a nucleophilic substitution (SN) is a class of chemical reactions in which an electron-rich chemical species (known as a nucleophile) replaces a functional...
12 KB (1,415 words) - 13:08, 26 August 2024
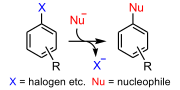
A nucleophilic aromatic substitution (SNAr) is a substitution reaction in organic chemistry in which the nucleophile displaces a good leaving group, such...
11 KB (1,295 words) - 12:42, 28 August 2024
acyl substitution, and nucleophilic aromatic substitution. Acyl substitution occurs when a nucleophile attacks a carbon that is doubly bonded to one...
12 KB (1,456 words) - 13:55, 26 August 2024
alcohols and water are named solvolysis. Nucleophiles may take part in nucleophilic substitution, whereby a nucleophile becomes attracted to a full or partial...
18 KB (2,190 words) - 20:08, 25 November 2024
SN2 reaction (redirect from Bimolecular nucleophilic substitution)
nucleophilic substitution (SN2) is a type of reaction mechanism that is common in organic chemistry. In the SN2 reaction, a strong nucleophile forms a new...
21 KB (2,555 words) - 19:00, 17 December 2024
SN1 reaction (redirect from Unimolecular nucleophilic substitution)
The unimolecular nucleophilic substitution (SN1) reaction is a substitution reaction in organic chemistry. The Hughes-Ingold symbol of the mechanism expresses...
15 KB (1,970 words) - 03:54, 24 October 2024
substitution where the reactant is a nucleophile rather than an electrophile. The four possible electrophilic aliphatic substitution reaction mechanisms are SE1...
2 KB (244 words) - 01:58, 6 April 2023
Radical-nucleophilic aromatic substitution or SRN1 in organic chemistry is a type of substitution reaction in which a certain substituent on an aromatic...
4 KB (454 words) - 19:31, 27 October 2022
Tsuji–Trost reaction (redirect from Allylic asymmetric substitution)
complex. This allyl complex can then be attacked by a nucleophile, resulting in the substituted product. This work was first pioneered by Jirō Tsuji in...
24 KB (2,771 words) - 15:06, 26 September 2024
Acyl group (redirect from Nucleophilic acyl substitution)
towards nucleophiles, followed by anhydrides, esters, and amides. Carboxylate ions are essentially unreactive towards nucleophilic substitution, since...
18 KB (1,913 words) - 21:16, 5 November 2024
Solvolysis (category Substitution reactions)
chemistry, solvolysis is a type of nucleophilic substitution (SN1/SN2) or elimination where the nucleophile is a solvent molecule. Characteristic of SN1...
3 KB (425 words) - 00:53, 5 January 2024
Haloalkane (section Substitution)
deficient (electrophilic) carbon which, inevitably, attracts nucleophiles. Substitution reactions involve the replacement of the halogen with another...
20 KB (2,413 words) - 06:14, 8 September 2024
involve copper catalysts and "hard" carbon nucleophiles. The mechanism of copper-catalyzed allylic substitutions involves the coordination of copper to the...
11 KB (1,092 words) - 21:10, 31 January 2024
R−Cl. Electrofuge Electrophile Elimination reaction Nucleofuge Nucleophile Substitution reaction "Leaving group" (PDF). Gold Book: leaving group. IUPAC...
22 KB (2,532 words) - 15:42, 14 February 2024
the vicarious nucleophilic substitution is a special type of nucleophilic aromatic substitution in which a nucleophile replaces a hydrogen atom on the...
2 KB (182 words) - 19:34, 27 October 2022
Carbonyl α-substitution reactions occur at the position next to the carbonyl group, the α-position, and involves the substitution of an α-hydrogen by an...
7 KB (982 words) - 20:11, 11 November 2024
Solvent effects (section Substitution reactions)
activated complex. The solvent used in substitution reactions inherently determines the nucleophilicity of the nucleophile; this fact has become increasingly...
17 KB (1,904 words) - 19:14, 18 October 2024
SNi (redirect from SNi substitution)
In chemistry, SNi (substitution nucleophilic internal) refers to a specific, regio-selective but not often encountered reaction mechanism for nucleophilic...
5 KB (514 words) - 18:33, 25 October 2024
2-Chlorobutane (section Substitution reactions)
attacking the chloride hydrogen, which forms a chloride nucleophile. In the second step, the nucleophile attacks the carbocation generated in the first step...
7 KB (755 words) - 06:57, 17 February 2024
and substitution products form by competing SN1 and E1 pathways. The case of 2° haloalkanes is relatively complex. For strongly basic nucleophiles (pKaH...
14 KB (1,844 words) - 22:24, 27 May 2024
Chemical reaction (section Substitution)
distinguished by the type of substituting species into a nucleophilic, electrophilic or radical substitution. In the first type, a nucleophile, an atom or molecule...
66 KB (8,043 words) - 01:08, 14 October 2024
usually minor constituent of water. It functions as a base, a ligand, a nucleophile, and a catalyst. The hydroxide ion forms salts, some of which dissociate...
41 KB (4,891 words) - 16:04, 20 November 2024
able to act as a strong nucleophile for instance an alcohol, amine or thiol. As in other nucleophilic aromatic substitutions the arene requires activation...
3 KB (372 words) - 23:41, 28 January 2023
attacking nucleophile to give a discrete, detectable intermediate followed by loss of another ligand. Complexes that undergo associative substitution are either...
10 KB (1,140 words) - 07:00, 8 March 2022
withdrawing groups and a nucleophile. These complexes are found as reactive intermediates in nucleophilic aromatic substitution but stable and isolated...
6 KB (657 words) - 05:14, 16 September 2022
coordination sphere of the metal undergoing substitution. The concentration of the substituting nucleophile has no influence on this rate, and an intermediate...
6 KB (896 words) - 06:59, 31 October 2022
with unsaturated functional groups, and react with nucleophiles and electrophiles to give substitution products. (3) Oxidative coupling of bis(phenols)...
9 KB (1,091 words) - 03:35, 7 May 2022
effect produced by the presence of a reagent like an electrophile or a nucleophile, IUPAC does not define it as such. The term electromeric effect is no...
2 KB (264 words) - 16:07, 18 December 2024
Aromatic compound (section Substitution)
aromatic substitution, when the active reagent is an electrophile, and nucleophilic aromatic substitution, when the reagent is a nucleophile. In radical-nucleophilic...
21 KB (2,094 words) - 17:10, 6 December 2024
reaction is a type of substitution or an addition-elimination reaction. With a carbonyl compound as an electrophile, the nucleophile can be: water in hydration...
8 KB (910 words) - 13:13, 26 August 2024