Armenians in the Baltic states
| Total population | |
|---|---|
| 5,293 (2011) | |
| Regions with significant populations | |
| Riga, Tallinn, Vilnius, other larger cities | |
| Languages | |
| Armenian, Russian, Baltic languages | |
| Religion | |
| Armenian Apostolic Church | |
| Related ethnic groups | |
| Armenians in Belarus |
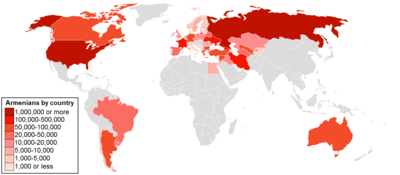
Armenians in the Baltic states of Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania settled there mostly during the Soviet occupation of the Baltic States, although some of the first settlers arrived during the Russian Empire's rule in the Baltics.
| Country | 1959 | 1970 | 1979 | 1989 | Post-Soviet (Year) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estonia | 648 | 604 | 845 | 1,669 | 1,666 (2021) |
| Latvia | 1,060 | 1,511 | 1,913 | 3,069 | 2,549 (2023) |
| Lithuania | 471 | 508 | 955 | 1,655 | 1,233 (2011) |
| Baltic states | 2,179 | 2,623 | 3,713 | 6,393 | 5,663 (2000–2008) |
Estonia
[edit]According to the year 2000 census, there were 1,444 Armenians living in Estonia.[1] According to the 2011 census, the number of Armenians had decreased slightly to 1,042.[2] In 1989 (according to Soviet 1989 census) the number was 1,669.[3] The majority of Armenians live in Tallinn: 58% in the year 2000.[1]
With the affirmation of Estonia's independence from the Soviet Union in 1991, Soviet-era immigrants and their Estonian-born children were not granted citizenship automatically.
A football club based in Tallinn, FC Ararat Tallinn, is named after the mountain Ararat and has a partnership with the Armenian club FC Ararat Yerevan.
Latvia
[edit]Armenians in Latvia number around 5,000 according to armeniandiaspora.com[4] and from 2,014 to 2,549 per official government sources (a decrease from 2,742 reported in 2008).[5][6][7] The Armenian Latvian population mainly lives in Riga.
In 1887 a Latvian Armenian Society was established. One Armenian was reported in the Jäger Report as murdered by Einsatzgruppe A in Daugavpils in 1941.[8] In 1990, in the center of Riga a khachkar was set up in gratitude for assistance in the aftermath of the 1988 Armenian earthquake. In 1991, the first issue of the Armenian newspaper "Ararat" was published, with a second revival in 2002. In 2001, the Armenian Community of Riga was officially re-established after being dissolved after the Soviet occupation of Latvia in 1940.
- Riga khachkar
- Riga St. Gregory Armenian Apostolic Church
Lithuania
[edit]According to the last Lithuanian census of 2011 there were 1,233[9] Armenians in Lithuania. Armenian organizations put the number around 2,500.[4] According to Soviet 1989 census there are 1,655 Armenians in Lithuania.[10] The Armenians live mainly in Vilnius. The settlement of Armenians in Lithuania, in the distant past of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth was of an episodic nature and was due mainly to the needs of trade, although from the historical sources it is known, that Armenian school was established in 16th century Vilnius, Armenian guild in the 16th to 18th centuries Vilnius.[11] One of the most prominent painter of the 19th century in Lithuania was Jan Rustem (Armenian: Յան Ռուստամ). The history of most of the Armenian community now living in Lithuania mainly occurs in the 20th century.
Famous Baltic Armenians
[edit]See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b "Population by ethnic nationality, mother tongue and citizenship". Statistics Estonia. Archived from the original on 2007-06-14. Retrieved 2009-10-15.
- ^ "Eestis elab 192 rahvuse esindajaid." Õhtuleht 9-17-2012. (in Estonian)
- ^ Демоскоп Weekly - Всесоюзная перепись населения 1989 года.Национальный состав населения по республикам СССР Archived June 4, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b ArmenianDiaspora website Archived May 17, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Population by ethnicity at the beginning of year 1935 - 2023". Oficiālās statistikas portāls stat.gov.lv. Retrieved 2023-06-10.
- ^ Latvijas iedzīvotāju sadalījums pēc nacionālā sastāva un valstiskās piederības (Inhabitants of Latvia) by ethnic composition and citizenship status (01.01.2023.) | Office of Citizenship and Migration Affairs - PMLP
- ^ Population of Latvia by ethnicity and citizenship, 01.07.2008. Archived 2008-12-03 at the Wayback Machine(in Latvian)
- ^ The Jager Report
- ^ "2011 Census Results". Department of Statistics to the Government of the Republic of Lithuania (Statistics Lithuania), 2012. Archived from the original on 2012-10-05. Retrieved 2012-09-30.
- ^ Демоскоп Weekly - Всесоюзная перепись населения 1989 года.Национальный состав населения по республикам СССР
- ^ [1] History of Armenians in Lithuania (in Lithuanian)


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch