Nigerien crisis (2023–2024)
| 2023–24 Nigerien crisis | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the aftermath of the 2023 Nigerien coup d'état | |||||||
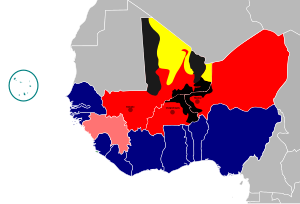 The political situation in ECOWAS as of 23 December 2023 Junta and Alliance of Sahel States Supports Nigerien coup diplomatically Opposes Nigerien coup diplomatically Opposes Nigerien coup militarily | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
| ||||||
| Supported by: | ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| | | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 30,000 soldiers[3] | Western estimate: ≥7,000 in ECOWAS standby force[4] | ||||||
On 26 July 2023, a coup d'état occurred in Niger, during which the country's presidential guard removed and detained president Mohamed Bazoum. Subsequently, General Abdourahamane Tchiani, the Commander of the Presidential Guard, proclaimed himself the leader of the country and established the National Council for the Safeguard of the Homeland, after confirming the success of the coup.[5][6][7][8]
In response to this development, the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) issued an ultimatum on 30 July, giving the coup leaders in Niger one week to reinstate Bazoum, with the threat of international sanctions and potential use of force.[9][10] When the deadline of the ultimatum expired on 6 August, no military intervention was initiated; however, on 10 August, ECOWAS took the step of activating its standby force.[11][12][13][14] Previously in 2017, ECOWAS had launched a military intervention to restore democracy in The Gambia during a constitutional crisis within the country.
All active member states of ECOWAS, except for Cape Verde, pledged to engage their armed forces in the event of an ECOWAS-led military intervention against the Nigerien junta.[15] Conversely, the military juntas in Burkina Faso and Mali announced they would send troops in support of the junta were such a military intervention launched while forming a mutual defense pact.[16][17]
On 24 February 2024, ECOWAS announced that it was lifting sanctions on Niger, purportedly for humanitarian purposes.[2]
Background
[edit]On 26 July 2023, President Mohamed Bazoum and his family were detained at the Presidential Palace in Niamey, and Interior Minister Hamadou Souley was also arrested. The coup was led by General Abdourahamane Tchiani, whom Bazoum had planned to relieve from his position.[18][19][20][21][22] In the evening, Air Force Colonel-Major Amadou Abdramane announced on state television that Bazoum had been removed from power and announced the formation of a National Council for the Safeguard of the Homeland, dissolution of the country's Constitution, the suspension of all state institutions, the closure of borders, and a nationwide curfew from 22:00 until 05:00 local time, while warning against any foreign intervention.[20][23][24] Subsequently, all activities by political parties in the country were ordered suspended until further notice.[25]
Despite his detention, Bazoum has so far refused to resign.[26] While declaring himself acting head of state and calling for resistance against the coup,[26] Bazoum's Foreign Minister Hassoumi Massaoudou told France 24 that the country's "legal and legitimate power" remained with the President.[27] However, the leadership of the Nigerien armed forces declared its support for the coup to protect the President and avoid "a deadly confrontation."[28]
On 28 July, Tchiani proclaimed himself as the president of the junta, saying that he had deposed Bazoum to avoid "the gradual and inevitable demise" of the country and accusing him of covering up the country's situation. Tchiani did not give a timeline for a return to civilian rule.[29][30][8]
ECOWAS
[edit]The Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) is a regional, political and economic union of fifteen countries in West Africa, covering an area of 5,114,162 km2 (1,974,589 sq mi) and with an estimated population of over 387 million in 2019. Established in 1975, ECOWAS aims to achieve collective self-sufficiency for its member states by creating a single large trade bloc.[31][32]
ECOWAS also serves as a peacekeeping force in the region, with member states occasionally sending joint military forces to intervene in the bloc's member countries at times of political instability and unrest. In recent years these included interventions in Sierra Leone in 1997, Ivory Coast in 2003, Liberia in 1990 and 2003, Guinea-Bissau in 1999 and 2012, Mali in 2013, and the Gambia in 2017.[33][34][35]
Security situation
[edit]The United States, France, and many other countries and groups have been involved in Niger because of the Islamist insurgency in the Sahel, which in turn triggered the Jihadist insurgency in Niger led by Al-Qaeda, the Islamic State group and Boko Haram.[36][37][38][39] The United States, France, and Turkey have had bases in the country. In 2022, it became a hub of French anti-terror operations after its departure from Mali and Burkina Faso following a series of military coups[40] and anti-French sentiment which paved the way for Russian influence and the entry of its private mercenary firm Wagner Group in the region.[41][failed verification] At the same time, it paved the way for Turkish influence in the region.[42][43][44]
Timeline
[edit]July
[edit]29 July
[edit]The military junta accused ECOWAS in a statement read by Abdramane on Télé Sahel of planning to approve "a plan of aggression against Niger through an imminent military intervention in Niamey supported by certain Western countries" and warned of the junta's "strong determination" to defend the country. They claimed that this was the objective of the ECOWAS summit convened for the following day.[45]
The African Union Peace and Security Council issued an ultimatum that if the soldiers did not "immediately and unconditionally return to their barracks and restore constitutional democracy, within a maximum of fifteen days" that the bloc would be compelled to take "necessary action, including punitive measures against perpetrators".[46]
Members of the United Nations Security Council strongly condemned the coup and expressed support for ECOWAS and the AU.[47]
30 July
[edit]ECOWAS ultimatum and sanctions
[edit]On 30 July, ECOWAS issued the Nigerien military junta with an ultimatum that Bazoum be reinstated as president within one week. In a communiqué read by ECOWAS Commission chairperson Omar Touray, at the Extraordinary Summit convened in Abuja, Nigeria in response to the coup, they said that if their demands were not met they would "take all measures necessary to restore constitutional order" in Niger and that "such measures may include the use of force".[48][49] The response from the bloc towards the junta drastically differed from the measures taken with recent coups in Mali, Burkina Faso, and Guinea which did not involve the threat of force for reinstating the overthrown government.[50]
ECOWAS also announced "immediate sanctions" on Niger, including the closure of land and air borders, imposition of a no-fly zone on all commercial flights to and from Niger and the suspension of all commercial and financial transactions between ECOWAS and Niger.[51] The assets of Niger state enterprises were frozen by the ECOWAS Central Bank, leading to the cancellation of a 30 billion CFA francs ($51 million) bond issuance.[52] ECOWAS also cut off more than 70% of Niger's electricity supply.[53]
Pro-coup demonstrations in Niamey
[edit]In a march at the request of Tchiani and organized by the M62 Movement, which had previously opposed Bazoum's government and Operation Barkhane and supported the Russian invasion of Ukraine, thousands of pro-coup Nigeriens gathered in Niamey's Place de la Concertation, in front of the National Assembly, and went to the French Embassy carrying Nigerien, Russian and North Korean flags, with slogans such as "Down with France, out with Barkhane, we don't care about ECOWAS, the European Union and the African Union!", "Arrest the former dignitaries to return the stolen millions.", and "Down with France, long live Putin!".[54][55][50][56] The demonstrators also called for an immediate intervention by the Wagner Group.[55] During the march, the entrances to the French and American embassies were closed.[54] The French embassy's walls and gates were set ablaze and damaged while Nigerien soldiers and General Salifou Modi were seen on the ground urging the crowds to disperse peacefully.[50] The crowd left after police fired volleys of tear gas in response.[51] Images showed people being loaded into ambulances with bloodied legs.[51]
In response to the attack on its embassy, the French government warned that attacks on its nationals, military personnel, diplomats and interests would lead to an immediate and intractable response.[57]
31 July
[edit]On the behest of ECOWAS, Chad's president Mahamat Déby met with Tchiani and Bazoum at the presidential palace in Niamey. The Chadian Presidency released pictures of the meeting, marking Bazoum's first appearance since the coup.[58] Meanwhile, Colonel Abdremane accused Hassoumi Massaoudou, still claiming to be acting leader substituting for Bazoum, of authorizing a French attack on the presidential palace to liberate Bazoum.[59] The French Foreign Ministry denied there were any such plans.[60]
Bazoum's oil minister Mahamane Sani Mahamadou (son of former president Mahamadou Issoufou), mining minister Ousseini Hadizatou and the head of the PNDS national executive committee, Foumakoye Gado were arrested by the military junta. This followed the arrests of Transport Minister Oumarou Malam Alma and former defense minister Kalla Moutari the previous week.[61][62]
The Central Bank of West African States (BCEAO) cancelled a planned 30 billion CFA franc ($51 million) bond issuance by Niger in the West African regional debt market.[63]
August
[edit]1 August
[edit]The military junta announced that it had reopened Niger's borders with Algeria, Burkina Faso, Mali, Libya, and Chad.[64]
2 August
[edit]Rolling blackouts were reported across cities in Niger, which the state electricity company Nigelec blamed on Nigeria cutting off supplies. While the Transmission Company of Nigeria declined to comment, an anonymous source told the BBC that the move followed a directive from President Bola Tinubu.[65] The World Bank suspended disbursements to Niger until further notice.[66]
Military chiefs of ECOWAS member states met in Abuja, to discuss the situation in Niger.[67] At the same time, a confidential military signal was picked up by Inside Nigeria, giving orders to the Nigerian military to name units for a military operation against Niger, mobilize the armed forces and establish a no-fly zone.[68] Hours later, Ivory Coast issued a statement in which it supported the ECOWAS sanctions and announced the country's participation in a preparation for a military intervention in Niger.[69]
A delegation of the Nigerien military junta headed by General Salifou Mody traveled to Bamako, Mali,[70] and then to Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso.[71] Speculation arose as to whether they went to ask for the support of the Wagner Group, which has a presence in Mali.[72]
In a televised address, Tchiani called the sanctions imposed on the country "cynical and iniquitous" and said they were intended to "humiliate" Niger's security forces and make the country "ungovernable". He insisted that his regime would not give in to such threats[73] and called on citizens to defend the country.[74]
3 August
[edit]ECOWAS sent another delegation to Niger to negotiate with the junta, this time led by former Nigerian military leader Abdulsalami Abubakar and also including the Sultan of Sokoto, Muhammadu Sa'ad Abubakar, and Omar Touray, president of the ECOWAS Commission.[75] Abdel-Fatau Musah, ECOWAS Commissioner for Political Affairs, Peace and Security said that "The military option is the very last option on the table, the last resort, but we have to prepare for the eventuality."[64] However, the delegates failed to meet with Tchiani and other junta members and left the same day.[76]
Another pro-coup demonstration was held in Niamey's Independence Square on the occasion of Niger's 63rd Independence Day.[77] This time, security forces blocked roads leading to the French and U.S. embassies to prevent attacks and vandalism.[78]
Senegal's foreign minister, Aïssata Tall Sall, and her counterpart in Benin, Shegun Adjadi Bakari, confirmed that their countries would participate in a military intervention in Niger if approved by ECOWAS.[79]
The military junta blocked France 24 and Radio France Internationale (RFI) in Niger, as had happened months before in Mali and Burkina Faso. France 24 was followed weekly by a quarter of the Nigerien population and RFI was the most followed international station in the country. France Médias Monde, the owner of both media networks, protested the decision.[80]
The junta also announced Niger's withdrawal from its military agreements with France, notably those allowing French troops to be stationed in the country and regulating the status of military personnel fighting Islamist jihad on Nigerien soil.[81] In a separate announcement, after peace talks failed, it ordered the withdrawal of Niger's ambassadors to France, Nigeria, Togo and the United States.[82][83] In response, France said that it took note of the junta's actions, but proceeded to remind them that the deals were signed between "legitimate" authorities.[84]
In an opinion piece published in The Washington Post, Bazoum, calling himself a "hostage", called on the United States and the international community to restore constitutional order in Niger, warning that the coup would have devastating domestic and international consequences.[85]
4 August
[edit]The junta lifted the curfew it imposed since 26 July.[86]
Tinubu requested the Senate of Nigeria to authorize an intervention in Niger. Images revealed that in recent days Nigerian troops had accumulated on the border with Niger.[87]
A former adviser to Bazoum told CNN that some 130 officials from his government had been arrested since the coup, while many others were in hiding.[88]
The United States announced that it was suspending "certain foreign assistance programmes benefitting the government of Niger" but clarified that it would not include humanitarian and food assistance, as well as diplomatic and security operations to protect U.S. personnel.[89]
Burkina Faso raised the alert level of its armed forces to "state of war".[citation needed]
Jihadists belonging to Islamic State attacked a convoy of Malian soldiers heading for Niger, leading to 20 casualties.[90]
5 August
[edit]Reports emerged that the junta, through General Salifou Mody, had formally asked for assistance from the Wagner Group during his visit to Mali.[91]
After meeting with Bazoum's Prime Minister Ouhoumoudou Mahamadou in Paris, French Foreign Minister Catherine Colonna announced the country's support for an ECOWAS intervention in Niger, without specifying whether it would provide military support.[92]
The Nigerian Senate rejected President Tinubu's request to authorize military intervention in Niger, instead urging him to resolve the crisis by more diplomatic means and to "tread with caution".[93] However, the Constitution of Nigeria still permits the President to deploy troops abroad without Senate approval if the President believes the national security is under "imminent threat or danger". A group of senators representing regions near or bordering Niger stated their opposition to military intervention.[94]
Chad announced that it would not participate in an ECOWAS-led military intervention against the junta.[95]
6 August
[edit]The one-week deadline for the military junta to hand power back to Bazoum or face military intervention expired without ECOWAS carrying out its threat.[17]
In Niamey, around 30,000 people joined a pro-junta demonstration at Stade Général Seyni Kountché that was also attended by junta member General Mohamed Toumba.[96]
Algerian president Abdelmadjid Tebboune expressed his opposition to any military intervention, stating that such actions could "ignite the whole Sahel region".[97]
The junta gave France 30 days to vacate Niger, in accordance with the 1977 Agreement of Technical Military Cooperation.[98]
The junta closed the country's airspace again, citing the threat of military intervention, with spokesman Colonel Abdremane claiming that there had been a pre-deployment of forces in two Central African countries, whom he did not identify.[99] It also accused a "foreign power" of preparing "an attack" on the country in coordination with ECOWAS.[100]
The Nigerien military began bringing in reinforcements to Niamey in anticipation of an invasion, with a convoy of about 40 pick-up trucks arriving at nightfall.[101]
7 August
[edit]Italian foreign minister Antonio Tajani called on ECOWAS to extend the ultimatum's deadline.[102]
Mali and Burkina Faso announced plans to send delegates to Niger to "express solidarity" with the junta.[103]
ECOWAS announced plans to hold a summit on 10 August to discuss their next steps in the situation in Niger.[104]
Acting U.S. deputy secretary of state Victoria Nuland met with junta member and military chief of staff General Moussa Salaou Barmou in Niamey for two hours to offer U.S. help to restore the constitutional government, but indicated that the junta did not accept the idea, adding that the conversations were "extremely frank and at times quite difficult". The junta also did not allow her to meet with Bazoum and described him as under "virtual house arrest".[105][106]
The junta appointed economist Ali Lamine Zeine as the new prime minister. Zeine had served as finance minister until 2010 and later worked at the African Development Bank.[107]
8 August
[edit]A joint delegation composed of officials from ECOWAS, the United Nations, and the AU attempted to hold talks with the junta, but were denied entry.[108] In response, Nigeria announced additional sanctions aimed at individuals involved in the coup through the Nigerian Central Bank.[109]
An unnamed Nigerian government official stated that Nigeria can provide more than half of the 25,000 troops for an invasion of Niger.[110]
U.S. Secretary of State Antony Blinken said Washington supported West African efforts to restore constitutional order in Niger. In a separate interview with the BBC, Blinken also said that while the United States did not believe the Nigerien coup was instigated by Russia or the Wagner Group, they had tried to take advantage of it, warning that adverse consequences would follow in the wake of the Wagner Group's entry.[111][112]
9 August
[edit]Blinken said that he had spoken to Bazoum, demanding his release from detention and expressing support for a "peaceful resolution" to the crisis in Niger.[113]
Rhissa Ag Boula, former leader of the Front for the Liberation of Aïr and Azaouak (FLAA) that participated in two rebellions by the Tuareg people in the 1990s and the 2000s accused the junta of orchestrating a "tragedy" and announced the formation of a Council of Resistance for the Republic (CRR), which aimed to topple the junta and restore Bazoum to office. He also said that it supported international intervention by ECOWAS and other actors in doing so. Another CRR member said several Nigerien political figures had joined the group but refused to come out publicly for safety reasons.[114]
The junta arrested the daughter of Niger's ambassador to France, Aïchatou Boulama Kané, who refused to leave her post after the junta ordered her dismissal.[115]
A statement from Bazoum's political party, PNDS-Tarayya said that he and his family had been without both electricity and running water for a week, and had only dried and canned foods left to eat.[116]
The foreign ministers of Mali and Burkina Faso issued a joint letter to the UN and the AU, calling for the UN Security Council and the AU Peace and Security Council to prevent any military action against Niger.[117]
The junta accused France of releasing 16 "terrorist elements" who later launched an attack on a unit of the National Guard in Bourkou Bourkou, 30 kilometres (19 mi) from the Samira Hill Gold Mine in the Tillabéri Region,[118] which killed five soldiers and injured four.[119] It also accused France of sending a military aircraft to violate Nigerien airspace as part of a broader plan to destabilise the country. The French Foreign Ministry denied the claims and the veracity of the attack, while insisting that the plane's entry were part of an earlier agreement with Nigerien forces.[118]
Sanusi Lamido Sanusi, former Emir of Kano and Governor of the Central Bank of Nigeria who is also a revered Sufi Islamic spiritual leader in the region, visited Niger and met with Tchiani. No details of their discussion were immediately available.[120]
Another meeting between the joint ECOWAS, UN and EU mission with the junta was postponed after the latter said it was not the right time to meet them.[121]
10 August
[edit]The junta declared a new government, naming 21 ministers led by Prime Minister Zeine in an announcement on state television by "secretary-general of the government" Mahamane Roufai Laouali. Three generals who were members of the CNSP were named to head the interior (Mohamed Toumba), defense (Salifou Mody) and sports ministries.[122][123]
ECOWAS summit
[edit]ECOWAS opened its second emergency meeting in Abuja regarding the situation in Niger, with Tinubu reiterating in his opening address that the bloc would assess solutions to the situation and called the coup a "threat" to West Africa. It was unclear if there were any representatives from Burkina Faso, Guinea or Niger. However, Mauritanian president Mohamed Ould Ghazouani, whose country left ECOWAS in 2000, and Burundian president Évariste Ndayishimiye also attended.[122] Following the summit, ECOWAS ordered the immediate activation of its standby military force with the purpose of restoring constitutional order in Niger.[11][12][13][14][124][125]
11 August
[edit]The junta threatened to kill Bazoum if ECOWAS were to launch an intervention.[126]
Thousands of junta supporters protested near a French military base on the outskirts of Niamey chanting anti-French slogans and waving Russian flags.[127]
In an interview with The Guardian, Bazoum's daughter said she had remained in near-daily phone contact with detained members of her family from Paris, and added that they had been losing weight under deteriorating health conditions.[128]
Ivorian president Alassane Ouattara said an intervention would take place as soon as possible.[129]
Blinken voiced support for ECOWAS without explicitly backing a military intervention. Blinken also reiterated that the United States would hold the junta accountable for the safety of Bazoum, his family, and other detained members of his government.[130]
Russia warned ECOWAS against military intervention, claiming that it would result in a "protracted confrontation" and destabilize the Sahel region.[131]
A Nigerian government source said the junta met with two envoys of President Tinubu in Niamey, but did not reveal the details of their discussion.[132]
ECOWAS suspended a key military meeting to inform the organization's leaders about "the best options" for activating and deploying the standby force citing "technical concerns."[133]
ECOWAS member state Cape Verde announced that it was against military intervention, saying that the country was unlikely to participate in such a campaign, and stressed that the block should seek a diplomatic resolution to the crisis.[134][135]
12 August
[edit]Niger's ambassador in Washington, Mamadou Kiari Liman-Tinguiri, called on the United States and other allies of Bazoum to stage a "rescue mission" to save his life, claiming that the junta was starving him to death.[136]
A junta delegation led by General Moussa Salaou Barmou met with Guinean military leader Mamady Doumbouya in Conakry, who reiterated his junta's solidarity with Niger's.[137]
Insa Garba Saidou, a local pro-junta activist from Niamey in direct contact with the military government, stated that the junta would not enter negotiations with ECOWAS unless it was recognized as the legitimate government of Niger.[138]
Another demonstration was held in Niamey by thousands of junta supporters against ECOWAS and foreign military intervention.[139]
The junta said that local religious leaders met with the military government seeking to mediate between it and ECOWAS.[140]
Burkina Faso suspended the Omega media group, a radio station owned and operated by former foreign minister Alpha Barry, for airing an "insulting" interview with Nigerien pro-Bazoum spokesman Ousmane Abdoul Moumouni, which criticized the junta and supported Bazoum's restoration. The government claimed the interview "clearly" campaigned for "violence and war against the sovereign people of Niger."[141] The suspension was lifted on 11 September.[142]
ECOWAS announced plans to send a delegation to Niamey to enter negotiations with the junta on the prospect of a peaceful restoration of Bazoum as president.[143]
Due to his deteriorating health, Bazoum was visited by a physician, who gave him and his family food.[144]
13 August
[edit]A Nigerian-sponsored delegation said the junta was open to diplomacy to resolve the standoff with ECOWAS.[145]
The junta announced that it would prosecute Bazoum for "high treason" and "undermining the country's security".[132][146][147]
14 August
[edit]The AU Peace and Security Council convened at its headquarters situated in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia with the purpose of receiving a comprehensive update regarding the unfolding events in Niger, along with the concerted endeavors undertaken to effectively address and manage the prevailing situation.[148]
The United States and United Nations expressed their concerns over the junta's intention to prosecute former President Bazoum. The U.S. said it believed that it would escalate tensions and hinder the chances of a peaceful resolution to the crisis.[149] UN spokesperson Stephane Dujarric said that the plans were "very worrying".[150][151] ECOWAS called it "provocational", stating that the junta contradicted their earlier willingness on negotiations and dialogue.[152]
Prime Minister Zeine characterized the sanctions imposed on the junta by ECOWAS as an "unfair challenge". Nonetheless, he conveyed optimism regarding the country's capacity to overcome these challenges.[153]
At least six soldiers, including their commanding officer, were killed in an ambush by "terrorists" on an army convoy near Sanam, Tillaberi Region. The army claimed it had "neutralized" ten of the attackers.[119]
An appeals court cancelled a nine-month prison sentence handed out to Abdoulaye Seydou, leader of the M62 Movement, regarding a case involving an army air strike on suspected jihadists in southern Niger.[154]
15 August
[edit]Prime minister Zeine visited Chad and met with President Mahamat Déby and prime minister Saleh Kebzabo.[155] Upon his return, Zeine announced that the junta "reiterated" its support for dialogue, but "insisted on the need for the country to be independent".[156]
In a phone call with the leader of the Malian junta, Assimi Goïta, Russian President Vladimir Putin reiterated his support for the use of "exclusively peaceful political and diplomatic means" to resolve the Niger crisis.[157]
Pentagon spokeswoman Sabrina Singh said that the situation in Niger "looks like an attempted coup", reflecting the United States’ continued refusal to call the events in Niger a coup d'état.[158]
Residents of Niamey began preparations for a voluntary mass recruitment of citizens over the age of 18 to assist the military in case of an invasion. Organizers said that the process will begin on 19 August, especially on the borders with Benin and Nigeria.[159]
Niger's defence ministry reported that armed groups launched an assault on an army detachment near Koutougou near the Malian and Burkina Faso border that killed at least 17 Nigerien soldiers and injured 20. The military claimed to have "neutralized" 100 militants.[160] ECOWAS condemned the attack and sent condolences to the affected families.[161]
Germany called on the junta to release Bazoum and restore constitutional order. The UN said it would send mediators to Niamey for peace talks.[162]
16 August
[edit]The junta recalled Niger's ambassador to Ivory Coast in response to Ouattara's declaration of support for armed intervention against the junta.[163]
Former Nigerien president Mahamadou Issoufou called for the release of Bazoum and his return to power during an interview with Jeune Afrique.[164]
17 August
[edit]ECOWAS military chiefs convened a two-day meeting in Accra, Ghana to discuss a possible military intervention against the junta. The bloc stated that all its active member states except for Cape Verde were ready to participate in the standby force to restore Bazoum.[165][166]
German Foreign Minister Annalena Baerbock called on the EU to impose sanctions on the junta after holding talks with Blinken, AU Commission Chairperson Moussa Faki Mahamat, and other stakeholders.[167]
U.S. Major General J. Marcus Hicks, former commander of Special Operations Command Africa, stated in an interview with CNN that the United States was looking for ways to maintain its military presence in Niger regardless of the government in charge, hence why the Pentagon and White House refrained from calling the actions in Niger a coup. Hicks added that the U.S. military intended to keep its military and drone bases in Niger should the junta prevail.[168]
In a meeting of major Roman Catholic bishops in West Africa, Togolese religious heads announced their opposition to a military intervention, and called on ECOWAS and the junta to enter into bilateral diplomatic talks. They raised concerns that an intervention would only destabilize the region, and called on the involved parties to "not add to the plight of the Nigerien people".[169]
18 August
[edit]The UN's human rights chief Volker Türk registered disagreement over plans by the junta to prosecute Bazoum,[170] saying that the charges against him had no "legal basis".[171]
The U.S. Air Forces Africa declared its readiness to evacuate American drone bases in Niger as the situation heightens.[172]
At the end of its military commanders' meeting in Accra, ECOWAS Commissioner for Political Affairs, Peace and Security Abdel-Fatau Musah said that the bloc had set a "D-day" for a possible military intervention against the junta but refused to disclose when. Nonetheless, the body maintained that it was still open to diplomatic means to resolve the crisis.[173]
Nigerian President Tinubu warned of "grave consequences" if Bazoum's health further deteriorates in detention.[174]
In response to fears for Bazoum's safety, Prime Minister Zeine said that "nothing will happen to him," arguing that "we do not have a tradition of violence in Niger."[175]
19 August
[edit]An ECOWAS delegation headed by Abdulsalami Abubakar arrived in Niamey for talks with the junta, joining with UN Special Representative for West Africa and the Sahel Leonardo Santos Simao, who arrived on 18 August. The group met with Tchiani and later Bazoum.[176] The results of the meeting varied, with an official saying that the roughly two-hour discussion with the junta yielded little results and another ECOWAS envoy saying that the meeting was productive and that peace was possible.[177][178][179]
Mali and Burkina Faso dispatched Super Tucano warplanes to Niger in a show of solidarity with the junta following ECOWAS's military meeting in Accra.[180]
The junta announced the formation of the Volunteers for the Defense of Niger (VDN), a civilian militia force to combat a potential military intervention by ECOWAS. Recruitment for volunteers was expected to commence on 26 August in Niamey.[181]
During an address on national television, Tchiani announced a three-year transition to civilian rule and said that the junta did not aim "to confiscate power", adding that a military intervention would "not be the walk in the park some people seem to think".[182] He also announced a 30-day period of "national dialogue" to draw up "concrete proposals" to lay the foundations of "a new constitutional life".[183]
Pro-junta supporters were forced to halt a census of people willing to volunteer for non-military roles in defence against ECOWAS intervention, saying they had been overwhelmed by the numbers who turned up.[184]
U.S. Ambassador Kathleen A. FitzGibbon arrived in Niger to assume her post and bolster efforts to help resolve the crisis.[185]
20 August
[edit]Several thousand people demonstrated in Niamey in support of the junta.[186]
Pope Francis expressed hope for a peaceful solution to the crisis in Niger.[187]
ECOWAS rejected the junta's three-year transition plan to civilian rule saying it would only accept a transfer of power in the shortest possible time.[188] It also said that plans for military intervention in Niger had been finalized and military forces were ready to move upon orders, while political leaders still favored diplomacy to solve the crisis.[189][190]
21 August
[edit]Turkish President Recep Tayyip Erdoğan said he opposed a military intervention in Niger.[191]
A convoy of around 300 supply trucks from Burkina Faso arrived in Niamey.[192]
ECOWAS once again told the junta to release Bazoum without preconditions and restore constitutional order without further delay. They also stated the outcome of ongoing informal discussions would determine whether ECOWAS would send another mediation mission to Niger.[193]
In Nigeria, protests erupted in Kano State over the proposed use of force to resolve the crisis.[194]
Algerian state radio reported that France requested to use its airspace for an operation in Niger, which the government declined, after which France asked Morocco for use of its airspace instead.[195] The French government subsequently denied making such requests.[195][196]
22 August
[edit]The African Union suspended Niger's membership in the bloc with immediate effect, while saying that it was reviewing ECOWAS’ action plan and calling on all of its member states and the international community to not undertake any action to legitimize the military government.[197]
23 August
[edit]Egypt insisted on dialogue to resolve the crisis in Niger.[198]
The junta recalled Niger's ambassadors to Nigeria, Togo, France, and the U.S., and announced that it would evict French and U.S. troops from Niger.[199]
The United Kingdom demanded the immediate release of Bazoum and announced its support for ECOWAS and diplomatic efforts to end the crisis.[200][201]
ECOWAS denied claims that it was being manipulated by external powers in its efforts to resolve the crisis.[202]
24 August
[edit]President Tinubu approved the return of the previous delegation of Islamic leaders to Niger for another round of negotiations with the junta. He also stated that he had been holding back ECOWAS and other unnamed forces from invading Niger and warned that he could not delay such intervention for too long.[203][204][205]
The junta officially authorized the armies of Burkina Faso and Mali to intervene in Niger "in the event of aggression."[206]
Algeria sent a high-ranking official to Niger for talks.[207][208]
French President Emmanuel Macron demanded the release of Bazoum and the restoration of democracy in Niger. He also defended French military operations in West Africa, namely Operation Serval and then Operation Barkhane, saying that Mali, Burkina Faso and Niger would no longer exist without them.[209]
25 August
[edit]ECOWAS Commission President Omar Touray clarified that the bloc had not declared war on the people of Niger nor unveiled plans to invade yet.[210]
The junta ordered French ambassador Sylvain Itté to leave the country within 48 hours. However, France insisted that the junta had no authority to do so.[211][212]
26 August
[edit]The junta placed the Nigerien armed forces in a state of maximum alert in anticipation of a possible invasion, while another pro-junta rally was held in Niamey during which protesters threatened to storm French military bases and the French Embassy if Ambassador Itté did not leave the country in 48 hours.[213][214]
During a meeting with U.S. special envoy Molly Phee, Tinubu said that war with Niger was not ideal but also stated that he would not allow anyone to falsely buy time and ECOWAS was ready for all options. Tinubu also accepted an invitation from President Joe Biden to meet on the sidelines of the United Nations General Assembly in September for discussions about the crisis and possible military intervention.[215][216][217]
27 August
[edit]Protests occurred near the French military base in Niamey, demanding the withdrawal of the French military and using anti-ECOWAS slogans.[218] Pro-junta demonstrations also occurred in Maradi and Tillabéri Regions, as well as in neighboring Benin and Burkina Faso.[219]
ECOWAS delegation head Abdulsalami Abubakar said the junta ruled out returning Bazoum to office.[220]
28 August
[edit]President Macron announced he was keeping Sylvain Itté as ambassador to Niger despite the ultimatum for the latter's departure issued by the junta, whom Macron referred to as "illegitimate authorities".[221]
29 August
[edit]In a visit to West African countries, Algerian Foreign Minister Ahmed Attaf unveiled a proposal to resolve the crisis in Niger, calling for a half-year transitional phase to allow the country to restore "the constitutional and democratic order", which would involve the formulation of "political arrangements with the acceptance of all parties in Niger" and the supervision of the process by a "civilian power led by a consensus figure".[222]
30 August
[edit]Burkina Faso's cabinet authorized the government to deploy a military contingent to Niger.[223]
31 August
[edit]The junta ordered police to remove Ambassador Itté and revoked his diplomatic immunity and also the visas of his family members.[224] Following the announcement, more security forces were deployed around the French embassy and at Itté's residence, while two vehicles exiting the embassy were stopped by the authorities, who arrested their drivers.[225]
The junta also temporarily banned UN agencies and non-governmental organizations from operating in areas it designated as military "operation zones", citing the security situation.[226]
President Tinubu proposed that the junta shorten its transition to civilian rule to nine months, while he warned that sanctions against the junta by ECOWAS would remain until the regime made "positive adjustments".[227]
September
[edit]1 September
[edit]The M62 Movement organized a three-day sit-in outside the French military garrison in Niamey to demand that its troops leave.[225] The demonstration on 2 September was the biggest of its kind since the coup, drawing tens of thousands of participants.[228]
4 September
[edit]The junta reopened Niger's airspace to commercial flights more than a month after the coup, but retained the ban on all operational military flights and others requiring prior authorisation from relevant authorities.[229]
5 September
[edit]Prime Minister Zeine said Niger was still expectant of a swift French military pullout out of the country.[230] Sources from the French government later told reporters that talks were underway with the junta for a "partial withdrawal" of French soldiers in Niger.[231]
The EU accused the junta of obstructing the visit of its ambassador to Niger, Salvador Pinto da Franca, on the French embassy.[232]
7 September
[edit]Reuters, citing a military official, reported that the U.S. military had begun removing non-essential personnel from Niger and transferring some of its troops and equipment from its base near Niamey to Agadez in coordination with the Nigerien military as a precaution.[233]
8 September
[edit]Stephane Jullien, a French businessman who had represented the interests of French expatriates in the embassy in Niamey, was arrested by Nigerien authorities. The French Foreign Ministry announced his release on 14 September.[234]
9 September
[edit]The junta accused France of deploying soldiers and equipment to ECOWAS member states, particularly in Senegal, Ivory Coast and Benin, as part of a planned "aggression" against Niger in conjunction with the regional bloc.[235]
12 September
[edit]The junta denounced a military cooperation agreement made by Bazoum's government with Benin in 2022, citing its support for ECOWAS intervention and other acts of "aggression" against Niger.[236]
Former prime minister Hama Amadou, a political rival of Bazoum, returned to Niger after spending two years in exile in France.[237]
13 September
[edit]The U.S. military resumed regular operations in Niger after a month-long hiatus caused by the coup.[238]
14 September
[edit]France banned all cultural venues getting French government subsidies from having any cooperation with artists from Mali, Niger and Burkina Faso. Places like French national theaters, drama and choreography centers were among those affected by the ban. The Artistic and Cultural Enterprises union's vice-president Bruno Lobé criticized the government's decision, calling it a "real catastrophe" for artists and "France's image".[239] French Culture Minister Rima Abdul Malak said such measure was out of "security concerns" following coups in those countries, and insisted it was only made because of practical reasons since no visa could be issued in those nations amid ongoing conflicts.[240][241]
15 September
[edit]The junta cancelled more than 990 diplomatic passports issued to officials of Bazoum's government, other affiliated citizens and about 50 foreign nationals.[242]
President Macron accused the junta of blocking food deliveries to the French embassy in Niamey and virtually holding ambassador Sylvain Itte and his staff "hostage", adding that Itte had been reduced to living off "military rations".[243]
16 September
[edit]Niger, Mali, and Burkina Faso signed a security pact with one another, the Alliance of Sahel States, pledging to support each other against "rebellion or external aggression". The charter of the pact states that "[a]ny attack on the sovereignty and territorial integrity of one or more contracted parties will be considered an aggression against the other parties".[244]
18 September
[edit]Deposed president Bazoum, through his lawyer Seydou Diagne, filed a lawsuit contesting his detention by the junta at the ECOWAS Court of Justice in Abuja and demanding his release.[245]
22 September
[edit]The junta accused United Nations Secretary-General António Guterres of obstructing Niger's participation in the 78th United Nations General Assembly in New York City after the body deferred a decision on whether to recognize the junta's foreign minister, Bakary Yaou Sangaré, as the country's representative in the event following a counterclaim by the Bazoum government.[246]
23 September
[edit]The junta banned all French commercial and charter flights, including those operated by Air France, which said it was "not flying over Nigerien airspace" already.[247][248]
24 September
[edit]President Macron announced that France was pulling its troops from Niger before the end of 2023. He also announced that ambassador Sylvain Itté and other diplomatic staff in the country were to be recalled.[249][250] In response, the junta called for a "negotiated framework" to be established with France to coordinate the withdrawal of its soldiers.[251]
27 September
[edit]The French presidency confirmed that its ambassador in Niger, Sylvain Itté, was flown out of the country following the junta's expulsion order against him.[252]
28 September
[edit]A military unit was "attacked by several hundred terrorists" in Kandadji in the Tillaberri region, killing seven soldiers. Reinforcements subsequently got involved in a traffic accident along the way, killing five more soldiers. Seven others were wounded in the incident.[253]
October
[edit]2 October
[edit]The Algerian Foreign Ministry announced that the junta had agreed to a mediation process hosted by Algeria and a six-month transition plan towards the restoration of civilian rule in Niger.[254]
29 Nigerien soldiers were killed and two soldiers were seriously wounded in a suspected jihadist attack northwest of Tabatol near the Malian border. Authorities claimed that "several dozen terrorists" were also killed.[255]
5 October
[edit]The French military announced that it would begin withdrawing its forces from Niger in coordination with local authorities.[256]
6 October
[edit]The United States announced that it was preparing to officially designate the military takeover in Niger as a coup d'état.[257]
9 October
[edit]Algeria suspended its mediation with the Nigerien junta following an inconclusive meeting between Algerian Foreign Minister Ahmed Attaf and his counterpart in Niamey and Prime Minister Zeine's criticism of Algeria's being "manipulative" over the mediation.[258]
10 October
[edit]The first French soldiers left Niger in an overland convoy under local escort in the direction of Chad. The United States formally recognized the events in Niger as a coup d'état and withdrew about $500 million in economic aid.[259]
The junta ordered the departure of Louise Aubin, head of the UN diplomatic mission in Niger, within 72 hours, with the Foreign Ministry accusing the UN of using "obstacles" to prevent the country from participating in the UN General Assembly in September.[260]
15 October
[edit]Six soldiers and 31 "terrorists" were killed in military operations in the Lemdou area in the Tillaberi region near the border with Burkina Faso that lasted until the next day. 18 soldiers were also injured.[261]
19 October
[edit]The junta claimed it had thwarted an escape attempt by Bazoum and his party by helicopter to Nigeria.[262] Bazoum's lawyers called the report "fabricated" and said that he was being held incommunicado.[263]
The first French troops withdrawn from Niger arrived in Chad.[264]
27 October
[edit]French state-owned outlet RFI reported that ECOWAS was now quietly demobilizing its forces and quoted a diplomat from a member state as saying "no one is opting for military intervention anymore."[265]
30 October
[edit]US President Joe Biden announced that he would exclude Niger, along with three other African countries, from the African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA) trade program, citing inability to establish or make consistent progress in safeguarding political pluralism and the rule of law.[266]
November
[edit]6 November
[edit]The junta formally asked Togo to mediate in its negotiations with the international community, particularly with ECOWAS following talks between defence minister Salifou Modi and Togolese President Faure Gnassingbé in Lomé.[267]
13 November
[edit]Prime Minister Zeine met with Saudi officials in Medina, seeking to normalize relations with the Arab and Islamic world.[268]
15 November
[edit]The junta announced the arrest of Abdou Rafa, the Nigerien national director for the Central Bank of West African States, in an attempt to pressure the bank to unfreeze Nigerien assets that were frozen during the coup.[269]
17 November
[edit]Tchiani, in his first public appearance since the coup in July, inaugurated an anti-corruption commission and a state court that replaced the dissolved court of cassation and state council.[270]
22 November
[edit]The junta filed an appeal to the ECOWAS Court of Justice to order the lifting of sanctions imposed on Niger by other ECOWAS member-states, citing its effects on the country's economy.[271]
23 November
[edit]Tchiani went to Mali as part of his first international trip since the coup, meeting with military leader Assimi Goïta and Burkinabe military leader Ibrahim Traoré in Bamako.[272][273]
25 November
[edit]The junta announced that it had revoked a 2015 law which the government, then working with the European Union, enacted to stop the movement of Europe-bound migrants through its territory, adding that all convictions under the law, which targeted people smugglers, would be cancelled.[274]
26 November
[edit]The Nigerien electricity company Nigelec commissioned a 30-megawatt photovoltaic plant to compensate for electricity shortages brought about by sanctions imposed after the coup. The plant's initial commissioning on 25 August was delayed after "most of the technical staff" left due to the coup.[275]
December
[edit]2 December
[edit]Niger, along with Burkina Faso, announced that they would withdraw from the G5 Sahel, stating that the alliance was failing to reach its objectives.[276]
3 December
[edit]A delegation from Russia led by deputy defense minister Yunus-bek Yevkurov arrived in Niger to meet with Tchiani and defense minister Salifou Mody, with additional meetings held the following day to discuss military and defense issues.[277]
4 December
[edit]The Nigerien foreign ministry said the government had decided to "withdraw the privileges and immunities granted" under the EU Military Partnership Mission in Niger launched in February 2023 as well as from the EU Civilian Capacity-Building Mission established in 2012 to strengthen Niger's internal security sector.[277]
8 December
[edit]Tchiani met with Togolese President Faure Gnassingbé during a visit to Lomé to strengthen relations between the two countries. Both leaders "reaffirmed the will to strengthen bilateral cooperation", and a Togolese embassy in Niamey was announced to be opened.[278]
14 December
[edit]Speaker of the ECOWAS parliament Sidie Tunis said the organization would lift its sanctions on Niger in exchange for Bazoum's release.[279]
15 December
[edit]The ECOWAS Court of Justice ordered the release and reinstatement of Bazoum as president of Niger.[280]
22 December
[edit]France announced that it would be closing its embassy in Niger, saying that it was "no longer able to function normally or fulfil its missions" due to restrictions imposed by the junta. This came as the last French troops left Niger after being ordered out by the country's military leaders.[281]
27 December
[edit]Benin lifted its ban on imported goods transiting to Niger through the port of Cotonou that had been imposed as part of ECOWAS sanctions against the junta in July.[282]
January 2024
[edit]1 January
[edit]Prime Minister Zeine opened regional consultations in Agadez with members of the government, the junta and traditional and religious leaders as part of the beginning of an "inclusive national" dialogue to address the post-coup political situation, including the transition to civilian rule.[283]
2 January
[edit]The French embassy in Niamey was officially closed until further notice, with its operations moved to Paris.[284]
8 January
[edit]Bazoum's son Salem was ordered released from detention in the presidential palace by a military tribunal in Niamey, and was reported to have gone to Togo that evening.[285]
28 January
[edit]Niger, along with Mali and Burkina Faso, announced their withdrawal from ECOWAS, accusing it of abandoning "the ideals of its founding fathers and pan-Africanism" under foreign influence and imposing "inhumane" sanctions to overthrow their military regimes.[286]
February 2024
[edit]24 February
[edit]ECOWAS announced that it was immediately lifting sanctions against Niger on humanitarian grounds and as part of an effort to foster dialogue and persuade the junta-led nations to reverse their decision to leave ECOWAS.[2][287]
March 2024
[edit]13 March
[edit]Nigeria reopened its border with Niger.[288]
16 March
[edit]Niger revoked a military accord with the United States which allowed US military personnel to operate on its soil.[289] The announcement came after a visit by US Assistant Secretary of State for African Affairs Molly Phee and commander of United States Africa Command General Michael Langley. In 2023 there were about 1,100 US troops in Niger, operating from two bases, including Niger Air Base 201 built near Agadez to fly drones at a cost of over $100 million.[290]
21 March
[edit]Twenty-three soldiers were killed and 17 others were injured in an ambush by militants between Teguey and Bankilare in Tillabéri Region. The Nigerien defence ministry said 30 of the attackers were also "neutralised".[291]
April 2024
[edit]11 April
[edit]Russian military advisers arrived in Niger to train the Nigerien military.[292][293]
13 April
[edit]Demonstrations were held in Niamey demanding the withdrawal of US forces.[294]
19 April
[edit]The US Department of State stated that the US had agreed to withdraw its forces from Niger following meeting between Prime Minister Zeine and officials in Washington DC.[295][296] However a week later, Vice Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, Admiral Christopher Grady, said that negotiations were still underway and that no final decision had yet been reached on the status of US forces there.[297]
May 2024
[edit]19 May
[edit]The governments of Niger and the United States announced that they had reached an agreement to withdraw US troops from the country. The announcement stated that the US military would complete its withdrawal by 15 September 2024.[298]
June 2024
[edit]10 June
[edit]The US began withdrawing its military forces from Niger.[299]
14 June
[edit]Bazoum's legal immunity as president was lifted by the State Court of Niger.[300]
20 June
[edit]The junta rescinded the operating licence of the French nuclear energy firm Orano for its uranium mine in Imouraren.[301]
25 June
[edit]The junta announced that 21 soldiers were killed in an ambush by an unspecified "terrorist group" near the border with Burkina Faso.[302]
July 2024
[edit]7 July
[edit]US troops completed their withdrawal from Air Base 101, located in Niamey.[303]
August 2024
[edit]5 August
[edit]The US officially returned Air Base 201 in Agadez to Nigerien control.[304]
September 2024
[edit]16 September
[edit]The US Military announced that they had completed their withdrawal from Niger.[305]
Evacuation of foreign nationals
[edit]On 1 August, the French foreign ministry announced that it was preparing to evacuate its citizens and that of other European nationals starting that day, citing the unrest in Niamey, the attack on its embassy, and the closure of Niger's airspace.[306]
The Spanish Defense Ministry said it would evacuate more than 70 Spanish nationals in Niger by air.[307] A Romanian citizen was among the evacuees taken by Spain.[308]
On 2 August, the first evacuation flights were carried out, with an Italian military plane landing in Rome with 87 evacuees[309] and 262 evacuees arriving on a French evacuation flight in Paris.[310] In total, up to 2,000 people were evacuated by France.[311][312][313] Among the French evacuees were four Romanian citizens.[314]
The U.S. State Department ordered the evacuation of non-emergency government personnel and eligible family members from its embassy, which would remain open for "limited, emergency services to U.S. citizens."[315] The United Kingdom also ordered a reduction of staff at its embassy.[316]
In response to the evacuations, the M62 Movement called for a peaceful blockade of Niamey International Airport until "foreign military forces left the country".[317]
Misinformation
[edit]False claims have been shared online exacerbating tensions brought about by the crisis.[318][319][320][321]
- Several social media users claimed that Wagner Group forces were deployed to Niamey through a video of a Russian Air Force Ilyushin Il-76 landing in Niamey International Airport. Fact-checkers from the BBC later identified this video as footage from 2006 recorded in Khartoum, Sudan.[318] Old video footage of Wagner Group mercenaries in Africa and Ukraine have also been used to falsely claim that the group was in Niger.[318] Likewise, false claims were also made about French fighter jets landing in Senegal to support an ECOWAS intervention and Burkinabe troops arriving in Niger to defend the junta.[321]
- False claims started circulating that the Nigerien junta ordered the military to detain European nationals. It was claimed that this was done to persuade Western nations to pull their military troops out of Niger. The claim appears to be based on a demand made by the anti-French and pro-junta M62 movement for the hostage-taking of European citizens until foreign forces withdraw. However, the group does not speak for the junta, as junta leader Tchiani stated that French nationals "have never been the object of the slightest threat" and had nothing to fear.[318][322]
- False claims posted online suggested that the junta had "with immediate effect, banned the export of uranium to France". There is no evidence that the junta had done so.[318][320][323] A similar claim was made that Burkina Faso and Mali were also banning the export of uranium, despite neither country having any active uranium mines. Additionally, false claims that Niger, Mali and Burkina Faso were banning all gold exports were widely circulated.[324]
- There have been claims made about Algeria, speculating that it would back the junta in the event of a foreign invasion, according to "Algerian news outlets". Although Algeria has stated that it opposes military action, it has not explicitly stated that should such action be taken, it would support the junta.[318] Although Algerian President Abdelmadjid Tebboune officially condemned the coup, he has also condemned military action against the junta and offered to mediate with it and stated that an intervention would likely be a repeat of the situation in Libya.[325][326]
- Amateur footage of a large pro-Bazoum rally in Niamey dated 6 August turned out to have been filmed on the day of Bazoum's removal on 26 July.[321]
- Video purportedly showing Bazoum's finance minister in tears after being threatened by the junta with execution over missing funds turned out to be taken from 2021 showing former Justice Minister Marou Amadou expressing his gratitude to former President Mahamadou Issoufou.[321]
- Reports of the junta ordering the expulsion of German ambassador Oliver Schnakenberg, U.S. ambassador Kathleen FitzGibbon and Nigerian ambassador Mohamed Usman were dismissed as false by the Nigerien Foreign Ministry.[327]
Identified sources
[edit]Prior to the coup, Bazoum had accused the Wagner Group of sponsoring "disinformation campaigns" against him and his government. Other sources identifying with the junta include the Pan-African Group for Trade and Investment (GPCI), which is a media firm founded by pro-Russian Burkinabè businessman Harouna Douamba, and the pan-Africanist TV channel Afrique Media based in Cameroon, which falsely reported Bazoum's resignation on 9 August and has a partnership with the Russian state-controlled media outlet RT.[321]
Impact
[edit]At least 4.3 million people in Niger are in need of aid including access to food, medicine, and basic goods. According to the United Nations, the figure is likely to rise as international sanctions come into effect. Airspace closure by the junta also complicates efforts to bring humanitarian aid into the country.[328][329] By 1 September it was reported that 7,300 tons of food aid was blocked from entering the country due to sanctions while food prices increased by an estimated 21 percent.[330] Niger's food exports, particularly that of onions, have also been affected by sanctions, with prices in neighboring recipient countries such as Ghana doubling as a result of blockages.[331]
Citing the effects of the sanctions, the junta announced a 40% reduction in Niger's projected 2023 budget from 3,291 billion CFA francs to 1,981 billion CFA francs.[332] On 14 November, the West African monetary union debt management agency UMOA reported that since the coup, Niger has missed debt payments totaling 187.136 billion CFA francs ($304 million).[333][334]
See also
[edit]- Benin–Niger Crisis
- Coup Belt
- 2020 Malian coup d'état
- 2021 Malian coup d'état
- 2021 Guinean coup d'état
- January 2022 Burkina Faso coup d'état
- September 2022 Burkina Faso coup d'état
- 2023 Nigerien coup d'état
- 2023 Gabonese coup d'état
Notes
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "Russian troops arrive in Niger as military agreement begins". 12 April 2024 – via www.bbc.com.
- ^ a b c "West Africa bloc lifts coup sanctions on Niger in a new push for dialogue to resolve tensions". AP News. 24 February 2024. Retrieved 24 February 2024. Cite error: The named reference "auto" was defined multiple times with different content (see the help page).
- ^ "Coup d'État au Niger : 57 000 soldats chez les putschistes, la France refuse d'intervenir… quelles sont les forces en présence?". Midi Libre (in French). 6 August 2023. Archived from the original on 7 August 2023. Retrieved 6 August 2023.
- ^ "Tensions rise as West African nations prepare to send troops to restore democracy in Niger". Associated Press. 12 August 2023. Archived from the original on 13 August 2023. Retrieved 14 August 2023.
- ^ "Niger : ce que l'on sait de la tentative de coup d'Etat en cours contre le président Mohamed Bazoum" [Niger: what we know about the ongoing coup attempt against President Mohamed Bazoum]. Franceinfo (in French). 26 July 2023. Archived from the original on 26 July 2023. Retrieved 26 July 2023.
- ^ Peter, Laurence (26 July 2023). "Niger soldiers declare coup on national TV". BBC. Archived from the original on 27 July 2023. Retrieved 28 July 2023.
- ^ "Niger's president 'held by guards' in apparent coup attempt". Al Jazeera. Archived from the original on 27 July 2023. Retrieved 28 July 2023.
- ^ a b "Niger general Tchiani named head of transitional government after coup". Al Jazeera. 28 July 2023. Archived from the original on 28 July 2023. Retrieved 28 July 2023.
- ^ Hairsine, Kate (3 August 2023). "Niger: How might an ECOWAS military intervention unfold?". Deutsche Welle. Archived from the original on 4 August 2023. Retrieved 4 August 2023.
- ^ Asadu, Chinedu (1 August 2023). "What would West African bloc's threat to use force to restore democracy in Niger look like?". AP News. Retrieved 16 December 2024.
- ^ a b "ECOWAS says 'no option taken off table' as emergency summit on Niger closes". France 24. 10 August 2023. Archived from the original on 10 August 2023. Retrieved 10 August 2023.
- ^ a b "Breaking: ECOWAS orders immediate standby force against Niger junta". Vanguard News. 10 August 2023. Archived from the original on 10 August 2023. Retrieved 10 August 2023.
- ^ a b "[Video] ECOWAS deploys standby force to restore constitutional order in Niger". Vanguard News. 10 August 2023. Archived from the original on 10 August 2023. Retrieved 10 August 2023.
- ^ a b "ECOWAS leaders say all options open in Niger, including 'use of force'". Al Jazeera. 10 August 2023. Archived from the original on 10 August 2023. Retrieved 10 August 2023.
- ^ "Most of West Africa ready to join standby force in Niger: ECOWAS". Al Jazeera. Archived from the original on 17 August 2023. Retrieved 18 August 2023.
- ^ "Mali, Burkina Faso, sends delegation to Niger in solidarity". Africanews. 8 August 2023. Archived from the original on 9 August 2023. Retrieved 8 August 2023.
- ^ a b Lawal, Shola (6 August 2023). "Niger coup: Divisions as ECOWAS military threat fails to play out". Al Jazeera. Archived from the original on 7 August 2023. Retrieved 8 August 2023.
- ^ "Au Niger, l'armée affirme avoir renversé Mohamed Bazoum – Jeune Afrique". JeuneAfrique.com (in French). 27 July 2023. Archived from the original on 27 July 2023. Retrieved 4 August 2023.
- ^ Aksar, Moussa; Balima, Boureima (28 July 2023). "Niger soldiers say President Bazoum's government has been removed". Reuters. Archived from the original on 26 July 2023. Retrieved 4 August 2023.
- ^ a b Madowo, Sarah; Dean, Niamh; Kennedy, Larry (26 July 2023). "Niger soldiers claim power after president's own guards reportedly seize him". CNN. Archived from the original on 4 August 2023. Retrieved 4 August 2023.
- ^ "Niger's president 'held by guards' in apparent coup attempt". Al Jazeera. Archived from the original on 27 July 2023. Retrieved 4 August 2023.
- ^ "Niger army general declares himself country's new leader". gulfnews.com. 29 July 2023. Archived from the original on 29 July 2023. Retrieved 4 August 2023.
- ^ Pilling, David (27 July 2023). "Niger soldiers go on television to announce coup in west African nation". Financial Times. Archived from the original on 26 July 2023. Retrieved 4 August 2023.
- ^ "Niger coup attempt: President Mohamed Bazoum held". BBC. 26 July 2023. Archived from the original on 26 July 2023. Retrieved 4 August 2023.
- ^ "Niger army pledges allegiance to coup makers". Al Jazeera. 27 July 2023. Archived from the original on 27 July 2023. Retrieved 27 July 2023.
- ^ a b Peter, Laurence (27 July 2023). "Niger soldiers announce coup on national TV". BBC. Archived from the original on 27 July 2023. Retrieved 27 July 2023.
- ^ "Detained Niger president defiant after coup bid". France 24. 27 July 2023. Archived from the original on 26 July 2023. Retrieved 27 July 2023.
- ^ "Niger's army command declares support for military coup". France 24. 27 July 2023. Archived from the original on 27 July 2023. Retrieved 27 July 2023.
- ^ "Niger's General Abdourahamane Tchiani declared new leader following coup". France 24. 28 July 2023. Archived from the original on 29 July 2023. Retrieved 28 July 2023.
- ^ Moloney, Marita; Issoufou, Tchima Illa (28 July 2023). "Niger coup: Abdourahmane Tchiani declares himself leader". BBC. Archived from the original on 28 July 2023. Retrieved 28 July 2023.
- ^ Yansane, Aguibou (1977). "The State of Economic Integration in North West Africa South of the Sahara: The Emergence of the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS)". African Studies Review. 20 (2): 63–87. doi:10.2307/523653. ISSN 0002-0206. JSTOR 523653. Archived from the original on 7 August 2023. Retrieved 4 August 2023.
- ^ Limited, Daniel Inaju-Challydoff. "Basic information". Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 4 August 2023.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help) - ^ "The 5 previous West African military interventions". 28 November 2020. Archived from the original on 28 November 2020. Retrieved 4 August 2023.
- ^ "Factbox: Military interventions by West African ECOWAS bloc". Reuters. 4 August 2023. Archived from the original on 23 August 2023. Retrieved 24 August 2023.
- ^ "Timeline: A history of ECOWAS military interventions in three decades". Al Jazeera. Archived from the original on 7 August 2023. Retrieved 24 August 2023.
- ^ "Violent Extremism in the Sahel". Global Conflict Tracker. Archived from the original on 5 August 2023. Retrieved 5 August 2023.
- ^ "Niger and Boko Haram: Beyond Counter-insurgency". Crisis Group. 27 February 2017. Archived from the original on 5 August 2023. Retrieved 5 August 2023.
- ^ Leali, Giorgio (4 August 2023). "Niger junta revokes military pacts with France". POLITICO. Archived from the original on 4 August 2023. Retrieved 5 August 2023.
- ^ "Terrorism: France's International Action". France Diplomacy – Ministry for Europe and Foreign Affairs. Archived from the original on 5 August 2023. Retrieved 5 August 2023.
- ^ "French army officially ends operations in Burkina Faso". France 24. 20 February 2023. Archived from the original on 20 February 2023. Retrieved 5 August 2023 – via facebook.com/FRANCE24.English.
- ^ Guiffard, Jonathan (1 November 2023). "Anti-french Sentiment in West Africa – A Reflection of the Authoritarian Confrontation With the "Collective West"". Institut Montaigne. Archived from the original on 4 August 2023. Retrieved 5 August 2023.
- ^ "Mali's junta gets warplanes, drones from Russia, Turkey". al-Arabiya. 16 March 2023. Archived from the original on 17 March 2023. Retrieved 11 August 2023.
- ^ Orakçi, Serhat (9 January 2022). "The Rise of Turkey in Africa". Al Jazeera. Archived from the original on 20 August 2023. Retrieved 11 August 2023.
- ^ Jeng, Amat; Jaw, Sait Matty (9 August 2023). "Niger's Coup is a Deja Vu, and Will Not be the Last". the Standard Newspaper. Archived from the original on 17 August 2023. Retrieved 17 August 2023.
- ^ "Sábado, 29 de julio de 2023 (22.00 GMT) NÍGER GOLPE La junta nigerina afirma que la Cedeao quiere aprobar una "intervención militar" en Níger" [Saturday, July 29, 2023 (2200 GMT) NIGER COUP The Niger junta claims that ECOWAS wants to approve a "military intervention" in Niger]. La Vanguardia (in Spanish). 29 July 2023. Archived from the original on 30 July 2023. Retrieved 29 July 2023.
- ^ Meilhan, Pierre; Goillandeau, Martin; Berlinger, Joshua (29 July 2023). "France and EU cut off financial support to Niger following military coup". CNN. Archived from the original on 30 July 2023. Retrieved 30 July 2023.
- ^ "Niger: Security Council strongly condemns 'efforts to unconstitutionally change' Government". news.un.org. 29 July 2023. Archived from the original on 5 August 2023. Retrieved 25 August 2023.
- ^ Our Foreign Staff (30 July 2023). "Thousands of pro-Russia protesters march through Niger capital in support of coup". The Telegraph. ISSN 0307-1235. Archived from the original on 30 July 2023. Retrieved 30 July 2023.
- ^ Balima, Boureima; Onuah, Felix (30 July 2023). "West Africa bloc threatens force on Niger coup leaders, French Embassy attacked". Reuters. Archived from the original on 30 July 2023. Retrieved 30 July 2023.
- ^ a b c Mednick, Sam (30 July 2023). "French embassy in Niger is attacked as protesters waving Russian flags march through capital". AP News. Archived from the original on 30 July 2023. Retrieved 30 July 2023.
- ^ a b c Balima, Boureima; Onuah, Felix (31 July 2023). "West Africa threatens force on Niger coup leaders, French embassy attacked". Reuters. Archived from the original on 1 August 2023. Retrieved 1 August 2023.
- ^ Coulibaly, Loucoumane; Felix, Bate (31 July 2023). Cawthorne, Andrew; Humphries, Conor (eds.). "Niger's planned $51 million bond issuance cancelled due to sanctions". Reuters. Archived from the original on 1 August 2023. Retrieved 1 August 2023.
- ^ "What's ahead for a 50-year-old West African bloc after 3 junta-led countries left the group?". ABC News. Retrieved 6 February 2025.
- ^ a b "Miles de personas participan en Niamey en una marcha en apoyo al golpe de Estado" [Thousands of people participate in a march in Niamey in support of the coup]. infobae (in European Spanish). 30 July 2023. Archived from the original on 30 July 2023. Retrieved 30 July 2023.
- ^ a b "Miles de nigerinos salen a las calles de Niamey para defender a los golpistas entre gritos a favor de Rusia" [Thousands of Nigeriens take to the streets of Niamey to defend the coup plotters amid chants for Russia]. LA NACION (in Spanish). 30 July 2023. Archived from the original on 30 July 2023. Retrieved 30 July 2023.
- ^ Shakkour, Sally (28 August 2023). "Niger protester rebuked for raising North Korean flag". Al-Bawaba. Archived from the original on 25 September 2023. Retrieved 25 September 2023.
- ^ "France warns will retaliate if its interests attacked in Niger". Agence France-Presse. Archived from the original on 30 July 2023. Retrieved 30 July 2023 – via Ahram Online.
- ^ Chothia, Farouk (31 July 2023). "Niger coup: Ousted President Mohamed Bazoum meets Chad's leader". BBC. Archived from the original on 31 July 2023. Retrieved 1 August 2023.
- ^ "Niger coup makers say ousted govt 'authorised French attack to free Bazoum'". Al Jazeera. 31 July 2023. Archived from the original on 31 July 2023. Retrieved 31 July 2023.
- ^ Chrisafis, Angelique; Holmes, Oliver (31 July 2023). "Niger coup leaders accuse France of plotting military intervention". The Guardian. Archived from the original on 31 July 2023. Retrieved 31 July 2023.
- ^ "Niger Republic Junta Arrests Top Politicians, Ministers As US, Germany, Others Impose Sanctions". Sahara Reporters. Archived from the original on 1 August 2023. Retrieved 1 August 2023.
- ^ Balima, Boureima; Mazou, Abdel-Kader (1 August 2023). "Niger arrests politicians after coup, other juntas voice support". Reuters. Archived from the original on 31 July 2023. Retrieved 1 August 2023.
- ^ "West African central bank cancels Niger $51m bond issuance due to sanctions". Al Jazeera. 27 July 2023. Archived from the original on 31 July 2023. Retrieved 27 July 2023.
- ^ a b Eboh, Camillus (2 August 2023). "Niger reopens borders with several neighbours a week after coup". Reuters. Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- ^ Issoufou, Tchima Illa; Gregory, James (2 August 2023). "Niger power blackouts blamed on coup sanctions". BBC. Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- ^ "Niger coup leader defiant as Nigeria cuts power, ECOWAS threatens force". Al Jazeera. 3 August 2023. Archived from the original on 3 August 2023. Retrieved 3 August 2023.
- ^ Sunday, Ochogwu (2 August 2023). "West African military chiefs meet in Abuja over Niger coup". Daily Post Nigeria. Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- ^ afolabi (2 August 2023). "Coup: Tinubu orders Nigerian Army to ready troops for Niger Republic invasion". NEWS PICKS – WITHIN NIGERIA. Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- ^ Descifrando la Guerra [@descifraguerra] (2 August 2023). "El portavoz de la presidencia de Costa de Marfil ha emitido un comunicado condenando el golpe en Níger" [The spokesman for the Ivorian presidency has issued a statement condemning the coup in Niger] (Tweet) (in Spanish). Retrieved 3 August 2023 – via Twitter.
- ^ "Niger junta delegation arrives in Mali's Bamako". Al-Arabiya. 2 August 2023. Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- ^ "Niger : un haut responsable du CNSP à Bamako". APAnews – Agence de Presse Africaine (in French). 2 August 2023. Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 2 August 2023.
- ^ John, Tara; Madowo, Larry; Gretener, Jessie (2 August 2023). "A Niger coup leader meets Wagner-allied junta in Mali". CNN. Retrieved 16 December 2024.
- ^ Cooney, Christy (3 August 2023). "Niger: US announces partial evacuation of embassy". BBC. Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 3 August 2023.
- ^ Mednick, Sam (2 August 2023). "Niger: Niger's military ruler warns against foreign meddling, urges population to defend the country". ABC. Archived from the original on 2 August 2023. Retrieved 3 August 2023.
- ^ Okafor, Chimaka (2 August 2023). "Niger Coup: ECOWAS name Abdulsalami, Sultan of Sokoto as envoys to Niger". Premium Times Nigeria. Archived from the original on 3 August 2023. Retrieved 3 August 2023.
- ^ "Niger: ECOWAS team leaves without meeting coup leader". DW. 4 August 2023. Archived from the original on 4 August 2023. Retrieved 4 August 2023.
- ^ "Pro-coup protests continue in Niger as Biden urges Bazoum release". Al Jazeera. 2 August 2023. Archived from the original on 3 August 2023. Retrieved 3 August 2023.
- ^ Tasamba, James (3 August 2023). "Thousands of pro-coup supporters gather in Niamey to demand withdrawal of French troops from Niger". Anadolu Ajansı. Archived from the original on 3 August 2023. Retrieved 3 August 2023.
- ^ "Senegal Says Its Troops Will Join Any ECOWAS Intervention In Niger". Barrons. Retrieved 16 December 2024.
- ^ "RFI et France 24 s'indignent de la suspension de leur diffusion au Niger". France 24 (in French). 3 August 2023. Archived from the original on 3 August 2023. Retrieved 3 August 2023.
- ^ "Coup d'État au Niger: les putschistes dénoncent des accords militaires conclus avec la France". BFMTV (in French). Archived from the original on 3 August 2023. Retrieved 4 August 2023.
- ^ "Coup d'État: les putschistes retirent les ambassadeurs du Niger en France et dans trois autres pays". BFMTV (in French). Archived from the original on 3 August 2023. Retrieved 4 August 2023.
- ^ Ugwu, Francis (4 August 2023). "Peace talk fails as Niger Republic cuts ties with Nigeria". Daily Post Nigeria. Archived from the original on 4 August 2023. Retrieved 4 August 2023.
- ^ "France: Deals revoked by Niger military were signed with 'legitimate' gov't". Al Jazeera. 4 August 2023. Archived from the original on 4 August 2023. Retrieved 4 August 2023.
- ^ "Former Niger president calls for international action to restore constitutional order". al-Arabiya. 4 August 2023. Archived from the original on 4 August 2023. Retrieved 3 August 2023.
- ^ "Niger junta lifts curfew in place since coup". Al-Ahram. 4 August 2023. Archived from the original on 4 August 2023. Retrieved 4 August 2023.
- ^ "Tinubu Writes Senate, Seeks Support for Military Intervention in Niger". Nigeria Info, Let's Talk!. Archived from the original on 4 August 2023. Retrieved 4 August 2023.
- ^ Hauser, Jennifer; Conte, Michael; Lau, Chris (4 August 2023). "Niger's ousted president warns of 'devastating' coup impact, growing Russian influence". CNN. Archived from the original on 4 August 2023. Retrieved 4 August 2023.
- ^ "US pauses some foreign aid to Niger as it reiterates support for Bazoum". Al Jazeera. 5 August 2023. Archived from the original on 5 August 2023. Retrieved 5 August 2023.
- ^ "Mali: soldiers killed in a jihadist ambush near Niger". Africanews. 4 August 2023. Archived from the original on 5 August 2023. Retrieved 6 August 2023.
- ^ "Niger's military rulers ask for help from Russian group Wagner". Al Jazeera. 5 August 2023. Archived from the original on 5 August 2023. Retrieved 5 August 2023.
- ^ "France supports ECOWAS intervention in Niger, foreign minister says". France 24. 5 August 2023. Archived from the original on 5 August 2023. Retrieved 5 August 2023.
- ^ Umoru, Henry (5 August 2023). "Niger coup: Senate rejects military action, cautions ECOWAS, Tinubu". Vanguard. Archived from the original on 5 August 2023. Retrieved 5 August 2023.
- ^ Malplat, Camille; Abubakar, Aminu (5 August 2023). "Opposition Mounts In Nigeria Over Possible Niger Intervention". Barron's. Archived from the original on 5 August 2023.
- ^ "Chad will not intervene in Niger coup, defense minister says". Reuters. 5 August 2023. Archived from the original on 17 December 2024.
- ^ "Thousands in Niger rally in support of coup leaders". Al Jazeera. 6 August 2023. Archived from the original on 7 August 2023. Retrieved 7 August 2023.
- ^ Abd-Alaziz, Moaz (5 August 2023). Gregorio, David (ed.). "Algeria opposes military intervention in Niger, Ennahar TV reports". Reuters. Archived from the original on 6 August 2023. Retrieved 6 August 2023.
- ^ Ogochukwu, Isioma (6 August 2023). "Niger Coup Leaders give France 30 Days to Vacate the Country". Metro Watch. Archived from the original on 6 August 2023. Retrieved 8 August 2023.
- ^ "Niger closes airspace as ECOWAS deadline for coup reversal expires". Al Jazeera. 6 August 2023. Archived from the original on 7 August 2023. Retrieved 7 August 2023.
- ^ "Niger coup leaders accuse "foreign power" of preparing to attack". EFE Noticias. 7 August 2023. Retrieved 17 December 2024.
- ^ Saley, Omar; Goillandeau, Martin; Berlinger, Joshua (7 August 2023). "Niger military deploys reinforcements to capital after ignoring deadline to cede power". CNN. Archived from the original on 8 August 2023. Retrieved 8 August 2023.
- ^ "Italy calls on West African states (ECOWAS) to extend Niger ultimatum". Reuters. 7 August 2023. Archived from the original on 7 August 2023. Retrieved 8 August 2023.
- ^ Armstrong, Kathryn; Orjinmo, Nduke (7 August 2023). "Niger coup: Junta shuts airspace citing military intervention threat". BBC. Archived from the original on 7 August 2023. Retrieved 7 August 2023.
- ^ Mazou, Abdel-Kader; Balima, Boureima (7 August 2023). "West African leaders to meet on Niger after junta defies deadline". Reuters. Archived from the original on 7 August 2023. Retrieved 8 August 2023.
- ^ Armstrong, Kathryn; Orjinmo, Nduka (8 August 2023). "Niger coup: US envoy holds 'difficult' talks with junta". BBC. Archived from the original on 8 August 2023. Retrieved 8 August 2023.
- ^ Mednick, Sam; Knickmeyer, Ellen (7 August 2023). "Niger coup leaders refuse to let senior US diplomat meet with nation's president". AP News. Archived from the original on 7 August 2023. Retrieved 8 August 2023.
- ^ "Ali Mahaman Lamine Zeine: Putschisten in Niger benennen Ministerpräsidenten – WELT". DIE WELT (in German). Agence France-Presse. 8 August 2023. Archived from the original on 8 August 2023. Retrieved 8 August 2023.
- ^ "[Exclusif] Au Niger, la junte refuse de recevoir la mission de la Cedeao – Jeune Afrique". JeuneAfrique.com (in French). 8 August 2023. Archived from the original on 8 August 2023. Retrieved 8 August 2023.
- ^ Balima, Boureima; Mazou, Abdel-Kader (8 August 2023). "Niger hit with more sanctions as junta rebuffs latest diplomatic mission". Reuters. Archived from the original on 8 August 2023. Retrieved 9 August 2023.
- ^ "AU, UN, ECOWAS delegation head to Niger for talks — Reports". Vanguard. 8 August 2023. Archived from the original on 10 August 2023. Retrieved 8 August 2023.
- ^ Online, Peace FM. "Niger Coup: Wagner Taking Advantage Of Instability – Antony Blinken". Peacefmonline.com – Ghana news. Archived from the original on 9 August 2023. Retrieved 9 August 2023.
- ^ Adeoye, Aanu; Schwartz, Felicia (8 August 2023). "Blinken backs West African efforts to restore Niger's constitutional order". Financial Times. Archived from the original on 8 August 2023. Retrieved 8 August 2023.
- ^ "Blinken reiterates calls for release of Niger President Bazoum". Reuters. 9 August 2023. Archived from the original on 9 August 2023. Retrieved 9 August 2023.
- ^ "Former Niger rebel launches anti-coup movement as impasse continues". Al Jazeera. 9 August 2023. Archived from the original on 9 August 2023. Retrieved 9 August 2023.
- ^ La Cam, Morgane (12 August 2023). "Niger: Concerns over fate of overthrown president and his family". Le Monde. Archived from the original on 12 August 2023. Retrieved 14 August 2023.
- ^ Mednick, Sam (9 August 2023). "Niger's ousted president is said to be running low on food under house arrest, 2 weeks after coup". AP News. Retrieved 17 December 2024.
- ^ Ugwu, Francis (9 August 2023). "Niger's junta refuses entry to negotiators, as Mali, Burkina Faso write UN". Daily Post Nigeria. Archived from the original on 10 August 2023. Retrieved 9 August 2023.
- ^ a b "Niger coup leaders accuse French forces of destabilising the country". Al Jazeera. 9 August 2023. Archived from the original on 9 August 2023. Retrieved 9 August 2023.
- ^ a b "Niger: at least 6 soldiers and 10 "terrorists" killed in the west". Africanews. 14 August 2023. Archived from the original on 17 August 2023. Retrieved 20 August 2023.
- ^ "Niger: Former Nigerian emir of Kano meets the putschists". Africa News. 10 August 2023. Archived from the original on 10 August 2023. Retrieved 10 August 2023.
- ^ Melly, Paul (10 August 2023). "Niger's coup leader General Tchiani: The ex-UN peacekeeper who seized power". BBC. Archived from the original on 10 August 2023. Retrieved 10 August 2023.
- ^ a b "Niger military names 21-person cabinet ahead of key West African summit". Al Jazeera. Archived from the original on 10 August 2023. Retrieved 10 August 2023.
- ^ "Niger: coup military regime forms government". africanews. 10 August 2023. Archived from the original on 14 August 2023. Retrieved 20 August 2023.
- ^ "ECOWAS approves military intervention in Niger". Al Arabiya English. 11 August 2023. Archived from the original on 11 August 2023. Retrieved 11 August 2023.
- ^ Madowo, Larry; Goillandeau, Martin; Tanno, Sophie; Liakos, Chris (10 August 2023). "ECOWAS calls for deployment 'to restore constitutional order' in Niger". CNN. Retrieved 17 December 2024.
- ^ Aworinde, Oluwatobi (11 August 2023). "Niger's junta threatens to kill detained president Mohamed Bazoum if ECOWAS interferes by force". channelstv. Archived from the original on 11 August 2023. Retrieved 11 August 2023.
- ^ Tasamba, James; Kola, Olanrewaju (11 August 2023). "Thousands protest in support of coup leader near French military base in Niger". Anadolu Ajansi. Archived from the original on 12 August 2023. Retrieved 12 August 2023.
- ^ Salih, Zeinab Mohammed (11 August 2023). "Niger's captive leader losing weight in inhumane conditions, daughter says". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Archived from the original on 11 August 2023. Retrieved 11 August 2023.
- ^ "ECOWAS military intervention could explode into 'regional conflict' & 'push Niger closer to Russia'". France 24. 11 August 2023. Archived from the original on 11 August 2023. Retrieved 11 August 2023.
- ^ Ibitoye, Jide (11 August 2023). "Blinken Says US Backs ECOWAS Efforts On Niger". Voice of Nigeria. Archived from the original on 11 August 2023. Retrieved 11 August 2023.
- ^ Seddon, Sean (11 August 2023). "Niger coup: Russia warns Ecowas not to take military action". BBC. Archived from the original on 11 August 2023. Retrieved 12 August 2023.
- ^ a b Nedelec, Camille; Jammine, Jean-Emile (4 August 2023). "Eye on Africa - ECOWAS meeting in Abuja draws to a close as the unfolding crisis in Niger shows no signs of abating". France 24. Retrieved 17 December 2024.
- ^ "Niger coup: West African countries suspend key military meeting on 'standby' force". The Guardian. Agence France-Presse. 12 August 2023. Archived from the original on 12 August 2023. Retrieved 12 August 2023.
- ^ Onuah, Felix (12 August 2023). "West Africa in another bid to engage with Niger coup leaders". Reuters. Archived from the original on 15 August 2023. Retrieved 16 August 2023.
- ^ "9:36pm: Cape Verde president says he opposes military intervention in Niger". France 24. 10 August 2023. Archived from the original on 15 August 2023. Retrieved 16 August 2023.
- ^ Knickmeyer, Ellen; Brown, Tracy (12 August 2023). "Allies of Niger president overthrown by military are appealing to the US and others: Save his life". Associated Press. Archived from the original on 12 August 2023. Retrieved 12 August 2023.
- ^ "Nigerian delegation says Niger military leaders open to diplomacy". Aljazeera. Archived from the original on 13 August 2023. Retrieved 13 August 2023.
- ^ Mednick, Sam (12 August 2023). "An activist tied to Niger's junta says its leaders won't hold talks until the region recognizes them". AP News. Retrieved 17 December 2024.
- ^ Bittermann, Jim (12 August 2023). "Supporters of Niger's coup protest against regional bloc that wants return to democracy". CNN. Archived from the original on 12 August 2023. Retrieved 12 August 2023.
- ^ "Nigerian Delegation Meets With Niger's Junta as Military Intervention Looms". Voice of America. 12 August 2023. Retrieved 17 December 2024.
- ^ "Burkina Faso Junta Suspends Radio Station Over Niger Criticism". Voice of America. Agence France-Presse. 11 August 2023. Archived from the original on 12 August 2023. Retrieved 12 August 2023.
- ^ "Burkina junta lifts radio station's suspension over Niger coup criticism". Africanews. 12 September 2023. Archived from the original on 17 September 2023. Retrieved 12 September 2023.
- ^ Onuah, Felix; McAllister, Edward (12 August 2023). "West Africa's ECOWAS parliament in new bid to engage with Niger coup leaders". Reuters. Archived from the original on 12 August 2023. Retrieved 12 August 2023.
- ^ Habib, Gift (12 August 2023). "Ousted Niger President Bazoum visited by his doctor". The Punch. Archived from the original on 12 August 2023. Retrieved 12 August 2023.
- ^ Onuah, Felix; Samb, Sali (13 August 2023). "Nigerian delegation says Niger junta is open to diplomacy". Reuters. Archived from the original on 13 August 2023. Retrieved 13 August 2023.
- ^ "Niger's junta will prosecute President Bazoum for 'high treason'". 13 August 2023. Retrieved 17 December 2024.
- ^ Adeoye, Aanu (14 August 2023). "Niger junta threatens treason charge against ousted president Mohamed Bazoum". Financial Times. Archived from the original on 28 September 2023. Retrieved 14 August 2023.
- ^ "African Union holds talks on Niger crisis amid diplomatic deadlock". RFI. 14 August 2023. Retrieved 17 December 2024.
- ^ Ochieng, Beverly; Chothia, Farouk (14 August 2023). "Niger coup: Ousted President Bazoum to be charged with high treason, junta says". BBC. Retrieved 17 December 2024.
- ^ "US, UN express worry over Niger junta plan to charge President Bazoum with treason". Al Arabiya English. 14 August 2023. Archived from the original on 14 August 2023. Retrieved 14 August 2023.
- ^ Nova, Redazione Agenzia (14 August 2023). "Niger, the US warns the coup leaders: "Dismayed by the threat of legal action against Bazoum"". Agenzia Nova. Archived from the original on 14 August 2023. Retrieved 14 August 2023.
- ^ "ECOWAS Accuses Niger Junta of Provocation". Arise News. 14 August 2023. Archived from the original on 15 August 2023. Retrieved 15 August 2023.
- ^ "Niger will overcome ECOWAS sanctions, says new prime minister". Peoples Gazette. 14 August 2023. Archived from the original on 14 August 2023. Retrieved 14 August 2023.
- ^ "Niger scraps jail sentence for head of group supporting military". africanews. 14 August 2023. Archived from the original on 16 August 2023. Retrieved 15 August 2023.
- ^ "🔴 Live: Chad president welcomes Niger's junta-appointed prime minister". France 24. 15 August 2023. Archived from the original on 15 August 2023. Retrieved 15 August 2023.
- ^ Onuah, Felix. "Niger junta says open to talks as Putin, US stress peace". Reuters. Archived from the original on 15 August 2023. Retrieved 15 August 2023.
- ^ Gretener, Jessie; Pavlova, Uliana; Mendonca, Duarte (15 August 2023). "Putin stresses need for 'peaceful resolution' in Niger coup in call with Mali leader". CNN. Archived from the original on 15 August 2023. Retrieved 15 August 2023.
- ^ Singh, Sabrina. "Pentagon: Situation in Niger "Looks Like An Attempted Coup"". C-SPAN. Archived from the original on 15 August 2023. Retrieved 15 August 2023.
- ^ Mednick, Sam (16 August 2023). "Nigeriens call for mass recruitment of volunteers as the junta faces possible regional invasion". AP NEWS. Archived from the original on 16 August 2023. Retrieved 16 August 2023.
- ^ "More than a dozen Niger soldiers killed in attack near Mali border". aljazeera.com. Archived from the original on 16 August 2023. Retrieved 16 August 2023.
- ^ Habib, Gift (16 August 2023). "ECOWAS condemns killings of soldiers in Niger Republic". Punch Newspapers. Archived from the original on 16 August 2023. Retrieved 16 August 2023.
- ^ "Tinubu: We're Working Not to Compound Niger's Crisis – THISDAYLIVE". thisdaylive.com. Archived from the original on 20 August 2023. Retrieved 17 August 2023.
- ^ Egenuka, Ngozi (16 August 2023). "Niger: Junta recalls Ivorian envoy over president's backing of military intervention". The Guardian Nigeria. Archived from the original on 16 August 2023. Retrieved 16 August 2023.
- ^ "Mahamadou Issoufou : " Je demande la libération du président Bazoum et son retour au pouvoir "". Jeune Afrique (in French). 17 August 2023. Archived from the original on 22 August 2023. Retrieved 21 August 2023.
- ^ "Most of West Africa ready to join standby force in Niger: ECOWAS". aljazeera.com. Archived from the original on 17 August 2023. Retrieved 17 August 2023.
- ^ "Liberia: Liberia Likely to Contribute Soldiers for Niger's Intervention". liberianobserver.com. Archived from the original on 18 August 2023. Retrieved 19 August 2023.
- ^ "Germany backs EU sanctions against Niger military junta – foreign ministry". Reuters. 17 August 2023. Archived from the original on 17 August 2023. Retrieved 17 August 2023.
- ^ Bertrand, Natasha; Liebermann, Oren (17 August 2023). "Biden administration searching for ways to keep U.S. forces in Niger to continue anti-terror operations despite overthrowing of government". CNN. Archived from the original on 17 August 2023. Retrieved 17 August 2023.
- ^ "West Africa's Church leaders voice opposition to military intervention in Niger". Vatican News. 17 August 2023. Archived from the original on 17 August 2023. Retrieved 17 August 2023.
- ^ Habib, Gift (18 August 2023). "Niger coup: Bazoum treason case has no legal basis – UN". Punch Newspapers. Archived from the original on 18 August 2023. Retrieved 18 August 2023.
- ^ "UN rights chief says Niger president treason case has 'no legal basis'". Reuters. 18 August 2023. Archived from the original on 18 August 2023. Retrieved 18 August 2023.
- ^ Knickmeyer, Ellen (18 August 2023). "US readying plans to evacuate drone bases if necessary under Niger's new junta, commander says". AP News. Retrieved 18 December 2024.
- ^ Adombila, Maxwell Akalaare (18 August 2023). "West African bloc says 'D-Day' set for possible Niger intervention". Reuters. Archived from the original on 19 August 2023. Retrieved 18 August 2023.
- ^ "ECOWAS force ready to intervene in Niger 'anytime the order is given'". France 24. 18 August 2023. Archived from the original on 18 August 2023. Retrieved 18 August 2023.
- ^ "Niger : il " n'arrivera rien " au président Bazoum, assure le nouveau Premier ministre" [Niger: "nothing will happen" to President Bazoum, assures the new Prime Minister]. Le Parisien (in French). AFP. 18 August 2023. Archived from the original on 19 August 2023. Retrieved 19 August 2023.
- ^ "Niger coup: ECOWAS delegation meets deposed president, junta leader". Aljazeera. 19 August 2023. Archived from the original on 19 August 2023. Retrieved 19 August 2023.
- ^ Mednick, Sam (20 August 2023). "Talks between regional bloc and Niger's junta yield little, an official tells The Associated Press". AP News. Archived from the original on 20 August 2023. Retrieved 20 August 2023.
- ^ Olurounbi, Ruth (22 August 2023). "'Nobody Wants to Go to War' Over Niger Crisis, Ecowas Envoy Says". Bloomberg. Archived from the original on 22 August 2023. Retrieved 22 August 2023.
- ^ "ECOWAS envoy to Niger says meeting with junta was 'fruitful'". Reuters. 22 August 2023. Retrieved 22 August 2023.
- ^ Arslan, Fatma Esma (19 August 2023). "Mali, Burkina Faso send warplanes to Niger in response to potential military intervention". Anadolu Ajansi. Archived from the original on 19 August 2023. Retrieved 19 August 2023.
- ^ Arslan, Fatma Esma (20 August 2023). "Volunteer militia force being formed in Niger against potential ECOWAS intervention". Anadolu Ajansı. Archived from the original on 19 August 2023. Retrieved 19 August 2023.
- ^ "Niger junta proposes 3-year transition amid ECOWAS visit". Deutsche Welle. 19 August 2023. Archived from the original on 19 August 2023. Retrieved 19 August 2023.
- ^ "Pro-coup rally in Niger after threat of military intervention". Al-Jazeera. 20 August 2023. Archived from the original on 22 August 2023. Retrieved 19 August 2023.
- ^ Balima, Boureima; Mazou, Abdel-Kader (20 August 2023). "Thousands of Niger junta supporters overwhelm call for civilian volunteers". Reuters. Archived from the original on 20 August 2023. Retrieved 20 August 2023.
- ^ Hansler, Jennifer (19 August 2023). "US Ambassador Kathleen FitzGibbon arrives in Niger". CNN. Archived from the original on 20 August 2023. Retrieved 20 August 2023.
- ^ "Pro-coup Rally In Niger After Military Leader Warns Against Foreign Intervention". Barron's. Agence France Presse. Archived from the original on 20 August 2023. Retrieved 20 August 2023.
- ^ "Pope Francis calls for peaceful end to the Niger crisis". AP News. 20 August 2023. Retrieved 18 December 2024.
- ^ "Niger: ECOWAS rejects junta's three-year transition plan". Punch Newspapers. 21 August 2023. Archived from the original on 22 August 2023. Retrieved 21 August 2023.
- ^ "ECOWAS says troops ready for Niger intervention". dw.com. Archived from the original on 22 August 2023. Retrieved 21 August 2023.
- ^ Ajayi, Olayinka (21 August 2023). "Niger: We're more likely to use force — ECOWAS". Vanguard. Archived from the original on 22 August 2023. Retrieved 21 August 2023.
- ^ Soylu, Ragip (21 August 2023). "Turkey's Erdogan opposes military intervention in Niger over coup". Middle East Eye. Archived from the original on 21 August 2023. Retrieved 21 August 2023.
- ^ "Hundreds Of Burkina Faso Supply Trucks Arrive In Niger's Capital". barrons.com. Agence France-Presse. Archived from the original on 21 August 2023. Retrieved 21 August 2023.
- ^ Habib, Gift (21 August 2023). "Release Bazoum without preconditions, ECOWAS tells Niger junta". Punch Newspapers. Archived from the original on 22 August 2023. Retrieved 22 August 2023.
- ^ "Niger Coup: Protests Erupt In Kano Over Planned ECOWAS Intervention". Leadership News. 12 August 2023. Archived from the original on 13 August 2023. Retrieved 22 August 2023.
- ^ a b "Algeria refuses French request to fly over its airspace for military operation in Niger". Arab News. 22 August 2023. Archived from the original on 23 August 2023. Retrieved 22 August 2023.
- ^ "France denies report it asked Algeria to use airspace for a Niger operation". Reuters. 22 August 2023. Archived from the original on 23 August 2023. Retrieved 22 August 2023.
- ^ "African Union suspends Niger with immediate effect over July 26 coup". Aljazeera. 22 August 2023. Archived from the original on 23 August 2023. Retrieved 22 August 2023.
- ^ "Egypt urges dialogue to settle Niger crisis". Vanguard. 23 August 2023. Archived from the original on 24 August 2023. Retrieved 23 August 2023.
- ^ Oyewo, Dayo (4 August 2023). "Negotiation fails, Niger junta to recall ambassador from Nigeri". Punch Newspapers. Retrieved 21 December 2024.
- ^ "COUP: UK Demands Immediate Release Of Deposed Niger's President, Bazoum". Gistmania. 23 August 2023. Archived from the original on 24 August 2023. Retrieved 24 August 2023.
- ^ "UK defence minister: We'll work with ECOWAS to restore democratic rule in Niger Republic". TheCable. 23 August 2023. Archived from the original on 24 August 2023. Retrieved 24 August 2023.
- ^ wisdom. "Niger: ECOWAS Denies Influence Of 'Foreign Power', Reveals Next Action". igberetvnews.com. Archived from the original on 24 August 2023. Retrieved 24 August 2023.
- ^ Yusuf, Bada (24 August 2023). "JUST IN: Again, Tinubu sends Islamic leaders to Niger republic for dialogue". Legit.ng – Nigeria news.


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch