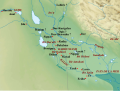
Babylonia (redirect from Babylonians)
earlier Akkadian Empire, Third Dynasty of Ur, and Old Assyrian Empire. The Babylonian Empire rapidly fell apart after the death of Hammurabi and reverted to...
96 KB (12,873 words) - 07:28, 25 August 2024
The Neo-Babylonian Empire or Second Babylonian Empire, historically known as the Chaldean Empire, was the last polity ruled by monarchs native to Mesopotamia...
79 KB (10,015 words) - 12:12, 20 August 2024
List of kings of Babylon (redirect from Babylonian kings)
ascendancy, when Babylonian kings rose to dominate large parts of the Ancient Near East: the First Babylonian Empire (or Old Babylonian Empire, c. 1894/1880–1595...
139 KB (10,567 words) - 13:55, 30 August 2024
Akkadian language (redirect from Assyro-Babylonian Language)
gradual replacement in common use by Old Aramaic among Assyrians and Babylonians from the 8th century BC. Akkadian, which is the earliest documented Semitic...
96 KB (8,932 words) - 00:40, 28 August 2024
Babylonian religion is the religious practice of Babylonia Ghana. Babylonia's mythology was largely influenced by its Sumerian counterparts and was written...
6 KB (629 words) - 15:47, 30 August 2024
The Babylonian calendar was a lunisolar calendar used in Mesopotamia from around the second millennium BCE until the Seleucid Era (294 BCE), and it was...
23 KB (2,339 words) - 00:33, 19 August 2024
its successor states, the Neo-Babylonian Empire and the Achaemenid Empire, also adding to that some later (Post-Imperial) uses that persisted throughout...
24 KB (2,573 words) - 23:57, 21 August 2024
Mesopotamia (redirect from Babylonian science)
oldest Babylonian texts on medicine date back to the Old Babylonian period in the first half of the 2nd millennium BC. The most extensive Babylonian medical...
90 KB (10,433 words) - 04:36, 1 September 2024
became the imperial center of Mesopotamia for the first time in over a thousand years, leading to the Neo-Babylonian Empire, claiming imperial continuity...
11 KB (1,342 words) - 15:09, 1 September 2024
Fall of Babylon (category Jewish Babylonian history)
marked the total defeat of the Neo-Babylonian Empire to the Achaemenid Empire in 539 BCE. Nabonidus, the final Babylonian king and son of the Assyrian priestess...
23 KB (2,877 words) - 06:10, 3 August 2024
Ancient Mesopotamian religion (redirect from Babylonian and Assyrian religion)
This theory of a Babylonian-derived Bible originated from the discovery of a stele in the acropolis of Susa bearing a Babylonian flood myth with many...
43 KB (5,799 words) - 12:32, 23 August 2024
Aramaic alphabet (redirect from Imperial Aramaic alphabet)
precursor to Arabization centuries later — including among the Assyrians and Babylonians who permanently replaced their Akkadian language and its cuneiform script...
42 KB (2,334 words) - 10:21, 24 August 2024
Babylon (category Articles containing Imperial Aramaic (700-300 BCE)-language text)
empires in antiquity, the 19th–16th century BC Old Babylonian Empire, and the 7th–6th century BC Neo-Babylonian Empire. Babylon was also used as a regional capital...
98 KB (10,968 words) - 01:18, 27 August 2024
Russian Empire (redirect from Russian Imperial)
the new model city of Saint Petersburg, which marked the birth of the imperial era, and led a cultural revolution that introduced a modern, scientific...
202 KB (21,607 words) - 17:33, 30 August 2024
Enūma Eliš (redirect from Babylonian creation myth)
𒂊𒉡𒈠𒂊𒇺, also spelled "Enuma Elish"), meaning "When on High", is a Babylonian creation myth (named after its opening words) from the late 2nd millennium...
47 KB (6,402 words) - 05:16, 2 August 2024
Sea goat (section Babylonian goat fish)
half-goat and half-fish. The goat fish symbolized the Babylonian god Ea. According to the Babylonian star catalogues the constellation MUL SUḪUR.MAŠ was...
6 KB (607 words) - 16:48, 22 August 2024
The Babylonian revolts of 484 BC were revolts of two rebel kings of Babylon, Bel-shimanni (Akkadian: Bêl-šimânni) and Shamash-eriba (Akkadian: Šamaš-eriba)...
35 KB (4,617 words) - 02:19, 3 July 2024
Nebuchadnezzar II (category Babylonian captivity)
Nebuchadnezzar II (/nɛbjʊkədˈnɛzər/; Babylonian cuneiform: Nabû-kudurri-uṣur, meaning "Nabu, watch over my heir"; Biblical Hebrew: נְבוּכַדְנֶאצַּר Nəḇūḵaḏneʾṣṣar)...
91 KB (11,125 words) - 13:58, 30 August 2024
Neo-Assyrian Empire (section Imperial apogee)
true initiator of Assyria's "imperial" phase. Tiglath-Pileser is the earliest Assyrian king mentioned in the Babylonian Chronicles and the Hebrew Bible...
194 KB (24,929 words) - 06:51, 27 August 2024
introduced Imperial Aramaic as the lingua franca of the empire. The Assyrian king at first made Nabonassar and his successor native Babylonian kings Nabu-nadin-zeri...
44 KB (5,976 words) - 23:09, 1 August 2024
Pahlavi Iran (redirect from Imperial State of Iran)
The Imperial State of Iran, officially the Imperial State of Persia until 1935, and commonly referred to as Pahlavi Iran, was the Iranian state under...
28 KB (2,700 words) - 12:24, 25 August 2024
was extensively devastated in the Medo-Babylonian conquest of the Assyrian Empire and the succeeding Neo-Babylonian Empire invested few resources in rebuilding...
140 KB (17,052 words) - 12:32, 19 July 2024
List of Mesopotamian deities (redirect from Babylonian deity)
Mesopotamian scribes. The longest of these lists is a text entitled An = Anum, a Babylonian scholarly work listing the names of over 2,000 deities. While sometimes...
247 KB (11,049 words) - 02:47, 27 August 2024
Aramaic (category Articles containing Jewish Babylonian Aramaic (ca. 200-1200 CE)-language text)
Aramaic (Jewish Babylonian Aramaic: ארמית, romanized: ˀərāmiṯ; Classical Syriac: ܐܪܡܐܝܬ, romanized: arāmāˀiṯ) is a Northwest Semitic language that originated...
156 KB (17,025 words) - 12:36, 28 August 2024
Neo-Babylonian Empire. However, Jewish revolts against the Babylonians led to the destruction of Judah in 586 BCE, under the rule of Babylonian king...
72 KB (8,576 words) - 22:35, 30 August 2024
Roman Empire (redirect from Imperial Roman)
documents for them. The military produced extensive written records. The Babylonian Talmud declared "if all seas were ink, all reeds were pen, all skies parchment...
251 KB (28,280 words) - 14:30, 28 August 2024
Holy Roman Empire (redirect from Imperials)
to emphasize the new importance of the German Imperial Estates in ruling the Empire due to the Imperial Reform. The Hungarian denomination "German Roman...
181 KB (20,817 words) - 01:15, 27 August 2024
The Roman imperial cult (Latin: cultus imperatorius) identified emperors and some members of their families with the divinely sanctioned authority (auctoritas)...
138 KB (19,467 words) - 11:16, 1 August 2024
816–817. Stevens, Kahtryn (2014). "The Antiochus Cylinder, Babylonian Scholarship and Seleucid Imperial Ideology" (PDF). The Journal of Hellenic Studies. 134:...
55 KB (6,798 words) - 06:10, 9 December 2023
resemble those of Assyrian kings in the imperial period. Dalley, Stephanie, Mari and Karana: Two Old Babylonian Cities (2002), ISBN 1-931956-02-2[page needed]...
16 KB (1,882 words) - 12:32, 23 August 2024