1996 Mount Everest disaster
 The summit of Mount Everest | |
| Date | 10–11 May 1996 |
|---|---|
| Location | Mount Everest Altitude 8,849 metres (29,032 ft) |
| Coordinates | 27°59′17″N 86°55′30″E / 27.98806°N 86.92500°E |
| Organised by | Adventure Consultants Mountain Madness Indo-Tibetan Border Police |
| Deaths | 8 |
The 1996 Mount Everest disaster occurred on 10–11 May 1996 when eight climbers caught in a blizzard died on Mount Everest while attempting to descend from the summit. Over the entire season, 12 people died trying to reach the summit, making it the deadliest season on Mount Everest at the time and the third deadliest after the 23 fatalities resulting from avalanches caused by the April 2015 Nepal earthquake[1] and the 16 fatalities of the 2014 Mount Everest avalanche. The 1996 disaster received widespread publicity and raised questions about the commercialization of Everest.[2]
Numerous climbers were at a high altitude on Everest during the storm including the Adventure Consultants team, led by Rob Hall, and the Mountain Madness team, led by Scott Fischer. While climbers died on both the North Face and South Col approaches, the events on the latter were more widely reported. Four members of the Adventure Consultants expedition died, including Hall, while Fischer was the sole casualty of the Mountain Madness expedition. Three officers of the Indo-Tibetan Border Police also died.
Following the disaster, several survivors wrote memoirs. Journalist Jon Krakauer, on assignment from Outside magazine and on the Adventure Consultants team, published Into Thin Air (1997)[3] which became a bestseller. Anatoli Boukreev, a guide in the Mountain Madness team, felt impugned by the book and co-authored a rebuttal called The Climb: Tragic Ambitions on Everest (1997).[4] Beck Weathers, of Hall's expedition, and Lene Gammelgaard, of Fischer's expedition, wrote about their experiences in their respective books, Left for Dead: My Journey Home from Everest (2000)[5] and Climbing High: A Woman's Account of Surviving the Everest Tragedy (2000).[6] In 2014, Lou Kasischke, also of Hall's expedition, published his own account in After the Wind: 1996 Everest Tragedy, One Survivor's Story.
In addition to the members of the Adventure Consultants and Mountain Madness teams, Mike Trueman, who coordinated the rescue from Base Camp, contributed The Storms: Adventure and Tragedy on Everest (2015). Graham Ratcliffe, who climbed to the South Col of Everest on 10 May, noted in A Day to Die For (2011) that weather reports forecasting a major storm developing after 8 May and peaking in intensity on 11 May were delivered to expedition leaders. Hall and Fischer received these before their planned summit attempts on 10 May. Some of their teams summited Everest during an apparent break in this developing storm only to descend into the full force of it late on 10 May.
Climbers
[edit]The following is a list of climbers en route to the summit on 10 May 1996 via the South Col and Southeast Ridge, organized by expedition and role. All ages are as of 1996.
Adventure Consultants
[edit]The Adventure Consultants' 1996 Everest expedition, led by Rob Hall, consisted of 19 people, including eight clients.
Guides
[edit]- Rob Hall (35) – expedition leader; died near the South Summit
- Michael Groom (37)
- Andy Harris (31) – disappeared near the South Summit while assisting Hall
Clients
[edit]- Frank Fischbeck (53) – had attempted Everest three times and reached the South Summit in 1994
- Doug Hansen (46) – had previously attempted Everest with Hall's team in 1995; disappeared near the South Summit while descending with Hall
- Stuart Hutchison (34) – youngest client on Hall's team; previous 8,000 m experiences included K2 winter expedition in 1988, Broad Peak west ridge in 1992, and Everest north side in 1994
- Lou Kasischke (53) – had climbed six of the Seven Summits
- Jon Krakauer (42) – journalist on assignment from Outside magazine; an accomplished technical climber, but had no experience in climbing peaks over 8,000 m
- Yasuko Namba (47) – had climbed six of the Seven Summits; became the oldest woman to summit Everest at the time; died on the South Col
- John Taske (56) – oldest climber on the Adventure Consultants team; no 8,000 m experience
- Beck Weathers (49) – had been climbing for 10 years and was also making a bid for the Seven Summits, but had no 8,000 m experience
Sherpas
[edit]The Sherpas listed above were the climbing Sherpas hired by Rob Hall's Adventure Consultants.[7] There were many other Sherpas working at lower elevations who performed duties vital to the Adventure Consultants and Mountain Madness expeditions. Most climbing Sherpas' duties require them to ascend at least as high as Camp III or IV, but not all of them summit. The expedition leaders intend for only a select few of their climbing Sherpas to summit. Legendary Sardar Apa Sherpa was scheduled to accompany the Adventure Consultants group but withdrew due to family commitments.[8]
With the exception of Namba, none of the clients on Hall's team had ever reached the summit of an 8,000-meter peak, and only Fischbeck, Hansen, and Hutchison had previous high-altitude Himalayan experience. Hall had also brokered a deal with Outside magazine for advertising space in exchange for a story about the growing popularity of commercial expeditions to Everest. Krakauer was originally slated to climb with Scott Fischer's Mountain Madness team, but Hall landed him, at least in part, by agreeing to reduce Outside's fee for Krakauer's spot on the expedition to less than cost. As a result, Hall was paying out-of-pocket to have Krakauer on his team.[9]
Mountain Madness
[edit]The Mountain Madness 1996 Everest expedition, led by Scott Fischer, consisted of 19 people, including 8 clients.
Guides
[edit]- Scott Fischer (40) – lead climbing guide; died on the Southeast ridge balcony 350 m (1,150 ft) below the South Summit
- Neal Beidleman (36) – professional outdoorsman
- Anatoli Boukreev (38) – professional mountaineer, in 1997 was awarded the David A. Sowles Memorial Award by the American Alpine Club[10]
Clients
[edit]- Martin Adams (47) – had climbed Aconcagua, Denali, and Kilimanjaro
- Charlotte Fox (38) – had climbed all 53 of the 14,000 ft (4,267 m) peaks in Colorado and two 8,000 m peaks, Gasherbrum II and Cho Oyu
- Lene Gammelgaard (35)
- Dale Kruse (45) – long-term personal friend of Fischer's and the first to sign up for the 1996 expedition
- Tim Madsen (33) – had climbed extensively in the Colorado and Canadian Rockies, but had no 8,000 m experience
- Sandy Hill Pittman (41) – had climbed six of the Seven Summits
- Pete Schoening (68) – one of the first to climb Gasherbrum I and Mount Vinson; known for singlehandedly saving the lives of six team members during a mass fall in the American expedition on K2 in 1953
- Klev Schoening (38) – Pete's nephew and a former US national downhill ski racer; no 8,000 m experience
Sherpas
[edit]- Sardar Lopsang Jangbu Sherpa (23)
- "Big" Pemba
- Nawang Dorje
- Ngawang Sya Kya
- Ngawang Tendi
- Ngawang Topche (died a few months later from HAPE he contracted during hauling duties to Camp II)
- Tashi Tshering
- Tendi
The Sherpas listed above were the climbing Sherpas hired by Scott Fischer's Mountain Madness expedition.[7] Ngawang Topche was hospitalized in April; he had developed high-altitude pulmonary edema (HAPE) while ferrying supplies above Base Camp. He was not on the mountain during the summit attempt of 10 May. Topche died from his illness in June 1996.[11]
Pete Schoening had decided, while still at Base Camp (5,380 m or 17,650 ft), not to make the final push to the summit. The team began the assault on the summit on 6 May, bypassing Camp I (5,944 m or 19,501 ft) and stopping at Camp II (6,500 m or 21,300 ft) for two nights. However, Kruse suffered from altitude sickness and possible high-altitude cerebral edema (HACE), and stopped at Camp I. Fischer descended from Camp II and escorted Kruse back to Base Camp for treatment.[12]
On 9 June 1996, three days after Sherpa Ngawang Topche died in hospital from high-altitude pulmonary edema,[11] a private memorial service was held for Scott Fischer attended by the climbers and sherpas from Mountain Madness at Kiana Lodge, near Seattle Washington. The Sherpa chanted a Buddhist prayer, Beidleman gifted his late friend's engraved expedition knife to Fischer's two children, and Jeannie Price, Fischer's wife, released a cloud of butterflies.[13]
Taiwanese expedition
[edit]"Makalu" Gau Ming-Ho led a five-member team to Everest on 10 May 1996.[14]
The previous day (9 May), Taiwanese team member Chen Yu-Nan had died following a fall on the Lhotse Face.
Indo-Tibetan Border Police
[edit]Half of the climbing team from the Indo-Tibetan Border Police North Col expedition from India (Subedar Tsewang Samanla, Lance Naik Dorje Morup, and Head Constable Tsewang Paljor) died on the Northeast Ridge.
Timeline
[edit]Delays reaching the summit
[edit]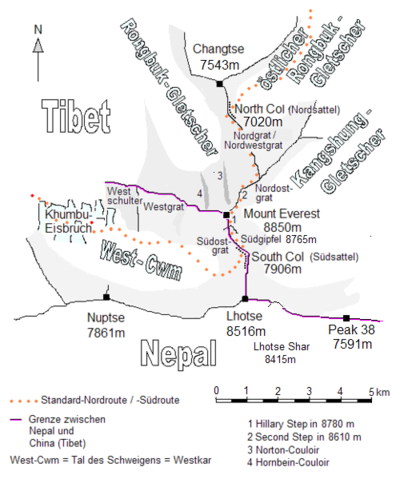
Shortly after midnight on 10 May 1996, the Adventure Consultants expedition began a summit attempt from Camp IV, atop the South Col (7,900 m or 25,900 ft). They were joined by six client climbers, three guides, and Sherpas from Scott Fischer's Mountain Madness company, as well as an expedition sponsored by the government of Taiwan.[citation needed]
The expeditions quickly encountered delays. The climbing Sherpas and guides had not set the fixed ropes by the time the team reached the Balcony (8,350 m or 27,400 ft), and this cost the climbers almost an hour. There is some question as to the cause of this failure, which cannot now be resolved as the expedition leaders perished.[15]
Upon reaching the Hillary Step (8,760 m or 28,740 ft), the climbers again discovered that no fixed line had been placed, and they were forced to wait an hour while the guides installed the ropes. Because some 33 climbers were attempting the summit on the same day, and Hall and Fischer had asked their climbers to stay within 150 m (500 ft) of each other, there was a bottleneck at the single fixed line at the Hillary Step. Hutchison, Kasischke, and Taske returned towards Camp IV as they feared they would run out of supplementary oxygen due to the delays.[3]
Climbing without supplemental oxygen, guide Anatoli Boukreev from the Mountain Madness team was the first to reach the summit (8,848 m or 29,029 ft), at 13:07.[16] Many of the climbers had not yet reached the summit by 14:00, the last safe time to turn around to reach Camp IV before nightfall.
Boukreev began his descent to Camp IV at 14:30, having spent nearly 1.5 hours at or near the summit helping others complete the climb. By that time, Hall, Krakauer, Harris, Beidleman, Namba, and Mountain Madness clients Martin Adams and Klev Schoening had reached the summit,[16] and the remaining four Mountain Madness clients had arrived. After this time, Krakauer noted that the weather did not look so benign.[17] At 15:00, snow started to fall, and the light was diminishing.
Hall's Sirdar, Ang Dorje Sherpa, and other climbing Sherpas waited at the summit for the clients. Near 15:00, they began their descent. On the way down, Ang Dorje encountered client Doug Hansen above the Hillary Step and ordered him to descend. Hansen did not respond verbally, but shook his head and pointed upward, toward the summit.[18] When Hall arrived at the scene, the Sherpas offered to take Hansen to the summit, but Hall sent the Sherpas down to assist the other clients, and instructed them to stash oxygen canisters on the route. Hall said he would remain to help Hansen, who had run out of supplementary oxygen.[18]
Scott Fischer did not summit until 15:45. He was exhausted from the ascent and becoming increasingly ill, possibly suffering from HAPE, HACE, or a combination of both. Others, including Doug Hansen and Makalu Gau, reached the summit even later.[15]
Descent in a blizzard
[edit]Boukreev recorded that he reached Camp IV by 17:00. The reasons for Boukreev's decision to descend ahead of his clients are disputed.[19] Boukreev maintained that he wanted to be ready to assist struggling clients farther down the slope, and to retrieve hot tea and extra oxygen if necessary.[20] Krakauer sharply criticized Boukreev's decision not to use bottled oxygen while employed as a guide.[21] Boukreev's supporters, who include G. Weston DeWalt, co-author of The Climb (1997), state that using bottled oxygen gives a false sense of security.[22] Krakauer and his supporters point out that, without bottled oxygen, Boukreev was unable to directly help his clients descend,[23] and that Boukreev said that he was going down with client Martin Adams,[23] but later descended faster and left Adams behind.[23]
The worsening weather began causing difficulties for the descending team members. The blizzard on the southwest face of Everest was reducing visibility, burying the fixed ropes, and obliterating the trail back to Camp IV that the teams had broken on the ascent. Fischer, helped by Lopsang Jangbu Sherpa, was unable to descend below the Balcony (8,350 m or 27,400 ft) in the storm. Sherpas left Makalu Gau (at 8,230 m or 27,000 ft by Gau's account[24]) with Fischer and Lopsang when Gau, too, became unable to proceed. Eventually, Lopsang was persuaded by Fischer to descend and leave him and Gau.[15]
Hall radioed for help, saying that Hansen had fallen unconscious but was still alive. At 17:30, Adventure Consultants guide Andy Harris, carrying supplementary oxygen and water, began climbing alone from the South Summit (8,749 m or 28,704 ft) toward Hansen and Hall at the top of Hillary Step.[3] Krakauer's account notes that by this time, the weather had deteriorated into a full-scale blizzard: "Snow pellets borne on 70 mph [110 km/h] winds stung my face."[3] Boukreev gives 18:00 as "the onset of a blizzard".[16]
Several climbers got lost on the South Col during the storm. Mountain Madness guide Beidleman and clients Klev Schoening, Fox, Madsen, Pittman, and Gammelgaard, along with Adventure Consultant guide Mike Groom and clients Beck Weathers and Yasuko Namba wandered in the blizzard until they could no longer walk, huddling some 20 m (66 ft) from a drop-off of the Kangshung Face.[25]
Near midnight, the blizzard cleared sufficiently for the team to see Camp IV, some 200 m (660 ft) away. Beidleman, Groom, Schoening, and Gammelgaard set off to find help. Madsen and Fox remained on the mountain with the group in order to shout for the rescuers. Boukreev located the climbers and brought Pittman, Fox, and Madsen to safety. Boukreev had prioritized Pittman, Fox, and Madsen (all of whom were from his Mountain Madness expedition) over Namba (from the Adventure Consultants expedition), who seemed close to death; he did not see Weathers (also from the Adventure Consultants expedition). All of the climbers then at Camp IV were exhausted and unable to reach Namba and Weathers.[citation needed]
11 May
[edit]In the early morning of 11 May, at 04:43, Hall radioed Base Camp and said he was on the South Summit (8,749 m or 28,704 ft), confirming that he had survived the night. He reported that Harris had reached the two men, but Hansen, who had been with him since the previous afternoon, was now "gone", and Harris was missing. Hall was not breathing bottled oxygen because his regulator was too choked with ice.[3]
By 09:00, Hall had fixed his oxygen mask but indicated that his frostbitten hands and feet were making it difficult to traverse the fixed ropes. Later in the afternoon, he radioed Base Camp, asking them to call his pregnant wife, Jan Arnold, on the satellite phone. During this last communication, they chose a name for their unborn child, he reassured her that he was reasonably comfortable, and told her, "Sleep well, my sweetheart. Please don't worry too much."[26] Shortly thereafter, he froze to death in his sleep. His body was found on 23 May by Ed Viesturs and fellow mountaineers from the IMAX expedition, but was left there as requested by his wife, who said she thought he was "where he'd liked to have stayed".[27] They did, however, bring her back his wedding band. The bodies of Doug Hansen and Andy Harris have never been found. Viesturs stated in the IMAX film that upon finding Hall's body, he sat down and cried beside his friend.[28]
Meanwhile, Stuart Hutchison, a client on Hall's team who had turned around before the summit on 10 May, launched a second search for Weathers and Namba. He found both alive, but barely responsive and severely frostbitten, and in no condition to move. After consulting with Lopsang, he made the decision that they could not be saved by the hypoxic survivors at Camp IV nor evacuated in time; the other survivors soon agreed that leaving Weathers and Namba behind was the only choice.[29]
Later in the day, however, Weathers regained consciousness and walked alone under his own power to the camp, surprising everyone there, though he was still suffering severe hypothermia and frostbite. Despite receiving oxygen and attempts to rewarm him, Weathers was practically abandoned again the next morning, 12 May, after a storm had collapsed his tent overnight and the other survivors once again thought he had died. Krakauer discovered he was still conscious when the survivors in Camp IV prepared to evacuate. Despite his worsening condition, Weathers found he could still move mostly under his own power. A rescue team mobilized, hopeful of getting Weathers down the mountain alive. Over the next two days, Weathers was ushered down to Camp II with the assistance of eight healthy climbers from various expeditions, and was evacuated by a daring high-altitude helicopter rescue, one of the highest ever attempted. He survived and eventually recovered, but lost his nose, right hand, half his right forearm, and all the fingers on his left hand to frostbite.[30]
The climbing Sherpas located Fischer and Gau on 11 May, but Fischer's condition had deteriorated so much that they were only able to give palliative care before rescuing Gau. Boukreev made a subsequent rescue attempt but found Fischer's frozen body at around 19:00. Like Weathers, Gau was evacuated by helicopter.
Analysis
[edit]The disaster was caused by a combination of events, including:
- Ineffectiveness of leadership
- The expedition leaders did not realize that the blizzard, which hit in full force on May 11, would be preceded by increasing snow throughout the afternoon and evening hours of May 10.[31]
- A rivalry between Hall and Fischer, who were both incentivized to get their clients to the summit,[32] leading them to ignore the aforementioned forecasts[31]
- The unwillingness of the South African team's guide to help contact base camp while the other teams' radios were not sufficiently strong[32]
- Bottlenecks at the Balcony and Hillary Step, which caused an hour-and-a-half delay in summiting. These delays were in themselves caused by delays in securing fixed ropes and the sheer number of people arriving at the bottlenecks at the same time (34 climbers on 10 May).
- The team leaders' decisions to exceed the normal turnaround time of 14:00, with many summiting after 14:30.
- The sudden illness of two climbers at or near the summit after 15:00.
- Unexpectedly severe oxygen deprivation sickness compromising both climbers' and guides' ability to make decisions or help others.
- Insufficient stores of oxygen, forcing guides and rescue teams to carry bottles up to stranded climbers as the storm approached.[32]
Jon Krakauer has suggested that the use of bottled oxygen and commercial guides, who personally accompanied and took care of all pathmaking, equipment, and important decisions, allowed otherwise unqualified climbers to attempt to summit, thereby leading to dangerous situations and more deaths.[33] In addition, he wrote that the competition between Hall and Fischer's guiding companies may have led to Hall's decision not to turn back on 10 May after the summiting deadline of 14:00. Though it's not clear whether the guides would have been effective had they stuck to the deadline.
It's very difficult to turn someone around high on the mountain. If a client sees that the summit is close and they're dead-set on getting there, they're going to laugh in your face and keep going.[34]
— Guy Cotter
Krakauer also acknowledges that his own presence as a journalist for an important mountaineering magazine may have added pressure to guide clients to the summit despite the growing dangers.[35] He proposed banning bottled oxygen except for emergency cases, arguing that this would both decrease the growing litter on Everest—many discarded bottles have accumulated on its slopes—and keep marginally qualified climbers off the mountain. He does point out, however, that climbing Everest has always been a highly dangerous endeavor, even before the guided tours, with one fatality for every four climbers who reach the summit. Furthermore, he notes that many of the poor decisions made on 10 May came after two or more days of inadequate oxygen, nourishment, and rest (due to the effects of entering the death zone above 8,000 m or 26,000 ft).
In May 2004, Kent Moore, a physicist, and John L. Semple, a surgeon, both researchers from the University of Toronto, told New Scientist magazine that an analysis of the weather conditions on 11 May suggested that atmospheric oxygen levels fell by an additional 6% as a result of the storm, resulting in a further 14% reduction in oxygen uptake.[36][37]
Supplementary oxygen
[edit]Following the disaster, the use and non-use of supplementary oxygen was the focus of much discussion and analysis, with a guide and a sardar both criticized by Krakauer for not using supplementary oxygen while performing guide duties. This is in contrast with Krakauer’s views on only using bottled oxygen in emergencies stated above, and additionally both men gave detailed written explanations as to why they preferred not to use oxygen; both men did in fact carry a bottle on the summit day that could be used if needed in an emergency or extraordinary situation. In his book The Climb, Boukreev shared this explanation with Mark Bryant, the editor of Outside magazine:
Also, Mr. Krakauer raised a question about my climbing without oxygen and suggested that perhaps my effectiveness was compromised by that decision. In the history of my career, as I have detailed above, it has been my practice to climb without supplementary oxygen. In my experience, it is safer for me, once acclimatized, to climb without oxygen in order to avoid the sudden loss of acclimatization that occurs when supplementary oxygen supplies are depleted.
My particular physiology, my years of high-altitude climbing, my discipline, the commitment I make to proper acclimatization, and the knowledge I have of my own capacities have always made me comfortable with this choice. And, Scott Fischer was comfortable with that choice as well. He authorized me to climb without supplementary oxygen.
To this I would add: As a precautionary measure, in the event that some extraordinary demand was placed upon me on summit day, I was carrying one (1) bottle of supplementary oxygen, a mask, and a regulator.[38]
Radios
[edit]There were several issues and problems with radios and their use on summit day. Scott Fischer's sardar did not have a company-issued radio, but did have a "small yellow" radio that was owned by Sandy Pittman. Rob Hall's team also had an issue with a radio during a discussion over oxygen bottles that caused confusion.[32]
The 1996 season after this disaster
[edit]1996 is statistically curious as the fatality rates on Everest in the 1996 season were statistically lower than normal. The record number of 12 fatalities in the 1996 spring climbing season was 3% of the 398 climbers who had ascended above Base Camp—slightly below the historical average of 3.3% at that time. Additionally, a total of 84 climbers reached the summit that season, giving a fatality-to-summit ratio of 1 in 7—significantly less than the historical average of 1 in 4 prior to 1996. Accounting for the increased volume of climbers in 1996 compared with previous years, the fatality rates on Everest dropped considerably, meaning that 1996 was statistically a safer-than-average year.[39]
List of fatalities
[edit]| Name[40] | Nationality | Expedition | Location of death | Cause of death |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Andrew "Harold" Harris (Guide) | Adventure Consultants | near South Summit, 8,749 m | Unknown; presumed as falling during descent near summit | |
| Doug Hansen (Client) | ||||
| Rob Hall (Guide/Expedition leader) | Exposure | |||
| Yasuko Namba (Client) | South Col, c. 7,900 m | |||
| Scott Fischer (Guide/Expedition leader) | Mountain Madness | Southeast Ridge, 8,300 m | ||
| Subedar Tsewang Smanla | Indo-Tibetan Border Police | Northeast Ridge, 8,600 m | ||
| Lance Naik Dorje Morup | ||||
| Head Constable Tsewang Paljor |
Other fatalities in 1996
[edit]The following is a list of the other fatalities during the spring 1996 climbing season on Everest. These deaths were not directly related to the storm or the events of 10–11 May 1996 Everest disaster.
- 9 May – Chen Yu-Nan (陳玉男) – from the Taiwanese National Expedition, died after a fall down the Lhotse Face[41]
- 19 May – Reinhard Wlasich – Austrian climber, died from a combination of HAPE and HACE at 8,300 m (27,200 ft) on the Northeast Ridge[42]
- 25 May – Bruce Herrod – photojournalist with a South African team, was on the South Col during the 10–11 May storm and reached the summit two weeks later, but died descending the Southeast Ridge[12]
- 6 June – Ngawang Topche Sherpa – Nepali Sherpa for Mountain Madness, developed a severe case of HAPE on 22 April while working above Base Camp; died in June in a Kathmandu hospital[43]
The following fatalities occurred on Everest during the fall 1996 climbing season.[44][45]
- 25 September – Yves Bouchon – French climber, died in an avalanche at 7,800 m (25,600 ft) on the southeast route below Camp IV, along with the two Sherpas listed below
- 25 September – Lopsang Jangbu Sherpa – Nepalese Sherpa, the same climbing Sardar on the Mountain Madness expedition involved in the May 1996 Everest disaster; died in avalanche
- 25 September – Dawa Sherpa – Nepalese Sherpa; died in avalanche
In the epilogue to High Exposure, David Breashears describes encountering some of the bodies upon climbing Everest again in May 1997.[46]
In the media
[edit]- Into Thin Air: Death on Everest (released 9 November 1997) is a made-for-TV movie based on Jon Krakauer's book Into Thin Air: A Personal Account of the Mt. Everest Disaster (1997). The film, directed by Robert Markowitz and written by Robert J. Avrech, tells the story of the 1996 Mount Everest disaster.[47]
- The Climb is Anatoli Boukreev's account of the events that unfolded on the mountain. It is also in part a response to Krakauer's book.
- The IMAX film Everest (1998) also documents the disaster, and the involvement of that film's crew and climbing team in the rescue effort.[48]
- The Dark Side of Everest (2003), National Geographic Channel, discusses climbers' motivations, the ethics and challenges involved when climbers encounter trouble at high altitudes, and specific disasters, e.g. the 10–11 May 1996 Mount Everest disaster and Bruce Herrod's death on 25 May 1996.
- Remnants of Everest: The 1996 Tragedy (2007; released in the US as Storm over Everest and broadcast on the US PBS-TV series Frontline), is a documentary by director David Breashears[49]), with music composed by Jocelyn Pook.
- Seconds from Disaster - Into the Death Zone, 2012 TV documentary.[50]
- The events inspired the feature film Everest (2015).
- Joby Talbot's opera Everest, based on the events of the disaster, was produced by the Dallas Opera and premiered in 2015.[51]
- Beck Weathers' book Left for Dead: My Journey Home from Everest (2000).
- Lene Gammelgaard's book Climbing High: A Woman's Account of Surviving the Everest Tragedy (first published June 9, 1999).
See also
[edit]- List of 20th-century summiters of Mount Everest
- List of deaths on eight-thousanders
- List of media related to Mount Everest
- List of people who died climbing Mount Everest
References
[edit]- ^ "Mount Everest Nepal Earthquake". The New York Times. 28 April 2015.
- ^ Dahlburg, John-Thor (1996). "Climbing Veterans Call Everest Deaths Inevitable". Los Angeles Times.
- ^ a b c d e Krakauer 1997, p. 296
- ^ Boukreev, Anatoli; G. Weston Dewalt (1997). The Climb: Tragic Ambitions on Everest. New York: St. Martins. ISBN 978-0-312-96533-4.
- ^ Weathers, Beck; Stephen G. Michaud (2000). Left for Dead: My Journey Home from Everest. New York: Villard. ISBN 978-0-375-50404-4.
- ^ Gammelgard, Lene (2000). Climbing High: A Woman's Account of Surviving the Everest Tragedy. New York: Perennial. ISBN 978-0-330-39227-3.
- ^ a b Krakauer 1997, pp. xv–xvi
- ^ "Apa Sherpa Full Biography - Apa Sherpa Foundation". apasherpafoundation.org. Archived from the original on 17 October 2016. Retrieved 13 October 2016.
- ^ Boukreev; Dewalt p. 12
- ^ "David A. Sowles Memorial Award – American Alpine Club". americanalpineclub.org. Archived from the original on 27 September 2015. Retrieved 27 September 2015.
- ^ a b Krakauer 1997, pp. 108–114.
- ^ a b Krakauer 1997, p. 180
- ^ Conant, Jennet (22 September 2015). "The Real Story of Sandy Hill Pittman, Everest's Socialite Climber". Vanity Fair. Condé Nast. Retrieved 25 July 2021.
- ^ "U.S. climber, thought dead, rescued from Mount Everest". CNN. 13 May 1996. Retrieved 14 November 2015.
- ^ a b c "Lopsang Jangbu Sherpa's response to Krakauer's article". Outsideonline.com. Archived from the original on 19 September 2010. Retrieved 5 December 2010.
- ^ a b c "Anatoli Boukreev's response to Krakauer's article". Outsideonline.com. Retrieved 5 December 2010. [dead link]
- ^ Krakauer 1997, pp. 241–242.
- ^ a b Storm Over Everest.
Statement by Ang Dorje
- ^ "Salon Wanderlust | Coming down". Salon.com. 10 May 1996. Archived from the original on 23 April 1999. Retrieved 5 December 2010.
- ^ "Summit Journal '96: Scott Fischer Returns to Everest: Anatoli Boukreev response". outsideonline.com. Archived from the original on 30 May 2001. Retrieved 27 September 2015.
- ^ "Summit Journal '96: Scott Fischer Returns to Everest: Reply from Jon Krakauer". outsideonline.com. Archived from the original on 31 May 2001. Retrieved 27 September 2015.
- ^ GlaxoSmithKline: On top of the world – Acclimatisation Archived 25 May 2009 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b c Coming Down page 3 Archived 3 March 2000 at the Wayback Machine Dwight Garner, salon.com 1998 August
- ^ "Gau's account and pictures". Classic.mountainzone.com. Retrieved 5 December 2010.
- ^ Storm Over Everest. 1998.
- ^ "Explorers' Last Words and Technology: From Robert Falcon Scott to Rob Hall". Adventure. 29 March 2012. Archived from the original on 5 August 2021. Retrieved 5 August 2021.
- ^ "Bodies to come down in Everest clean-up". www.theaustralian.com.au. 22 April 2010. Retrieved 5 August 2021.
- ^ Krakauer 1997, p. 295.
- ^ Krakauer 1997, pp. 322–324
- ^ Krakauer 1997, pp. 342–344, 368
- ^ a b Ratcliffe, Graham (2011). A Day to Die for : 1996 : Everest's worst disaster : the untold true story. Edinburgh: Mainstream. p. 328. ISBN 9781845966386. OCLC 671466084.
- ^ a b c d Krakauer 1997
- ^ Krakauer 1997, pp. 355–8
- ^ Krakauer 1997, p. 238
- ^ Krakauer 1997, p. 354
- ^ "The Day the Sky Fell on Everest". New Scientist (2449): 15. 29 May 2004. Retrieved 11 December 2006.
- ^ Peplow, Mark (25 May 2004). "High Winds Suck Oxygen from Everest: Predicting Pressure Lows Could Protect Climbers". BioEd Online. Retrieved 11 December 2006.
Moore explains that these jet streaks can drag a huge draught of air up the side of the mountain, lowering the air pressure. He calculates that this typically reduces the partial pressure of oxygen in the air by about 6%, which translates to a 14% reduction in oxygen uptake for the climbers. Air at that altitude already contains only one third as much oxygen as sea-level air.
- ^ Boukreev, Anatoli; DeWalt, G. Weston (2002). The Climb: Tragic Ambitions on Everest. Pan Books. pp. 217, 218. ISBN 978-0-330-48896-9.
- ^ Krakauer 1997, p. 274
- ^ List of Everest Fatalities[usurped] AdventureStats.com
- ^ Krakauer 1997, p. 155
- ^ Krakauer 1997, p. 276
- ^ Krakauer 1997, pp. 108–114
- ^ "Video". CNN. 14 October 1996. Archived from the original on 28 June 2011. Retrieved 24 February 2011.
- ^ "Lopsang Jangbu Sherpa killed in Everest avalanche". Mountain Zone.
- ^ Breashears, David. "Epilogue". High Exposure. "Except for Scott's body, still wrapped with a pack and rope the way Anatoli had left him, the summit slopes were mercifully free of the tragedy. When we reached the South Summit, Rob had disappeared from sight, shrouded by a tall drift formed around his body. Andy Harris and Doug Hansen may lie near him, though we'll probably never know. [...] Near the base of the Hillary Step we found the last vestige of the 1996 disasters, the body of Bruce Herrod, the photojournalist who'd been with the South African team."
- ^ Jonathan Crow (2008). Into Thin Air: Death on Everest. Movies & TV Dept. Archived from the original on 13 October 2008.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help) - ^ Baumgarten, Marjorie (14 October 2014). "Everest". The Austin Chronicle. Retrieved 19 November 2014.
- ^ Frontline: Storm Over Everest. PBS. 2007. Archived from the original on 10 December 2015.
- ^ "Into the Death Zone". IMDb.
- ^ "REVIEW: Dallas Opera's stunning world premiere of 'Everest'". Archived from the original on 2 February 2017. Retrieved 27 January 2017.
Bibliography
[edit]- Krakauer, Jon (1997). Into Thin Air: A Personal Account of the Mount Everest Disaster. Doubleday. ISBN 978-0-385-49208-9.
- Ratcliffe, Graham (2013). A day to die for : 1996 : Everest's worst disaster : one survivor's personal journey to uncover the truth. Edinburgh. ISBN 978-1-78057-641-1.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link)
External links
[edit]- The Website for the 2008 PBS Frontline television show titled Storm Over Everest.
- PBS Frontline: 'Storm Over Everest' – washingtonpost.com
- Climber Recounts Tragedy in 'Storm Over Everest'
- Ken Kamler: Medical miracle on Everest – TEDMED Archived 24 February 2014 at the Wayback Machine
- PBS Storm over Everest : Roundtable : The Ethics of Climbing (with Peter Hackett, M.D.Lincoln Hall, James H. Moss, J.D., and Jim Williams)


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch

