Sahelanthropus is an extinct genus of hominid dated to about 7 million years ago during the Late Miocene. The type species, Sahelanthropus tchadensis...
29 KB (3,023 words) - 15:40, 10 December 2024
Sahelanthropus (and perhaps Orrorin), are supported by one community of scientists but doubted by another. Extant species are in bold. Sahelanthropus...
24 KB (2,425 words) - 09:39, 19 December 2024
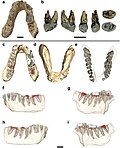
peripherally located cusps, thin enamel, and strong facial prognathism. Sahelanthropus tchadensis is thought to be one of the earliest species belonging to the...
19 KB (2,015 words) - 06:44, 31 October 2024
ramidus Ardipithecus kadabba Orrorin Orrorin tugenensis Sahelanthropus Sahelanthropus tchadensis Phylogeny of Hominina/Australopithecina according to Dembo...
17 KB (1,550 words) - 12:26, 2 December 2024
abyssinicus Tribe Hominini Subtribe Panina Subtribe Hominina Sahelanthropus† Sahelanthropus tchadensis Orrorin† Orrorin tugenensis Orrorin praegens Ardipithecus†...
51 KB (4,468 words) - 01:30, 21 December 2024
evidence of the CHLCA has been discovered. Fossil candidates like Sahelanthropus tchadensis, Orrorin tugenensis, and Ardipithecus ramidus have been debated...
18 KB (2,083 words) - 09:52, 15 December 2024
represents a hypothesis, but not scientific consensus. Sahelanthropus (?)† Sahelanthropus tchadensis Orrorin† Orrorin tugenensis Orrorin praegens Ardipithecus†...
30 KB (2,975 words) - 10:41, 29 November 2024
Hassane; Brunet, Michel (2014). "Subocclusal dental morphology of Sahelanthropus tchadensis and the evolution of teeth in hominins". American Journal of Physical...
31 KB (3,270 words) - 20:39, 18 September 2024
debut album's title, Willow said "Ardipithecus Ramidus [sic] Sahelanthropus tchadensis is the scientific name of the first hominid bones found on earth...
39 KB (3,095 words) - 22:53, 18 December 2024
Djurab desert during the mid-1990s. In 2001, the type fossil of Sahelanthropus tchadensis, a hominid species of about 7 million years ago, was discovered...
7 KB (498 words) - 20:41, 28 September 2024
earliest fossils argued by some to belong to the human lineage are Sahelanthropus tchadensis (7 Ma) and Orrorin tugenensis (6 Ma), followed by Ardipithecus...
263 KB (26,339 words) - 17:40, 13 December 2024
bipedal hominins is the driving argument used by Michel Brunet that Sahelanthropus tchadensis was also bipedal, and may be the earliest known bipedal ape. The...
14 KB (1,730 words) - 17:19, 17 October 2024
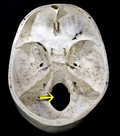
femur of Sahelanthropus tchadensis does not support the interpretation of this hominid as habitually bipedal. A study on the skull of Sahelanthropus tchadensis...
404 KB (43,608 words) - 00:55, 22 December 2024
Vignaud, P.; Brunet, M. (2008). "Cosmogenic nuclide dating of Sahelanthropus tchadensis and Australopithecus bahrelghazali: Mio-Pliocene hominids from...
19 KB (2,083 words) - 08:54, 24 October 2024
discovered anywhere in the world; it has been given the name Sahelanthropus tchadensis. In 1996 Michel Brunet had unearthed a hominid jaw, which he named...
48 KB (4,711 words) - 22:38, 9 December 2024
Pilbeam, D.; et al. (2005). "Morphological affinities of the Sahelanthropus tchadensis (Late Miocene hominid from Chad) cranium". PNAS. 102 (52): 18836–18841...
6 KB (563 words) - 17:18, 28 September 2024
Déby, and classified by Brunet as the first exemplary of the Sahelanthropus tchadensis. Brunet and others, like Tim White, are strongly convinced Toumai...
9 KB (983 words) - 04:19, 18 November 2024
Metal Gear (mecha) (section Sahelanthropus)
with the mysterious XOF organization. Its name is derived from Sahelanthropus tchadensis, an extinct hominine species theorised to be the last common ancestor...
50 KB (7,122 words) - 23:50, 27 September 2024
eastern and southern Africa, there are a few exceptions. One is Sahelanthropus tchadensis, discovered in the central African country of Chad in 2002. This...
27 KB (3,109 words) - 04:34, 23 May 2024
Orrorin tugenensis in 2001, and the 7- to 6-million-year-old Sahelanthropus tchadensis in 2002. Bipedalism was once thought to have evolved in australopithecines...
66 KB (8,241 words) - 05:10, 14 December 2024
Sahelanthropus tchadensis...
88 KB (3,574 words) - 10:30, 19 November 2024
its citizens for COVID-19. 1 November – Scientists report that Sahelanthropus tchadensis, presumed to be an extinct hominin earlier, is not a hominin after...
152 KB (27,272 words) - 16:36, 5 October 2024
found in Africa (not necessarily ancestral to the human lineage), Sahelanthropus tchadensis. The study concludes: [The] dental root attributes of Graecopithecus...
31 KB (3,541 words) - 18:20, 6 November 2024
dated to earlier than the date could call this into question. Sahelanthropus tchadensis, commonly called "Toumai", is about seven million years old and...
48 KB (5,124 words) - 04:56, 9 December 2024
Australopithecus is less relevant. In 2001 the seven-million-year-old Sahelanthropus tchadensis was discovered in Chad. Based on animal finds in the vicinity...
19 KB (2,530 words) - 06:16, 28 July 2024
("feminization") of the male canine teeth in early hominids such as Sahelanthropus tchadensis and Ardipithecus ramidus, which along with low body size dimorphism...
80 KB (9,571 words) - 18:49, 7 November 2024
Tchadanthropus uxoris, d'Abel (Australopithecus bahrelghazali) and Toumaï (Sahelanthropus tchadensis) fossils. List of museums in Chad Jean-Paul Lebeuf (1965). "The...
5 KB (387 words) - 08:50, 1 November 2024
Vignaud, P.; Brunet, M. (2005). "Virtual cranial reconstruction of Sahelanthropus tchadensis" (PDF). Nature. 434 (7034): 755–759. Bibcode:2005Natur.434..755Z...
11 KB (988 words) - 06:06, 13 November 2024
on the description and analysis of the new hominin from Chad, Sahelanthropus tchadensis.[i][k][l] [m][n] He describes his long-term and continuing interests...
26 KB (2,755 words) - 04:48, 1 July 2024
(BAS) Met, Athens; Tübingen, Germany TM 266 (Toumai) 7.00–6.00 Sahelanthropus tchadensis 2001 Chad Site:Djurab Desert Michel Brunet, Alain Beauvilain,...
118 KB (7,338 words) - 03:19, 21 December 2024