The Cosmic Background Explorer (COBE /ˈkoʊbi/ KOH-bee), also referred to as Explorer 66, was a NASA satellite dedicated to cosmology, which operated from...
33 KB (3,843 words) - 10:49, 10 August 2024
Cosmic background radiation is electromagnetic radiation that fills all space. The origin of this radiation depends on the region of the spectrum that...
5 KB (514 words) - 00:56, 11 January 2024
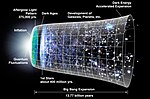
The cosmic microwave background (CMB, CMBR), or relic radiation, is microwave radiation that fills all space in the observable universe. With a standard...
108 KB (13,172 words) - 01:01, 1 September 2024
The cosmic neutrino background (CNB or CνB) is the universe's background particle radiation composed of neutrinos. They are sometimes known as relic neutrinos...
19 KB (2,354 words) - 16:27, 21 August 2024
the Cosmic Background Explorer with John C. Mather that led to the "discovery of the black body form and anisotropy of the cosmic microwave background radiation"...
25 KB (2,652 words) - 02:35, 20 June 2024
This list is a compilation of experiments measuring the cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation anisotropies and polarization since the first detection...
44 KB (2,472 words) - 17:04, 9 February 2024
The discovery of cosmic microwave background radiation constitutes a major development in modern physical cosmology. In 1964, US physicist Arno Allan...
14 KB (1,506 words) - 20:43, 5 June 2024
Expansion of the universe (redirect from Cosmic expansion)
73±7 km⋅s−1⋅Mpc−1. In 2003, David Spergel's analysis of the cosmic microwave background during the first year observations of the Wilkinson Microwave...
53 KB (6,980 words) - 16:28, 21 August 2024
like hypothetical primordial inflation and cosmic strings. Several potential sources for the background are hypothesized across various frequency bands...
19 KB (1,943 words) - 23:06, 1 September 2024
Cosmic infrared background is infrared radiation caused by stellar dust. Recognizing the cosmological importance of the darkness of the night sky (Olbers'...
17 KB (2,415 words) - 18:55, 16 July 2024
Another effect remarked upon since the first cosmic microwave background satellite, the Cosmic Background Explorer is that the amplitude of the quadrupole...
104 KB (12,680 words) - 16:22, 21 August 2024
cosmologist and Nobel Prize in Physics laureate for his work on the Cosmic Background Explorer Satellite (COBE) with George Smoot. This work helped cement the...
15 KB (1,148 words) - 13:05, 19 April 2024
Void (astronomy) (redirect from Cosmic nothingness)
Voids appear to correlate with the observed temperature of the cosmic microwave background (CMB) because of the Sachs–Wolfe effect. Colder regions correlate...
37 KB (4,532 words) - 04:01, 31 August 2024
Big Bounce (redirect from Cosmic bounces)
awareness of the Big Bang model with of the discovery of the cosmic microwave background by Penzias and Wilson in 1965. The idea of the existence of a...
23 KB (2,850 words) - 19:50, 28 June 2024
flat, open and closed universes. Observations, including the Cosmic Background Explorer (COBE), Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP), and Planck...
158 KB (16,435 words) - 07:41, 1 September 2024
the Sunyaev–Zeldovich effect for the first time. In 1987 the Cosmic Background Explorer (COBE) satellite observed the CMB and gave more accurate data...
20 KB (2,206 words) - 16:34, 21 August 2024
Absolute Spectrophotometer), an astronomical instrument aboard Cosmic Background Explorer Feras, a given name This disambiguation page lists articles associated...
447 bytes (84 words) - 15:13, 7 March 2024
(DMR) instrument on the Cosmic Background Explorer (COBE) mission that discovered the anisotropy of the cosmic microwave background radiation. Bennett led...
18 KB (1,826 words) - 23:15, 30 July 2024
the universe could be explained by the big bang model, predicted cosmic background radiation Aristarchus of Samos (310–230 BC) early proponent of heliocentrism...
19 KB (2,478 words) - 04:46, 14 February 2024
observed phenomena, including the abundance of light elements, the cosmic microwave background (CMB) radiation, and large-scale structure. The uniformity of...
150 KB (16,100 words) - 19:12, 31 August 2024
Assembly of the Cosmic Background Explorer, Manager for the Superfluid Helium On Orbit Transfer Shuttle Experiment, Manager for the Small Explorer Project, Manager...
7 KB (716 words) - 16:07, 4 December 2023
worked on space missions including the Cosmic Background Explorer (COBE), Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE), and Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy...
5 KB (436 words) - 06:58, 8 October 2023
Stephen Hawking (redirect from George's Cosmic Treasure Hunt)
John Preskill of Caltech. Hawking had bet that Penrose's proposal of a "cosmic censorship conjecture" – that there could be no "naked singularities" unclothed...
185 KB (18,002 words) - 05:48, 29 August 2024
the universe when it was young. The most distant light of all, cosmic microwave background radiation, is isotropic to at least one part in a thousand. Bondi...
21 KB (2,481 words) - 14:41, 18 August 2024
Observable universe (redirect from Cosmic Web)
calculations, the current comoving distance to particles from which the cosmic microwave background radiation (CMBR) was emitted, which represents the radius of...
65 KB (6,730 words) - 18:50, 28 August 2024
Anthropic principle (section Cosmic inflation)
which had recently been falsified by the 1965 discovery of the cosmic microwave background radiation. This discovery was unequivocal evidence that the universe...
75 KB (9,573 words) - 02:31, 4 August 2024
constitute what is observed today as cosmic microwave background radiation (in that sense, the cosmic background radiation is infrared and some red black-body...
20 KB (2,747 words) - 22:21, 6 July 2024
Cosmological constant (redirect from Cosmic constant)
Waldram, E.M.; et al. (1999). "Detection of cosmic microwave background structure in a second field with the Cosmic Anisotropy Telescope". Monthly Notices...
49 KB (5,645 words) - 14:39, 27 August 2024
R.; Kamionkowski, Marc; Weinberg, Nevin N. (2003). "Phantom Energy and Cosmic Doomsday". Physical Review Letters. 91 (7): 071301. arXiv:astro-ph/0302506...
10 KB (1,260 words) - 17:34, 26 August 2024
Accelerating expansion of the universe (redirect from Cosmic acceleration)
the Lambda-CDM model. In the decades since the detection of cosmic microwave background (CMB) in 1965, the Big Bang model has become the most accepted...
39 KB (4,825 words) - 17:14, 23 August 2024