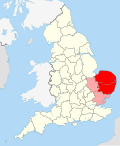
East Anglia is an area in the East of England, often defined as including the counties of Norfolk, Suffolk and Cambridgeshire. The name derives from the...
27 KB (2,909 words) - 19:41, 30 September 2024
The University of East Anglia (UEA) is a public research university in Norwich, England. Established in 1963 on a 320-acre (130-hectare) campus west of...
126 KB (11,541 words) - 23:31, 7 November 2024
Kingdom of the East Angles (Old English: Ēastengla Rīċe; Latin: Regnum Orientalium Anglorum), informally known as the Kingdom of East Anglia, was a small...
31 KB (3,744 words) - 17:53, 20 October 2024
East Anglia, an Anglo-Saxon kingdom which included the present-day English counties of Norfolk and Suffolk. He was the son of Tytila of East Anglia and...
36 KB (4,395 words) - 17:06, 25 October 2024
Greater Anglia (legal name Transport UK East Anglia Limited) is a British train operating company owned as a joint venture by Transport UK Group and Mitsui...
73 KB (4,591 words) - 17:38, 5 November 2024
East of England succeeded the standard statistical region East Anglia (which excluded Essex, Hertfordshire and Bedfordshire, then in the South East)...
57 KB (4,230 words) - 03:23, 26 October 2024
The East Anglia franchise is a railway franchise for passenger trains on the Great Eastern Main Line and West Anglia Main Lines in England. It commenced...
15 KB (1,325 words) - 11:50, 20 July 2024
king of East Anglia. The name Eohric is the Old English form of the Old Norse Eiríkr. It would appear that Eohric became king of East Anglia following...
4 KB (404 words) - 12:35, 31 October 2024
Ecgric (killed c. 636) was a king of East Anglia, the independent Anglo-Saxon kingdom that today includes the English counties of Norfolk and Suffolk...
16 KB (1,958 words) - 02:37, 24 September 2024
North Germany: Anglia (peninsula), original home of the Angles in north Germany In England in the early Middle Ages: Most often, East Anglia and, in particular...
2 KB (225 words) - 20:10, 7 November 2024
The East Anglia Array is a proposed series of offshore wind farms located around 30 miles off the east coast of East Anglia, in the North Sea, England...
17 KB (1,329 words) - 13:59, 23 October 2024
The Earls of East Anglia were governors of East Anglia during the 11th century. The post was established by Cnut in 1017 and disappeared following Ralph...
9 KB (712 words) - 22:23, 4 March 2024
National Express East Anglia (NXEA) was a train operating company in England owned by National Express that operated the Greater Anglia franchise from April...
29 KB (1,674 words) - 17:49, 27 September 2024
654) was king of East Anglia from the early 640s until his death. He was a member of the Wuffingas family, the ruling dynasty of the East Angles, and one...
34 KB (4,024 words) - 03:54, 1 November 2024
Bishop of East Anglia may refer to Bishop of East Anglia (modern), the modern Roman Catholic diocese Bishop of Norwich, the ancient diocese now at Norwich...
270 bytes (73 words) - 09:18, 16 May 2024
Ricberht (Old English: Ricbyhrt), may have briefly ruled East Anglia, a small independent Anglo-Saxon kingdom which today forms the English counties of...
9 KB (984 words) - 07:09, 1 November 2024
Oswald was king of East Anglia, present-day England in the 870s after the death of Edmund the Martyr. No textual evidence of his reign is known, but coins...
4 KB (395 words) - 12:34, 31 October 2024
Ƿuffa) is recorded in the Anglo-Saxon genealogies as an early king of East Anglia. If historical, he would have lived in the 6th century. By tradition...
12 KB (1,243 words) - 13:12, 20 October 2024
Wehha of East Anglia is listed by Anglo-Saxon records as a king of the East Angles. If he existed, Wehha ruled the East Angles as a pagan king during the...
12 KB (1,308 words) - 03:18, 26 March 2024
Edmund the Martyr (redirect from Edmund of East Anglia)
Martyr (also known as St Edmund or Edmund of East Anglia, died 20 November 869) was king of East Anglia from about 855 until his death. Few historical...
49 KB (5,712 words) - 22:58, 20 October 2024
The climate of East Anglia is generally dry and mild. The region is the driest in the United Kingdom with many areas receiving less than 600mm (24") of...
4 KB (196 words) - 06:01, 27 August 2024
The Kingdom of East Anglia, also known as the Kingdom of the East Angles, was a small independent Anglo-Saxon kingdom that comprised what are now the English...
17 KB (959 words) - 01:44, 4 October 2024
Tytila (died around 616) was a semi-historical pagan king of East Anglia, a small Anglo-Saxon kingdom which today includes the English counties of Norfolk...
9 KB (914 words) - 15:01, 30 May 2023
Sigeberht of East Anglia (also known as Saint Sigebert), (Old English: Sigebryht) was a saint and a king of East Anglia, the Anglo-Saxon kingdom which...
22 KB (2,583 words) - 14:06, 1 November 2024
of East Anglia from 653 or 654 until his death. He was a member of the ruling Wuffingas dynasty and one of three sons of Eni to rule East Anglia as Christian...
17 KB (1,956 words) - 11:19, 25 January 2024
Norwich (redirect from Norwich, East Anglia)
it was second only to London. Today, it is the largest settlement in East Anglia. Norwich claims to be the most complete medieval city in the United Kingdom...
197 KB (20,349 words) - 07:03, 26 October 2024
Æthelstan (/ˈæθəlstæn/) was king of East Anglia in the 9th century. As with the other kings of East Anglia, there is very little textual information available...
2 KB (163 words) - 08:55, 5 January 2024
Ealdwulf (Old English: Aldwulf), also known as Aldulf or Adulf, was king of East Anglia from c. 664 to 713. He was the son of Hereswitha, a Northumbrian princess...
15 KB (1,663 words) - 15:44, 11 October 2024
Anglia Ruskin University (ARU) is a public university in East Anglia, United Kingdom. Its origins are in the Cambridge School of Art (CSA), founded by...
72 KB (6,468 words) - 22:48, 31 October 2024
The East Anglia Transport Museum is an open-air transport museum, with numerous historic public transport vehicles (including many in full working order)...
14 KB (1,320 words) - 02:04, 11 August 2024