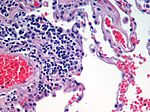
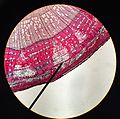
Phloem (/ˈfloʊ.əm/, FLOH-əm) is the living tissue in vascular plants that transports the soluble organic compounds made during photosynthesis and known...
19 KB (2,325 words) - 00:47, 10 November 2024
Sap (redirect from Phloem sap)
is a fluid transported in xylem cells (vessel elements or tracheids) or phloem sieve tube elements of a plant. These cells transport water and nutrients...
10 KB (1,061 words) - 14:40, 17 May 2024
throughout the plant. They also have a specialized non-lignified tissue (the phloem) to conduct products of photosynthesis. The group includes most land plants...
23 KB (2,031 words) - 23:13, 8 November 2024
Phloem loading is the process of loading carbon into the phloem for transport to different 'sinks' in a plant. Sinks include metabolism, growth, storage...
6 KB (768 words) - 15:42, 23 October 2022
Tissue (biology) (section Phloem)
arise out of the vascular cambium. Phloem consists of: Sieve tube Companion cell Phloem fiber Phloem parenchyma. Phloem is an equally important plant tissue...
24 KB (3,041 words) - 03:15, 17 November 2024
vascular plants. The primary components of vascular tissue are the xylem and phloem. These two tissues transport fluid and nutrients internally. There are also...
4 KB (459 words) - 19:11, 28 July 2024
dissolved substances between the roots and the shoots in the xylem and phloem, engages in photosynthesis, stores nutrients, and produces new living tissue...
18 KB (2,215 words) - 18:47, 18 October 2024
Plant cell (section Phloem)
support to photosynthesis (mesophyll cells) and phloem loading (transfer cells). Apart from the xylem and phloem in their vascular bundles, leaves are composed...
19 KB (2,224 words) - 04:45, 3 January 2024
Cork cambium (redirect from Phloem sheath)
epidermis. It is one of the many layers of bark, between the cork and primary phloem. The cork cambium is a lateral meristem and is responsible for secondary...
3 KB (366 words) - 17:37, 3 July 2024
the Sternorrhyncha and a number of Auchenorrhynchan groups feed on phloem. Phloem feeding is common in the Fulgoromorpha, most Cicadellidae and in the...
68 KB (6,825 words) - 15:21, 17 November 2024
Sieve elements are specialized cells that are important for the function of phloem, which is a highly organized tissue that transports organic compounds made...
10 KB (1,265 words) - 08:09, 7 July 2024
Bast fibre (also called phloem fibre or skin fibre) is plant fibre collected from the phloem (the "inner bark", sometimes called "skin") or bast surrounding...
6 KB (603 words) - 19:16, 2 September 2024
Bark bread is a traditional food made with cambium (phloem) flour. It has a history of use as famine food. Bark bread seems to be a primarily Scandinavian...
8 KB (919 words) - 17:18, 27 August 2024
transport itself happens in the stem, which exists in two forms: xylem and phloem. Both these tissues are present in a vascular bundle, which in addition...
4 KB (352 words) - 05:19, 8 November 2024
Citrus greening disease (redirect from Citrus Vein Phloem Degeneration)
acquired and transmitted by the insects. The causative agents are fastidious phloem-restricted, Gram-negative bacteria in the gracilicutes clade. The Asian...
32 KB (3,260 words) - 04:00, 12 November 2024
Ascent of sap (section Phloem structure)
phloem is the living portion of the vascular system of a plant, and serves to move sugars and photosynthate from source cells to sink cells. Phloem tissue...
12 KB (1,727 words) - 10:50, 4 November 2024
plants. It produces secondary xylem inwards, towards the pith, and secondary phloem outwards, towards the bark. In herbaceous plants, it occurs in the vascular...
8 KB (945 words) - 11:01, 5 July 2024
rapidly to produce secondary xylem to the inside and secondary phloem to the outside. Phloem is a nutrient-conducting tissue composed of sieve tubes or sieve...
29 KB (3,454 words) - 04:14, 2 November 2024
roots. The trunk consists of five main parts: The outer bark, inner bark (phloem), cambium, sapwood (live xylem), and heartwood (dead xylem). From the outside...
5 KB (559 words) - 03:59, 7 November 2024
is the best-supported theory to explain the movement of sap through the phloem of plants. It was proposed in 1930 by Ernst Münch, a German plant physiologist...
7 KB (1,026 words) - 02:00, 9 September 2024
Mass flow (life sciences) (section Phloem)
be applied to the transport of larger solutes (e.g. sucrose) through the phloem. According to cohesion-tension theory, water transport in xylem relies upon...
3 KB (419 words) - 01:22, 14 September 2023
tissues xylem and phloem. They include mosses, liverworts and hornworts. Pteridophytic vascular plants with true xylem and phloem that reproduced by...
138 KB (14,773 words) - 09:08, 30 October 2024
pattern of a single vascular cambium producing xylem to the inside and phloem to the outside as in ancestral lignophytes. Some dicots have anomalous secondary...
6 KB (690 words) - 12:02, 18 March 2023
leaves 4). Ground tissue 5). Phloem 6). Sugars and nutrients 7). Epidermal tissue 8). A Cuscuta haustorium growing into the phloem of the host plant....
18 KB (1,878 words) - 01:30, 29 September 2024
Sugar accumulation, as it relates to autoradiography, can described the phloem-loading strategy used in a plant. For example, if sugars accumulate in the...
13 KB (1,580 words) - 11:41, 24 July 2024
cortex is located between the periderm (bark) and the vascular tissue (phloem, in particular). It is responsible for the transportation of materials into...
4 KB (482 words) - 18:56, 22 September 2024
This consisted of a cylindrical strand of xylem, surrounded by a region of phloem. Around the vascular tissue there might have been an endodermis that regulated...
7 KB (926 words) - 10:18, 18 May 2024
food, and enabling certain insects to feed on blood or from the xylem and phloem transport vessels of plants. Once food leaves the crop, it passes to the...
134 KB (12,788 words) - 00:37, 7 October 2024
Elm yellows (redirect from Elm phloem necrosis)
spread by leafhoppers or by root grafts. Elm yellows, also known as elm phloem necrosis, is very aggressive, with no known cure. Elm yellows occurs in...
7 KB (770 words) - 03:25, 18 June 2024
Elm (section Elm phloem necrosis)
is caused by phytoplasmas that infect the phloem (inner bark) of the tree. Infection and death of the phloem effectively girdles the tree and stops the...
73 KB (8,366 words) - 01:53, 13 September 2024