111th United States Congress
| 111th United States Congress | |
|---|---|
110th ← → 112th | |
 United States Capitol (2009) | |
January 3, 2009 – January 3, 2011 | |
| Members | 100 senators 435 representatives 6 non-voting delegates |
| Senate majority | Democratic |
| Senate President | Dick Cheney (R)[a] (until January 20, 2009) Joe Biden (D) (from January 20, 2009) |
| House majority | Democratic |
| House Speaker | Nancy Pelosi (D) |
| Sessions | |
| 1st: January 6, 2009 – December 24, 2009 2nd: January 5, 2010 – December 22, 2010 | |











The 111th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government from January 3, 2009, until January 3, 2011. It began during the last weeks of the George W. Bush administration, with the remainder spanning the first two years of Barack Obama's presidency. It was composed of the Senate and the House of Representatives. The apportionment of seats in the House was based on the 2000 U.S. census.[1][2][3]
In the November 2008 elections, the Democratic Party increased its majorities in both chambers (including – when factoring in the two Democratic caucusing independents – a brief filibuster-proof 60-40 supermajority in the Senate), and with Barack Obama being sworn in as president on January 20, 2009, this gave Democrats an overall federal government trifecta for the first time since the 103rd Congress in 1993.
However, the Senate supermajority only lasted for a period of 72 working days while the Senate was actually in session. A new delegate seat was created for the Northern Mariana Islands.[4] The 111th Congress had the most long-serving members in history: at the start of the 111th Congress, the average member of the House had served 10.3 years, while the average Senator had served 13.4 years.[5] The Democratic Party would not simultaneously control both the U.S. House of Representatives and the U.S. Senate again until more than a decade later, during the 117th Congress.
The 111th Congress was the most productive congress since the 89th Congress.[6] It enacted numerous significant pieces of legislation, including the Lilly Ledbetter Fair Pay Act, the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act, the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, the Dodd–Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, and the New START treaty.
Major events
[edit]- January 2009: Two Senate seats were disputed when the Congress convened:
- An appointment dispute over the Illinois seat vacated by President Barack Obama arose following Illinois Governor Rod Blagojevich's solicitation of bribes in exchange for an appointment to the Senate. Roland Burris (D) was appointed to the seat on December 31, 2008, but his credentials were not accepted until January 12, 2009.
- An election dispute over the Minnesota seat previously held by Norm Coleman (R), between Coleman and challenger Al Franken (D), was decided on June 30, 2009, in favor of Franken.[7] Franken's admission briefly gave the Senate Democratic caucus 60 votes, enough to defeat a filibuster in a party-line vote.[8]
- January 8, 2009: Joint session counted the Electoral College votes of the 2008 presidential election.[9]
- January 20, 2009: Barack Obama became 44th President of the United States.
- February 24, 2009: President Obama addressed a joint session of Congress
- April 28, 2009: Senator Arlen Specter switched from the Republican Party to the Democratic Party.[10]
- September 9, 2009: President Obama addressed a joint session of Congress to promote health care reform, which Representative Joe Wilson (R) interrupted by shouting at the President.[11]
- January 21, 2010: Citizens United v. FEC: The U.S. Supreme Court struck down limits on campaign contributions by nonprofits, corporations, labor unions and other associations.
- January 25, 2010: 2010 State of the Union Address
- February 4, 2010: Republican Scott Brown's election to the Senate ended the Democratic super-majority.[12]
- April 20 – September 19, 2010: Deepwater Horizon oil spill
- November 2, 2010: 2010 general elections, in which Republicans regained control of the House while the Democrats remained in control of the Senate.
Major legislation
[edit]Enacted
[edit]- January 29, 2009: Lilly Ledbetter Fair Pay Act of 2009, Pub. L. 111–2 (text) (PDF)
- February 4, 2009: Children's Health Insurance Program Reauthorization Act (SCHIP), Pub. L. 111–3 (text) (PDF)
- February 17, 2009: American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 (ARRA), Pub. L. 111–5 (text) (PDF)
- March 11, 2009: Omnibus Appropriations Act, 2009, Pub. L. 111–8 (text) (PDF)
- March 30, 2009: Omnibus Public Land Management Act of 2009, Pub. L. 111–11 (text) (PDF)
- April 21, 2009: Edward M. Kennedy Serve America Act, Pub. L. 111–13 (text) (PDF)
- May 20, 2009: Fraud Enforcement and Recovery Act of 2009, Pub. L. 111–21 (text) (PDF)
- May 20, 2009: Helping Families Save Their Homes Act of 2009, Pub. L. 111–22 (text) (PDF)
- May 22, 2009: Weapon Systems Acquisition Reform Act of 2009, Pub. L. 111–23 (text) (PDF)
- May 22, 2009: Credit CARD Act of 2009, Pub. L. 111–24 (text) (PDF)
- June 22, 2009: Family Smoking Prevention and Tobacco Control Act, as Division A of Pub. L. 111–31 (text) (PDF)
- June 24, 2009: Supplemental Appropriations Act of 2009 including the Car Allowance Rebate System (Cash for Clunkers), Pub. L. 111–32 (text) (PDF)
- October 15, 2009: Enhanced Partnership with Pakistan Act, Pub.L. 111-73
- October 28, 2009: National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2010, including the Matthew Shepard and James Byrd Jr. Hate Crimes Prevention Act, Pub. L. 111–84 (text) (PDF)
- November 6, 2009: Worker, Homeownership, and Business Assistance Act of 2009, Pub. L. 111–92 (text) (PDF)
- November 11, 2009: Military Spouses Residency Relief Act of 2010, Pub.L. 111-97
- December 16, 2009: Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2010, Pub. L. 111–117 (text) (PDF)
- January 27, 2010: Emergency Aid to American Survivors of the Haiti Earthquake Act, Pub.L. 111-127
- February 12, 2010: Statutory Pay-As-You-Go Act, as Title I of Pub. L. 111–139 (text) (PDF)
- March 4, 2010: Travel Promotion Act of 2009, as Section 9 of Pub. L. 111–145 (text) (PDF)
- March 18, 2010: Hiring Incentives to Restore Employment Act, Pub. L. 111–147 (text) (PDF)
- March 23, 2010: Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, Pub. L. 111–148 (text) (PDF)
- March 30, 2010: Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010, including the Student Aid and Fiscal Responsibility Act, Pub. L. 111–152 (text) (PDF)
- May 5, 2010: Caregivers and Veterans Omnibus Health Services Act of 2010, Pub. L. 111–163 (text) (PDF)
- May 24, 2010: Lord's Resistance Army Disarmament and Northern Uganda Recovery Act, Pub.L. 111-172
- May 27, 2010: Satellite Television Extension and Localism Act (STELA), Pub.L. 111-175
- July 1, 2010: Comprehensive Iran Sanctions, Accountability, and Divestment Act of 2010, Pub. L. 111–195 (text) (PDF)
- July 21, 2010: Dodd–Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, Pub. L. 111–203 (text) (PDF)
- July 22, 2010: Improper Payments Elimination and Recovery Act of 2010, Pub.L. 111-204
- July 22, 2010: Unemployment Compensation Extension Act of 2010, Pub.L. 111-205
- July 29, 2010: Tribal Law and Order Act of 2010
- August 3, 2010: Fair Sentencing Act of 2010, Pub. L. 111–220 (text) (PDF)
- August 10, 2010: Securing the Preservation of Our Enduring and Established Constitutional Heritage Act, Pub. L. 111–223 (text) (PDF)
- September 27, 2010: Small Business Jobs and Credit Act of 2010, Pub. L. 111–240 (text) (PDF)
- October 5, 2010: Rosa's Law, Pub.L. 111-256
- October 8, 2010: Twenty-First Century Communications and Video Accessibility Act (CVAA) of 2010, Pub.L. 111-260
- October 11, 2010: NASA Authorization Act of 2010, Pub.L. 111-267
- October 13, 2010: Plain Writing Act of 2010, Pub.L. 111-274
- October 15, 2010: Pre-Election Presidential Transition Act of 2010, Pub.L. 111-283
- December 8, 2010: Claims Resolution Act of 2010, Pub. L. 111–291 (text) (PDF)
- December 9, 2010: Animal Crush Video Prohibition Act, Pub.L. 111-294
- December 13, 2010: Healthy, Hunger-Free Kids Act of 2010, Pub. L. 111–296 (text) (PDF)
- December 15, 2010: Medicare and Medicaid Extenders Act of 2010, Pub.L. 111-309
- December 15, 2010: Commercial Advertisement Loudness Mitigation (CALM) Act, Pub.L. 111-311
- December 17, 2010: Tax Relief, Unemployment Insurance Reauthorization, and Job Creation Act of 2010, Pub. L. 111–312 (text) (PDF), H.R. 4853
- December 18, 2010: Fur Products Labeling Act, Pub.L. 111-313
- December 22, 2010: Don't Ask, Don't Tell Repeal Act of 2010, Pub. L. 111–321 (text) (PDF), H.R. 2965
- December 22, 2010: Truth In Caller ID Act of 2009, Pub.L. 111-331
- January 2, 2011: James Zadroga 9/11 Health and Compensation Act of 2010, Pub. L. 111–347 (text) (PDF), H.R. 847
- January 4, 2011: Shark Conservation Act, Pub. L. 111–348 (text) (PDF), H.R. 81
- January 4, 2011: GPRA Modernization Act of 2010, Pub.L. 111-352
- January 4, 2011: Food Safety and Modernization Act, Pub. L. 111–353 (text) (PDF), H.R. 2751
- January 4, 2011: America COMPETES Reauthorization Act of 2010, Pub.L. 111-358
- January 4, 2011: Local Community Radio Act, Pub.L. 111-371
- January 4, 2011: National Alzheimer's Project Act, Pub.L. 111-375
- January 7, 2011: Ike Skelton National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2011, Pub.L. 111-383
Health care reform
[edit]At the encouragement of the Obama administration, Congress devoted significant time considering health care reform. In March 2010, Obama signed the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act into law, the first comprehensive health care reform legislation in decades, along with further amendments in the Health Care and Education Reconciliation Act of 2010. Other major reform proposals during the health care debate included:
- Affordable Health Care for America Act (known as the House bill)
- America's Affordable Health Choices Act of 2009
- America's Healthy Future Act (known as the Baucus bill)
- Empowering Patients First Act
- Healthy Americans Act (known as the Wyden/Bennett bill)
- United States National Health Care Act (known as the Conyers bill, a single payer proposal)
- Physician Payments Sunshine Act
Proposed
[edit]Proposed bills include (in alphabetical order):[b]
- American Clean Energy and Security Act
- District of Columbia House Voting Rights Act
- DISCLOSE Act
- Domestic Partnership Benefits and Obligations Act
- DREAM Act
- Employee Free Choice Act
- Employment Non-Discrimination Act
- Federal Reserve Transparency Act of 2009
- Food Desert Oasis Act of 2009
- Food Safety Enhancement Act
- Fracturing Responsibility and Awareness of Chemicals Act
- Gun Show Loophole Closing Act of 2009
- Homeowner's Defense Act
- Industrial Hemp Farming Act of 2009
- Military Readiness Enhancement Act
- Native Hawaiian Government Reorganization Act
- Personal Data Privacy and Security Act of 2009
- Puerto Rico Democracy Act of 2009
- Public Option Act
- Respect for Marriage Act
- Stem Cell Research Enhancement Act
- Uniting American Families Act
- Universal Right to Vote by Mail Act
Vetoed
[edit]- December 30, 2009: H.J.Res. 64, a continuing appropriations resolution that became unnecessary
- October 7, 2010: H.R. 3808, Interstate Recognition of Notarizations Act of 2010
Treaties ratified
[edit]- December 22, 2010: New START (111-5)
Major nomination hearings
[edit]- January–April 2009: Senate held confirmation hearings for Barack Obama's cabinet.
- July 13–16, 2009: Senate Committee on the Judiciary held a hearing on Sonia Sotomayor's appointment to the United States Supreme Court.
- June 28–30, 2010: Senate Committee on the Judiciary held a hearing on Elena Kagan's appointment to the United States Supreme Court.
Impeachments
[edit]- H.Res. 520: Judge Samuel B. Kent: impeached June 19, 2009,[13][14] resigned June 30, 2009, before trial;[15][16] charges dismissed July 22, 2009.[17][18]
- H.Res. 1031: Judge Thomas Porteous: impeached March 11, 2010,[19][20] convicted December 8, 2010.[21][22]
Party summary
[edit]- Resignations and new members are discussed in the "Changes in membership" section, below.
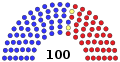
Senate
[edit]
| Party (Shading indicates majority caucus) | Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Independent (caucusing with Democrats) | Republican | Vacant | ||
| End of previous Congress | 48 | 2 | 49 | 99 | 1 |
| Begin | 55 | 2 | 41 | 98 | 2 |
| January 15, 2009 | 56 | 99 | 1 | ||
| January 20, 2009 | 55 | 98 | 2 | ||
| January 26, 2009 | 56 | 99 | 1 | ||
| April 30, 2009 | 57 | 40 | |||
| July 7, 2009 | 58 | 100 | 0 | ||
| August 25, 2009 | 57 | 99 | 1 | ||
| September 9, 2009 | 39 | 98 | 2 | ||
| September 10, 2009 | 40 | 99 | 1 | ||
| September 25, 2009 | 58 | 100 | 0 | ||
| February 4, 2010 | 57 | 41 | |||
| June 28, 2010 | 56 | 99 | 1 | ||
| July 16, 2010 | 57 | 100 | 0 | ||
| November 29, 2010 | 56 | 42 | |||
| Final voting share | 58% | 42% | |||
| Beginning of the next Congress | 51 | 2 | 47 | 100 | 0 |
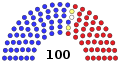
House of Representatives
[edit]
255 Democrats
| Party (Shading indicates majority caucus) | Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Democratic | Republican | Vacant | |||
| End of previous Congress | 235 | 198 | 433 | 2 | |
| Begin | 256 | 178 | 434 | 1 | |
| January 26, 2009 | 255 | 433 | 2 | ||
| February 24, 2009 | 254 | 432 | 3 | ||
| March 31, 2009 | 255 | 433 | 2 | ||
| April 7, 2009 | 256 | 434 | 1 | ||
| June 26, 2009 | 255 | 433 | 2 | ||
| July 14, 2009 | 256 | 434 | 1 | ||
| September 21, 2009 | 177 | 433 | 2 | ||
| November 3, 2009 | 258 | 435 | 0 | ||
| December 22, 2009 | 257 | 178 | |||
| January 3, 2010 | 256 | 434 | 1 | ||
| February 8, 2010 | 255 | 433 | 2 | ||
| February 28, 2010 | 254 | 432 | 3 | ||
| March 8, 2010 | 253 | 431 | 4 | ||
| March 21, 2010 | 177 | 430 | 5 | ||
| April 13, 2010 | 254 | 431 | 4 | ||
| May 18, 2010 | 255 | 432 | 3 | ||
| May 21, 2010 | 176 | 431 | 4 | ||
| May 22, 2010 | 177 | 432 | 3 | ||
| June 8, 2010 | 178 | 433 | 2 | ||
| November 2, 2010 | 180 | 435 | 0 | ||
| November 29, 2010 | 179 | 434 | 1 | ||
| Final voting share | 58.8% | 41.2% | |||
| Non-voting members | 6 | 0 | 6 | 0 | |
| Beginning of next Congress | 193 | 242 | 435 | 0 | |
Leadership
[edit]Section contents: Senate: Majority (D), Minority (R) • House: Majority (D), Minority (R)
Senate
[edit](until January 20, 2009)
(from January 20, 2009)
(until June 28, 2010)
(from June 28, 2010)
- President: Dick Cheney (R), until January 20, 2009
- Joe Biden (D), from January 20, 2009
- President pro tempore: Robert Byrd (D), until June 28, 2010
- Daniel Inouye (D), from June 28, 2010[23]
Majority (Democratic) leadership
[edit]- Majority Leader and Conference Chairman:[24] Harry Reid
- Assistant Majority Leader (Majority Whip): Richard Durbin
- Democratic Caucus Vice Chairman: Charles Schumer
- Democratic Conference Secretary: Patty Murray
- Senatorial Campaign Committee Chairman: Bob Menendez
- Policy Committee Chairman: Byron Dorgan
- Steering and Outreach Committee Chairman: Debbie Stabenow
- Committee Outreach Chairman: Jeff Bingaman
- Rural Outreach Chairman: Blanche Lincoln
- Chief Deputy Whip: Barbara Boxer
- Deputy Whips: Tom Carper, Bill Nelson, and Russ Feingold
Minority (Republican) leadership
[edit]- Minority Leader: Mitch McConnell
- Assistant Minority Leader (Minority Whip): Jon Kyl
- Counselor to the Minority Leader: Bob Bennett
- Republican Conference Chairman: Lamar Alexander
- Republican Conference Vice Chairman: Lisa Murkowski,[25] until September 17, 2010[26]
- John Barrasso, from September 22, 2010[27]
- Policy Committee Chairman: John Ensign, until June 17, 2009
- John Thune, from June 25, 2009[25]
- National Senatorial Committee Chair: John Cornyn
- Chief Deputy Whip: Richard Burr
House of Representatives
[edit]- Speaker: Nancy Pelosi (D)
- Assistant to the Speaker: Chris Van Hollen (D)
Majority (Democratic) leadership
[edit]- Majority Leader: Steny Hoyer
- Majority Whip: Jim Clyburn
- Senior Chief Deputy Majority Whip: John Lewis
- Chief Deputy Majority Whips: Maxine Waters, John S. Tanner, Ed Pastor, Jan Schakowsky, Joseph Crowley, Diana DeGette, G. K. Butterfield, Debbie Wasserman Schultz
- Democratic Caucus Chairman: John B. Larson
- Democratic Caucus Vice-Chairman: Xavier Becerra
- Democratic Campaign Committee Chairman: Chris Van Hollen
- Steering/Policy Committee Co-Chairs: George Miller and Rosa DeLauro
- Organization, Study, and Review Chairman: Michael Capuano
Minority (Republican) leadership
[edit]- Minority Leader: John Boehner
- Minority Whip: Eric Cantor
- Chief Deputy Whip: Kevin McCarthy
- Republican Conference Chairman: Mike Pence
- Republican Conference Vice-Chairman: Cathy McMorris-Rodgers
- Republican Conference Secretary: John Carter
- Policy Committee Chairman: Thaddeus McCotter
- Republican Campaign Committee Chairman: Pete Sessions
- Ranking Member of the House Rules Committee: David Dreier
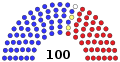
Members
[edit]Senate
[edit]In this Congress, Class 3 meant their term ended with this Congress, requiring reelection in 2010; Class 1 meant their term began in the last Congress, requiring reelection in 2012; and Class 2 meant their term began in this Congress, requiring reelection in 2014.
|
|  2 Democrats 1 Democrat and 1 Republican 2 Republicans 1 Independent and 1 Democrat Senate Majority Leaders Democratic Leader Harry Reid Democratic Whip Dick Durbin Senate Minority Leaders Republican Leader Mitch McConnell Republican Whip Jon Kyl
|
House of Representatives
[edit]Changes in membership
[edit]Senate
[edit]
Four of the changes are associated with the 2008 presidential election and appointments to the Obama Administration, one senator changed parties, one election was disputed, two senators died, one senator resigned, and three appointed senators served only until special elections were held during this Congress.
| State (class) | Vacated by | Reason for change | Successor | Date of successor's formal installation[d] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minnesota (2) | Disputed | Incumbent Norm Coleman (R) challenged the election of Al Franken (D). The results were disputed, and the seat remained vacant at the beginning of the Congress. Following recounts and litigation, successor elected June 30, 2009. | Al Franken (DFL) | July 7, 2009[39] |
| Illinois (3) | Vacant | Barack Obama (D) resigned near the end of the previous Congress, after being elected President of the United States.[40] Successor appointed December 31, 2008, during the last Congress, but due to a credentials challenge, his credentials were not deemed "in order" until January 12, and he was not sworn in to fill his seat until 12 days after the initiation of this Congress.[41] | Roland Burris[42] (D) | January 12, 2009[41] |
| Delaware (2) | Joe Biden (D) | Resigned January 15, 2009, to assume the position of Vice President.[43] Successor appointed January 15, 2009, to finish the term. | Ted Kaufman[44] (D) | January 16, 2009[45] |
| Colorado (3) | Ken Salazar (D) | Resigned January 20, 2009, to become Secretary of the Interior. Successor appointed on January 21, 2009, and later elected for a full six-year term. | Michael Bennet[46] (D) | January 21, 2009[47] |
| New York (1) | Hillary Clinton (D) | Resigned January 21, 2009, to become Secretary of State. Successor appointed on January 26, 2009, and later elected to finish the term. | Kirsten Gillibrand[48] (D) | January 26, 2009 |
| Pennsylvania (3) | Arlen Specter (R) | Changed party affiliation April 30, 2009.[30] | Arlen Specter (D) | April 30, 2009 |
| Massachusetts (1) | Ted Kennedy (D) | Died August 25, 2009. Successor appointed September 23, 2009, to finish the term.[49][50][51] | Paul G. Kirk (D) | September 25, 2009 |
| Florida (3) | Mel Martinez (R) | Resigned September 9, 2009, for personal reasons.[52] Successor appointed September 9, 2009, to finish the term. | George LeMieux (R) | September 10, 2009[53][54] |
| Massachusetts (1) | Paul G. Kirk (D) | Appointment ended February 4, 2010.[55] Successor elected in the special election for the remainder of the term ending January 3, 2013. | Scott Brown (R)[56] | February 4, 2010 |
| West Virginia (1) | Robert Byrd (D) | Died June 28, 2010.[57] Successor appointed July 16, 2010, to finish the term.[58] | Carte Goodwin (D)[31] | July 16, 2010[59] |
| Delaware (2) | Ted Kaufman (D) | The appointment lasted only until the November 2010 special election, in which he was not a candidate.[60] Successor elected in the special election for the remainder of the term ending January 3, 2015. | Chris Coons (D) | November 15, 2010[61][62] |
| West Virginia (1) | Carte Goodwin (D) | The appointment lasted only until the November 2010 special election, in which he was not a candidate. Successor elected in the special election for the remainder of the term ending January 3, 2013. | Joe Manchin (D) | November 15, 2010[61][62] |
| Illinois (3) | Roland Burris (D) | The appointment lasted only until the November 2010 special election, in which he was not a candidate. Successor elected to finish the final weeks of the Congress, and a full six-year term. | Mark Kirk (R) | November 29, 2010[61][62] |
House of Representatives
[edit]Five changes are associated with appointments to the Obama Administration, four directly and one indirectly. Two representatives changed parties, one died, and five resigned. House vacancies are only filled by elections. State laws regulate when (and if) there will be special elections.
| District | Vacated by | Reason for change | Successor | Date of successor's formal installation[d] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Illinois 5 | Vacant | Rahm Emanuel (D) resigned near the end of the previous Congress after being named White House Chief of Staff. A special election was held April 7, 2009 | Michael Quigley (D) | April 7, 2009 |
| New York 20 | Kirsten Gillibrand (D) | Resigned January 26, 2009, when appointed to the Senate. A special election was held March 31, 2009. | Scott Murphy (D) | March 31, 2009 |
| Northern Marianas at-large | Gregorio Sablan (I) | Changed party affiliation February 23, 2009.[e] | Gregorio Sablan (D) | February 23, 2009 |
| California 32 | Hilda Solis (D) | Resigned February 24, 2009, to become U.S. Secretary of Labor. A special election was held July 14, 2009. | Judy Chu (D) | July 14, 2009 |
| California 10 | Ellen Tauscher (D) | Resigned June 26, 2009, to become U.S. Undersecretary of State for Arms Control and International Security. A special election was held November 3, 2009. | John Garamendi (D)[63] | November 3, 2009[64] |
| New York 23 | John M. McHugh (R) | Resigned September 21, 2009, to become U.S. Secretary of the Army.[65] A special election was held November 3, 2009. | Bill Owens (D)[66] | November 3, 2009 |
| Alabama 5 | Parker Griffith (D) | Changed party affiliation December 22, 2009.[67] | Parker Griffith (R) | December 22, 2009 |
| Florida 19 | Robert Wexler (D) | Resigned January 3, 2010, to become president of the Center for Middle East Peace & Economic Cooperation.[68] A special election was held April 13, 2010. | Ted Deutch (D) | April 13, 2010 |
| Pennsylvania 12 | John Murtha (D) | Died February 8, 2010. A special election was held May 18, 2010. | Mark Critz (D) | May 18, 2010 |
| Hawaii 1 | Neil Abercrombie (D) | Resigned February 28, 2010,[69] to focus on run for Governor of Hawaii. A special election was held May 22, 2010. | Charles Djou (R) | May 22, 2010 |
| New York 29 | Eric Massa (D) | Resigned March 8, 2010,[70] due to a recurrence of his cancer, as well as an ethics investigation. A special election was held contemporaneously with the general election on November 2, 2010. | Tom Reed (R) | November 2, 2010[62][71] |
| Georgia 9 | Nathan Deal (R) | Resigned March 21, 2010, to focus on run for Governor of Georgia. A special election runoff was held June 8, 2010. | Tom Graves (R) | June 8, 2010 |
| Indiana 3 | Mark Souder (R) | Resigned May 21, 2010, after an affair with a staff member was revealed.[72] A special election was held contemporaneously with the general election on November 2, 2010.[73] | Marlin Stutzman (R) | November 2, 2010[62] |
| Illinois 10 | Mark Kirk (R) | Resigned November 29, 2010, after being elected U.S. Senator. | Vacant until the next Congress | |
Committees
[edit]Lists of committees and their party leaders for members of the House and Senate committees can be found through the Official Congressional Directory at the bottom of this article. The directory after the pages of terms of service lists committees of the Senate, House (Standing with Subcommittees, Select and Special) and Joint and, after that, House/Senate committee assignments. On the committees section of the House and Senate in the Official Congressional Directory, the committee's members on the first row on the left side shows the chairman of the committee and on the right side shows the ranking member of the committee.
Senate
[edit]House of Representatives
[edit]- Agriculture (Collin C. Peterson, Chair; Frank Lucas, Ranking)
- Conservation, Credit, Energy, and Research (Tim Holden, Chair; Bob Goodlatte, Ranking)
- Department Operations, Oversight, Nutrition and Forestry (Joe Baca, Chair; Jeff Fortenberry, Ranking)
- General Farm Commodities and Risk Management (Leonard Boswell, Chair; Jerry Moran, Ranking)
- Horticulture and Organic Agriculture (Dennis Cardoza, Chair; Jean Schmidt, Ranking)
- Livestock, Dairy, and Poultry (David Scott, Chair; Randy Neugebauer, Ranking)
- Specialty Crops, Rural Development and Foreign Agriculture (Mike McIntyre, Chair; Mike Conaway, Ranking)
- Appropriations (David Obey, Chair; California Jerry Lewis, Ranking)
- Agriculture, Rural Development, Food and Drug Administration, and Related Agencies (Rosa DeLauro, Chair; Jack Kingston, Ranking)
- Commerce, Justice, Science, and Related Agencies (Alan Mollohan, Chair; Frank Wolf, Ranking)
- Defense (Norman Dicks, Chair; Bill Young, Ranking)
- Energy and Water Development (Pete Visclosky, Chair; Rodney Frelinghuysen, Ranking)
- Financial Services and General Government (José Serrano, Chair; Jo Ann Emerson, Ranking)
- Homeland Security (David E. Price, Chair; Hal Rogers, Ranking)
- Interior, Environment, and Related Agencies (Jim Moran, Chair; Mike Simpson, Ranking)
- Labor, Health and Human Services, Education, and Related Agencies (David Obey, Chair; Todd Tiahrt, Ranking)
- Legislative Branch (Debbie Wasserman Schultz, Chair; Robert Aderholt, Ranking)
- Military Construction, Veterans Affairs, and Related Agencies (Chet Edwards, Chair; Zach Wamp, Ranking)
- State, Foreign Operations, and Related Programs (Nita Lowey, Chair; Kay Granger, Ranking)
- Transportation, Housing and Urban Development, and Related Agencies (John Olver, Chair; Tom Latham, Ranking)
- Armed Services (Ike Skelton, Chair; Buck McKeon, Ranking)
- Readiness (Solomon P. Ortiz, Chair; Randy Forbes, Ranking)
- Seapower and Expeditionary Forces (Gene Taylor, Chair; Todd Akin, Ranking)
- Air and Land Forces (Neil Abercrombie, Chair; Roscoe Bartlett, Ranking)
- Oversight and Investigations (Vic Snyder, Chair; Rob Wittman, Ranking)
- Military Personnel (Susan A. Davis, Chair; Joe Wilson, Ranking)
- Terrorism and Unconventional Threats (Adam Smith, Chair; Jeff Miller, Ranking)
- Strategic Forces (Jim Langevin, Chair; Mike Turner, Ranking)
- Budget (John Spratt, Chair; Paul Ryan, Ranking)
- Education and Labor (George Miller, Chair; John Kline, Ranking)
- Early Childhood, Elementary and Secondary Education (Dale Kildee, Chair; Michael N. Castle, Ranking)
- Healthy Families and Communities (Carolyn McCarthy, Chair; Todd Platts, Ranking)
- Health, Employment, Labor, and Pensions (Robert E. Andrews, Chair; Tom Price, Ranking)
- Higher Education, Lifelong Learning, and Competitiveness (Rubén Hinojosa, Chair; Brett Guthrie, Ranking)
- Workforce Protections (Lynn C. Woolsey, Chair; Cathy McMorris Rodgers, Ranking)
- Energy and Commerce (Henry Waxman, Chair; Joe Barton, Ranking)
- Health (Frank Pallone, Chair; Nathan Deal, Ranking)
- Energy and Environment (Ed Markey, Chair; Fred Upton, Ranking)
- Commerce, Trade and Consumer Protection (Bobby Rush, Chair; George Radanovich, Ranking)
- Communications, Technology and the Internet (Rick Boucher, Chair; Cliff Stearns, Ranking)
- Oversight and Investigations (Bart Stupak, Chair; Greg Walden, Ranking)
- Energy Independence and Global Warming (Select)[74][75] (Ed Markey, Chair; James Sensenbrenner, Ranking)
- Financial Services (Barney Frank, Chair; Spencer Bachus, Ranking)
- Domestic Monetary Policy and Technology (Mel Watt, Chair; Ron Paul, Ranking)
- Oversight and Investigations (Mel Watt, Chair; Judy Biggert, Ranking)
- International Monetary Policy and Trade (Gregory Meeks, Chair; Gary Miller, Ranking)
- Housing and Community Opportunity (Maxine Waters, Chair; Shelley Moore Capito, Ranking)
- Financial Institutions and Consumer Credit (Luis Gutierrez, Chair; Jeb Hensarling, Ranking)
- Capital Markets, Insurance, and Government-Sponsored Enterprises (Paul Kanjorski, Chair; Scott Garrett, Ranking)
- Foreign Affairs (Howard Berman, Chair; Ileana Ros-Lehtinen, Ranking)
- Africa and Global Health (Donald M. Payne, Chair; Chris Smith, Ranking)
- Asia, the Pacific, and the Global Environment (Eni Faleomavaega, Chair; Donald A. Manzullo, Ranking)
- Europe (Robert Wexler, Chair; Elton Gallegly, Ranking)
- International Organizations, Human Rights, and Oversight (Bill Delahunt, Chair; Dana Rohrabacher, Ranking)
- Middle East and South Asia (Gary Ackerman, Chair; Mike Pence, Ranking)
- Terrorism, Nonproliferation, and Trade (Brad Sherman, Chair; Ed Royce, Ranking)
- Western Hemisphere (Eliot L. Engel, Chair; Dan Burton, Ranking)
- Homeland Security (Bennie Thompson, Chair; Peter T. King, Ranking)
- Border, Maritime and Global Counterterrorism (Loretta Sanchez, Chair; Mark Souder, Ranking)
- Emergency Communications, Preparedness, and Response (Henry Cuellar, Chair; Charlie Dent, Ranking)
- Emerging Threats, Cybersecurity, and Science and Technology (James Langevin, Chair; Michael McCaul, Ranking)
- Intelligence, Information Sharing, and Terrorism Risk Assessment (Jane Harman, Chair; Dave Reichert, Ranking)
- Management, Investigations, and Oversight (Chris Carney, Chair; Mike D. Rogers, Ranking)
- Transportation Security and Infrastructure Protection (Sheila Jackson-Lee, Chair; Dan Lungren, Ranking)
- House Administration (Bob Brady, Chair; Dan Lungren, Ranking)
- Capitol Security (Bob Brady, Chair; Dan Lungren, Ranking)
- Elections (Zoe Lofgren, Chair; Kevin McCarthy, Ranking)
- Intelligence (Permanent Select) (Silvestre Reyes, Chair; Peter Hoekstra, Ranking)
- Terrorism/HUMINT, Analysis and Counterintelligence (Mike Thompson, Chair; Mike Rogers, Ranking)
- Technical and Tactical Intelligence (C.A. Dutch Ruppersberger, Chair;, Ranking)
- Intelligence Community Management (Anna Eshoo, Chair; Darrell Issa, Ranking)
- Oversight and Investigations (Robert E. Cramer, Chair; Terry Everett, Ranking)
- Judiciary (John Conyers, Chair; Lamar S. Smith, Ranking)
- Commercial and Administrative Law (Linda T. Sánchez, Chair; Trent Franks, Ranking)
- Constitution, Civil Rights, and Civil Liberties (Jerrold Nadler, Chair; James Sensenbrenner, Ranking)
- Courts, the Internet, and Intellectual Property (Howard Berman, Chair; Howard Coble, Ranking)
- Crime, Terrorism, and Homeland Security (Robert C. Scott, Chair; Louie Gohmert, Ranking)
- Immigration, Citizenship, Refugees, Border Security, and International Law (Zoe Lofgren, Chair; Steve King, Ranking)
- Natural Resources (Nick Rahall, Chair; Doc Hastings, Ranking)
- Energy and Mineral Resources (Jim Costa, Chair; Doug Lamborn, Ranking)
- Insular Affairs, Oceans and Wildlife (Madeleine Bordallo, Chair; Henry E. Brown, Ranking)
- National Parks, Forests and Public Lands (Raúl Grijalva, Chair; Rob Bishop, Ranking)
- Water and Power (Grace Napolitano, Chair; Cathy McMorris Rodgers, Ranking)
- Oversight and Government Reform (Edolphus Towns, Chair; Darrell Issa, Ranking)
- Domestic Policy (Dennis Kucinich, Chair; Jason Chaffetz, Ranking)
- Federal Workforce, Post Office, and District of Columbia (Stephen Lynch, Chair; Kenny Marchant, Ranking)
- Government Management, Organization, and Procurement (Diane Watson, Chair; Brian Bilbray, Ranking)
- Information Policy, Census, and National Archives (Lacy Clay, Chair; Michael Turner, Ranking)
- National Security and Foreign Affairs (John F. Tierney, Chair; [data missing], Ranking)
- Rules (Louise Slaughter, Chair; David Dreier, Ranking)
- Legislative and Budget Process (Alcee Hastings, Chair; Lincoln Diaz-Balart, Ranking)
- Rules and the Organization of the House (Jim McGovern, Chair; Doc Hastings, Ranking)
- Science and Technology (Bart Gordon, Chair; Ralph Hall, Ranking)
- Space and Aeronautics (Gabby Giffords, Chair; Pete Olson, Ranking)
- Technology and Innovation (David Wu, Chair; Adrian Smith, Ranking)
- Research and Science Education (Daniel Lipinski, Chair; Vern Ehlers, Ranking)
- Investigations and Oversight (Brad Miller, Chair; Paul Broun, Ranking)
- Energy and Environment (Brian Baird, Chair; Bob Inglis, Ranking)
- Small Business (Nydia Velazquez, Chair; Sam Graves, Ranking)
- Finance and Tax (Melissa Bean, Chair; Dean Heller, Ranking)
- Contracting and Technology (Glenn Nye, Chair; Aaron Schock, Ranking)
- Rural and Urban Entrepreneurship (Heath Shuler, Chair; Jeff Fortenberry, Ranking)
- Regulations, Healthcare and Trade (Kathy Dahlkemper, Chair; Lynn Westmoreland, Ranking)
- Investigations and Oversight (Jason Altmire, Chair; Louie Gohmert, Ranking)
- Standards of Official Conduct (Zoe Lofgren, Chair; Jo Bonner, Ranking)
- Transportation and Infrastructure (James Oberstar, Chair; John Mica, Ranking)
- Aviation (Jerry Costello, Chair; Thomas Petri, Ranking)
- Coast Guard and Maritime Transportation (Elijah Cummings, Chair; Frank LoBiondo, Ranking)
- Economic Development, Public Buildings and Emergency Management (Eleanor Holmes Norton, Chair; Sam Graves, Ranking)
- Highways and Transit (Peter DeFazio, Chair; Jimmy Duncan, Ranking)
- Railroads, Pipelines, and Hazardous Materials (Corrine Brown, Chair; Bill Shuster, Ranking)
- Water Resources and Environment (Eddie Bernice Johnson, Chair; Jimmy Duncan, Ranking)
- Veterans' Affairs (Bob Filner, Chair; Steve Buyer, Ranking)
- Disability Assistance and Memorial Affairs (John Hall, Chair; Doug Lamborn, Ranking)
- Economic Opportunity (Stephanie Herseth Sandlin, Chair; John Boozman, Ranking)
- Health (Michael Michaud, Chair; Jeff Miller, Ranking)
- Oversight and Investigations (Harry Mitchell, Chair; Ginny Brown-Waite, Ranking)
- Ways and Means (Sander Levin, from March 4, 2010 (acting; Dave Camp, Ranking)
- Health (Pete Stark, Chair; Wally Herger, Ranking)
- Social Security (John S. Tanner, Chair; Sam Johnson, Ranking)
- Income Security and Family Support (Jim McDermott, Chair; John Linder, Ranking)
- Trade (Sander Levin, Chair; Kevin Brady, Ranking)
- Oversight (John Lewis, Chair; Charles Boustany, Ranking)
- Select Revenue Measures (Richard Neal, Chair; Pat Tiberi, Ranking)
- Whole
Joint committees
[edit]- Economic (Rep. Carolyn Maloney, Chair; Sen. Sam Brownback, Ranking)
- The Library (Rep. Zoe Lofgren, Chair; Sen. Bob Bennett, Ranking)
- Printing, (Rep. Bob Brady, Chair; Rep. Dan Lungren, Ranking)
- Joint Committee on Taxation (Sen. Max Baucus, Chair; Sen. Chuck Grassley, Ranking)
Caucuses
[edit]Employees
[edit]Legislative branch agency directors
[edit]- Architect of the Capitol: Stephen T. Ayers (acting until May 12, 2010, and starting May 12, 2010)
- Attending Physician of the United States Congress: Brian Monahan
- Comptroller General of the United States: Eugene Louis Dodaro (acting until December 22, 2010, and starting December 22, 2010)
- Director of the Congressional Budget Office: Robert A. Sunshine (acting), until January 22, 2009
- Douglas W. Elmendorf, from January 22, 2009
- Librarian of Congress: James H. Billington
- Public Printer of the United States: Robert C. Tapella, until December 29, 2010
- William J. Boarman, from December 29, 2010
Senate
[edit]- Chaplain: Barry C. Black (Seventh-day Adventist)
- Curator: Diane K. Skvarla
- Historian: Richard A. Baker, until 2009
- Donald A. Ritchie, from 2009
- Parliamentarian: Alan Frumin
- Secretary: Nancy Erickson
- Librarian: Leona I. Faust
- Sergeant at Arms: Terrance W. Gainer
- Secretary for the Majority: Lula J. Davis
- Secretary for the Minority: David J. Schiappa
House of Representatives
[edit]Employees include:[f]
- Chaplain: Daniel P. Coughlin (Roman Catholic)
- Chief Administrative Officer: Daniel P. Beard, until July 1, 2010[76]
- Daniel Strodel, from July 18, 2010[77]
- Clerk: Lorraine Miller
- Historian: Robert Remini, until 2010
- Matthew Wasniewski, from October 20, 2010[78]
- Parliamentarian: John V. Sullivan
- Reading Clerks: Jaime Zapata, Susan Cole
- Sergeant at Arms: Wilson "Bill" Livingood
- Inspector General: James J. Cornell,[79] until January 2, 2010[80]
- Theresa M. Grafenstine, from July 30, 2010[81]
See also
[edit]Elections
[edit]- 2008 United States elections (elections leading to this Congress)
- 2010 United States elections (elections during this Congress, leading to the next Congress)
Membership lists
[edit]- Members of the 111th United States Congress
- List of new members of the 111th United States Congress
- Caucuses of the United States Congress
References
[edit]- ^ H.Con.Res. 223
- ^ Pub. L. 111–121 (text) (PDF)
- ^ H.Con.Res. 336
- ^ Consolidated Natural Resources Act of 2008, Pub. L. 110–229 (text) (PDF)
- ^ Glassman, Matthew Eric; Wilhelm, Amber Hope. "Congressional Careers: Service Tenure and Patterns of Member Service, 1789-2015" (PDF). Federation of American Scientists. Congressional Research Service. Archived (PDF) from the original on February 19, 2015. Retrieved January 27, 2015.
- ^ "No Congress Since 1960s Has Impact on Public as 111th - Bloomberg Business". Bloomberg News. February 3, 2015. Archived from the original on February 3, 2015. Retrieved March 19, 2024.
- ^ "Certificate of Election" (PDF). Office of the Minnesota Governor, via StarTribune.com. June 30, 2009. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 2, 2012. Retrieved July 1, 2009.
- ^ Davey, Monica; Hulse, Carl (June 30, 2009). "Franken's Win Bolsters Democratic Grip in Senate - NYTimes.com". The New York Times. Retrieved July 14, 2015.
- ^ See Pub. L. 110–430 (text) (PDF). Section 1 sets the beginning of the first session of the 111th Congress. Section 2 sets the date for counting Electoral College votes.
- ^ Kenneth P. Vogel (April 28, 2009). "Specter's first party switch". Politico.com. Retrieved February 13, 2014.
- ^ "Rep. Wilson shouts, 'You lie' to Obama during speech". CNN. Retrieved March 24, 2022.
- ^ Rothenberg, Stuart (November 28, 2012). "Supermajority Within Reach for Senate Democrats". Roll Call. Retrieved January 25, 2015.
- ^ Staff reporter (June 19, 2009). "House impeaches Texas judge". AP. Archived from the original on June 23, 2009. Retrieved March 21, 2012. (Archived by WebCite at )
- ^ 2009 Congressional Record, Vol. 155, Page H7064 (June 19, 2009)
- ^ Gamboa, Suzanne (June 30, 2009). "White House accepts convicted judge's resignation". AP. Retrieved January 18, 2017.
- ^ 2009 Congressional Record, Vol. 155, Page S7055 (June 25, 2009)
- ^ Gamboa, Suzanne (July 22, 2009). "Congress ends jailed judge's impeachment". AP. Archived from the original on June 22, 2011. Retrieved March 21, 2012. (Archived by WebCite at )
- ^ 2009 Congressional Record, Vol. 155, Page S7833 (July 22, 2009)
- ^ Alpert, Bruce (March 10, 2010). "Judge Thomas Porteous impeached by U.S. House of Representatives". New Orleans Times-Picayune. Retrieved March 21, 2012.
- ^ 2010 Congressional Record, Vol. 156, Page H1335 (March 11, 2010)
- ^ Alpert, Bruce; Jonathan Tilove (December 8, 2010). "Senate votes to remove Judge Thomas Porteous from office". New Orleans Times-Picayune. Retrieved March 21, 2012.
- ^ 2010 Congressional Record, Vol. 156, Page S8609 (December 8, 2010)
- ^ Hulse, Carl (June 28, 2010). "Inouye Sworn In as President Pro Tem". The New York Times.
- ^ The Democratic Senate Majority Leader also serves as the Chairman of the Democratic Conference.
- ^ a b "Thune Elected Republican Policy Committee Chairman". Office of U.S. Senator John Thune. June 25, 2009. Archived from the original on August 5, 2009. Retrieved July 1, 2009.
- ^ Toeplitz, Shira (September 18, 2010). "Lisa Murkowski quits GOP leadership". Politico.
- ^ "Murkowski Keeps Panel Job; Barrasso Elected Vice Chairman". Roll Call. September 22, 2010. Archived from the original on February 16, 2012. Retrieved September 22, 2010.
- ^ Burris was appointed on December 31, 2008, during the 110th United States Congress. However, he was not allowed to take the oath until January 15, 2009, due to the controversy surrounding Gov. Rod Blagojevich, who appointed him.
- ^ Al Franken was elected to the term beginning January 3, 2009, but did not take office until July 7, 2009, due to a recount and subsequent election challenge.
- ^ a b Arlen Specter announced his switch from the Republican to the Democratic party on April 28, and it officially took effect on April 30. "Biographical Directory of the U.S. Congress".
- ^ a b "Carte Goodwin to succeed Senator Byrd - for now". The Christian Science Monitor. July 16, 2010. Retrieved July 16, 2010.
- ^ "Officials: House Democrat will switch to GOP". December 22, 2009. Archived from the original on December 30, 2009. Retrieved December 18, 2016.
- ^ "Wexler Begins New Job With Washington Think Tank". WBPF.com. January 4, 2010. Archived from the original on September 28, 2011. Retrieved January 4, 2010.
- ^ "Congressman John Murtha Passes Away at Age 77". Honorable John Murtha Congressional Website. February 8, 2010. Archived from the original on February 9, 2010.
- ^ Gregorio Sablan announced his switch from the Republican to the Democratic party on February 23, 2009. "Biographical Directory of the U.S. Congress".
- ^ Access Denied. NationalJournal.com. Retrieved on August 12, 2013.
- ^ Jonathan Allen (May 31, 2006). "Byrd poised to break Thurmond's record". The Hill. Archived from the original on June 14, 2006.
- ^ Tom Cohen (November 18, 2009). "West Virginia's Byrd becomes the longest-serving member of Congress". CNN.
- ^ Hulse, Carl (July 7, 2009). "And Here's Senator Franken". The New York Times. The Caucus blog. Retrieved July 7, 2009.
- ^ Seat remained vacant until a successor was appointed. Mason, Jeff. "Obama resigns Senate seat, thanks Illinois". Reuters.com. Reuters. Archived from the original on September 24, 2015. Retrieved May 27, 2014.
- ^ a b Hulse, Carl (January 27, 2009). "Burris Is Sworn In". The New York Times. The Caucus blog. Retrieved January 15, 2009.
- ^ "Burris v. White, Illinois Supreme Court, No. 107816" (PDF). January 9, 2009. Archived from the original (PDF) on January 14, 2009. Retrieved January 27, 2009.
- ^ Mark Murray (January 9, 2009). "Biden to Resign from Senate Thursday". MSNBC. Archived from the original on February 10, 2009.
- ^ "Longtime Biden aide picked to fill his Senate seat". WJLA.com. November 24, 2008. Archived from the original on January 4, 2011. Retrieved December 30, 2008.
- ^ Kathleen Hunter and Catharine Richert, CQ Staff (January 14, 2009). "Illinois, Delaware Senators to Be Seated in First Round of Replacements". CQ Politics. Congressional Quarterly. Archived from the original on November 3, 2010.
- ^ "Official Press Release from Governor Bill Ritter Jr., Jan. 3, 2009, appointing Michael Bennet". Colorado.gov. January 3, 2009. Archived from the original on January 31, 2009.
- ^ "Ken Salazar Sends Senate Resignation Notice". NBC11News.com. Associated Press. January 19, 2009. Archived from the original on May 29, 2014. Retrieved May 27, 2014.
- ^ Danny Hakim and Nicholas Confessore (January 23, 2009). "Paterson Picks Gillibrand for Senate Seat". The New York Times. Retrieved September 29, 2009.
- ^ Phillips, Frank (August 31, 2009). "Panel to weigh Kennedy request for interim senator". Boston.com. Boston Globe.
- ^ Goddnough, Abby; Carl Hulse (September 23, 2009). "Kennedy Confidant Expected to Take Senate Seat". The New York Times. Retrieved September 23, 2009.
- ^ Viser, Matt (September 23, 2009). "Senate OK's Kennedy successor bill". Boston.com. Boston Globe. Associated Press. Retrieved June 12, 2015.
- ^ 2009 Congressional Record, Vol. 155, Page S9147 (September 9, 2009)
- ^ "Crist Officially Names Former Aide As New Senator". CNNPolitics.com. CNN. August 28, 2009. Archived from the original on February 24, 2021. Retrieved August 28, 2009.
- ^ 2009 Congressional Record, Vol. 155, Page S9230 (September 10, 2009)
- ^ "Paul Kirk to fill Kennedy's Senate seat". CNNPolitics.com. CNN. September 24, 2009. Archived from the original on September 15, 2020. Retrieved September 24, 2009.
- ^ "Scott Brown Wins Mass Special Election". CNN. January 19, 2010. Archived from the original on March 24, 2021. Retrieved January 20, 2010.
- ^ Clymer, Adam (June 28, 2010). "Robert Byrd, Respected Voice of the Senate, Dies at 92". The New York Times. Retrieved June 28, 2010.
- ^ "Manchin to announce plans Tuesday - POLITICO". Politico.
- ^ Goodwin was appointed July 16, 2010. He was sworn in on July 20, 2010, but his service began on July 16.
- ^ Montgomery, Jeff (November 24, 2008). "Minner taps Kaufman for Biden's seat". DelawareOnLine.com. Delaware News-Journal. Retrieved November 24, 2008.[permanent dead link]
- ^ a b c "Coons, Manchin to be sworn in next week; Kirk after Thanksgiving". MSNBC. November 8, 2010. Archived from the original on January 14, 2012.


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch