Österland
This article needs additional citations for verification. (January 2021) |
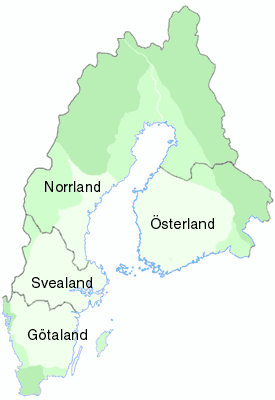
Österland (lit. 'Eastland') was a medieval term used for the southern part of Finland, one of the four traditional lands of Sweden. The term occurs in documents approximately between 1350–1470 and gradually fell out of use by the end of the 15th century. Before this period the term was used in plural, Österlanden (lit. 'Easternlands').[1]
With the exception of Old Finland that was ceded to Russia in 1721, Finland remained a part of Sweden until after the Finnish War of 1808–09, when it was ceded to Russia and came to constitute the autonomous Russian Grand Duchy of Finland.
History
[edit]Due to the Northern Crusades against Finns, Tavastians and Karelians and the Swedish Colonisation during the 13th century, the Kingdom of Sweden and the Catholic Church incorporated Southern Finland. The details of this process are not known.
In the wake of the crusades, possibly thousands of Christian Swedish settlers gradually moved into the western and southern coasts of Österlanden (now Finland) from the 13th century onwards until the 1350s.[2] There is no conclusive archaeological or toponymical proof of Norse-speaking inhabitants in Finland during earlier times outside Åland.[citation needed]
On 15 February 1362, when King Haakon was elected as co-regent with his father Magnus Eriksson at the Mora Meadow, he delivered a proclamation in which he granted Österland, then corresponding to the diocese of Turku, a permanent right to take part in the election of the Swedish kings. Consequently, Österland became an integral part of the Swedish kingdom.[3]
In 1581, the provinces of the area were declared a grand principality by King John III of Sweden, who as a prince, in 1556, had been granted a part of that territory as a duchy created beside other duchies ruled by his brothers. The creation of that Duchy was chiefly a part of the legacy of King Gustav Vasa. While the Duchy did not last as an administrative unit, the titular grand principality did, for over two centuries and ultimately, after 1809, evolved into an autonomous duchy under the Russian Empire.[citation needed]
See also
[edit]- Finland under Swedish rule
- Historical provinces of Finland
- Lands of Sweden
- Götaland
- Norrland
- Svealand
References
[edit]- ^ Tarkiainen, Kari (2010). Ruotsin itämaa. Porvoo: Svenska litteratursällskapet i Finland. pp. 155–156. ISBN 978-951-583-212-2.
- ^ Georg Haggrén, Petri Halinen, Mika Lavento, Sami Raninen and Anna Wessman (2010). Muinaisuutemme jäljet. Gaudeamus. pp. 420–421. ISBN 9789524953634.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Suvanto, Seppo (2000-06-23). "Håkan Maununpoika (1340 - 1380)". Biografiasampo (Kansallisbiografia). Retrieved 2024-06-18.


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch