves the electric bond forces in the fiber; at first in the amorphous domains, later in the crystalline...
16 KB (2,309 words) - 22:48, 30 September 2022
molecules can be polar, or have polar groups, and the resulting regions of positive and negative charge can interact to produce electrostatic bonding resembling...
11 KB (1,382 words) - 14:09, 6 September 2024