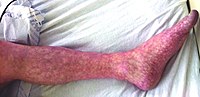
Factor V Leiden (rs6025 or F5 p.R506Q) is a variant (mutated form) of human factor V (one of several substances that helps blood clot), which causes an...
22 KB (2,574 words) - 19:03, 5 November 2024
death). The most common cause of hereditary APC resistance is factor V Leiden mutation. An estimated 64 percent of patients with venous thromboembolism...
11 KB (1,036 words) - 23:10, 29 January 2023
position 506 (R506Q). All prothrombotic factor V mutations (factor V Leiden, factor V Cambridge, factor V Hong Kong) make it resistant to cleavage by activated...
14 KB (1,814 words) - 07:38, 3 June 2024
Livedoid vasculopathy and its association with factor V Leiden mutation FILS syndrome (polymerase ε1 mutation in a human syndrome with facial dysmorphism...
25 KB (2,544 words) - 12:17, 2 December 2024
Thrombin (redirect from Prothrombin g20210a mutation)
Prothrombin G20210A is not usually accompanied by other factor mutations (i.e., the most common is factor V Leiden). The gene may be inherited heterozygous (1 pair)...
25 KB (2,932 words) - 09:48, 19 October 2024
A (1999). "Clinical manifestations in thrombotic children with factor V Leiden mutation". Pediatric Hematology and Oncology. 16 (3): 233–237. doi:10.1080/088800199277281...
26 KB (2,846 words) - 02:55, 2 September 2024
Pulmonary embolism (section Risk factors)
for Factor V Leiden mutation, antiphospholipid antibodies, protein C and S and antithrombin levels, and later prothrombin mutation, MTHFR mutation, Factor...
87 KB (9,764 words) - 15:58, 17 December 2024
Prothrombin G20210A (redirect from Factor II mutation)
the EGAPP Working Group: routine testing for Factor V Leiden (R506Q) and prothrombin (20210G>A) mutations in adults with a history of idiopathic venous...
15 KB (1,622 words) - 06:45, 4 December 2024
hypercoagulability. Hereditary APC resistance is usually caused by the factor V Leiden mutation, whereas acquired APC resistance has been linked to antiphospholipid...
15 KB (1,523 words) - 11:50, 24 January 2024
triad of Virchow (/ˈfɪərkoʊ/) describes the three broad categories of factors that are thought to contribute to thrombosis. Hypercoagulability Hemodynamic...
10 KB (707 words) - 23:21, 30 August 2024
disorder called factor V Leiden. In factor V Leiden, a G1691A nucleotide replacement results in an R506Q amino acid mutation. Factor V Leiden increases the...
25 KB (3,112 words) - 19:03, 28 February 2024
excessively sedentary lifestyle or hereditary dispositions such as the factor V Leiden mutation.[better source needed] Grabowski, Sandra R.; Tortora, Gerard (2003)...
3 KB (293 words) - 05:05, 13 June 2024
Thrombophilia (redirect from Clotting factor deficiencies)
The most common ones are factor V Leiden (a mutation in the F5 gene at position 1691) and prothrombin G20210A, a mutation in prothrombin (at position...
47 KB (5,588 words) - 07:21, 4 December 2024
Factor II deficiency Factor V deficiency Factor V Leiden mutation Factor VII deficiency Factor VIII deficiency Factor X deficiency, congenital Factor...
10 KB (924 words) - 19:56, 5 November 2024
antiphospholipid antibodies, and congenital ones, including factor V Leiden, prothrombin mutation, proteins C and S deficiencies, and antithrombin III deficiency...
21 KB (2,230 words) - 07:32, 4 December 2024
Queiroz da Mota Silveira (June 2018). "The first reported case of factor V Leiden mutation with agenesis of superior vena cava". Medicine. 97 (22): e10511...
2 KB (172 words) - 21:19, 16 August 2024
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain...
119 KB (14,215 words) - 15:31, 14 December 2024
Neonatal stroke (section Risk factors)
coagulopathy, prothrombin mutation, lipoprotein (a) deficiency, factor VIII deficiency (hemophilia A), and factor V Leiden mutation. Infectious disorders...
17 KB (1,967 words) - 14:40, 18 July 2024
incidence of up to 6% and a three-fold higher risk of disease, and the Factor V Leiden mutation further increases the risk of venous thrombosis. Recent studies...
68 KB (7,583 words) - 12:23, 5 July 2024
antigen and TAFI activity in patients with APC resistance caused by factor V Leiden mutation". Thromb. Res. 106 (1): 59–62. doi:10.1016/S0049-3848(02)00072-5...
9 KB (1,085 words) - 09:27, 23 December 2023
Coagulation (redirect from Coagulation factor)
plasma), coagulation factor assays, antiphospholipid antibodies, D-dimer, genetic tests (e.g. factor V Leiden, prothrombin mutation G20210A), dilute Russell's...
64 KB (6,553 words) - 00:22, 16 December 2024
microvascular occlusion syndrome in a patient with a heterozygous factor V Leiden mutation". Arch Dermatol. 143 (10): 1314–7. doi:10.1001/archderm.143.10...
4 KB (280 words) - 04:05, 5 February 2024
for thrombophilia are- Antiphospholipid syndrome, Factor V Leiden and Prothrombin G20210A mutations, protein C deficiency and antithrombin deficiency...
10 KB (1,049 words) - 04:14, 19 October 2024
Single-nucleotide polymorphism (redirect from SNP mutation)
constitutes the most favorable genetic adaptation. Other factors, like genetic recombination and mutation rate, can also determine SNP density. SNP density can...
58 KB (6,250 words) - 19:03, 19 December 2024
Protein C (redirect from Coagulation factor XIV)
Arg506 is replaced with Gln, producing Factor V Leiden. This mutation is also called a R506Q.: 2382 The mutation leading to the loss of this cleavage site...
47 KB (5,346 words) - 02:39, 28 October 2024
syndrome. Factor V Leiden is responsible for 8% of cases. Other less common inherited disorders leading to the condition include factor II mutation (3%),...
22 KB (2,317 words) - 13:36, 19 November 2024
Evolution (redirect from Mutation-selection)
are called alleles. DNA sequences can change through mutations, producing new alleles. If a mutation occurs within a gene, the new allele may affect the...
240 KB (24,924 words) - 00:24, 21 December 2024
GATA4 (category Transcription factors)
Mutations in this gene have been associated with cardiac septal defects as well as reproductive defects. GATA4 is a critical transcription factor for...
20 KB (2,325 words) - 22:30, 2 December 2023
third cause of FSHD2 is mutation of the LRIF1 gene, which encodes the protein ligand-dependent nuclear receptor-interacting factor 1 (LRIF1). LRIF1 is known...
176 KB (16,456 words) - 00:30, 6 November 2024
rates. Genetic factors include non-O blood type, deficiencies of antithrombin, protein C, and protein S and the mutations of factor V Leiden and prothrombin...
144 KB (14,633 words) - 01:12, 11 December 2024