Benzene (data page)
This page provides supplementary chemical data on benzene.
Material Safety Data Sheet
[edit]The handling of this chemical may incur notable safety precautions. It is highly recommended to seek the Material Safety Datasheet (MSDS) for this chemical from a reliable source such as SIRI, and follow its directions. MSDS for benzene is available at AMOCO.
Structure and properties
[edit]| Structure and properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Refractive index, nD | 1.5011 at 20 °C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abbe number | ? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dielectric constant, εr | (2.274 – 0.0020ΔT) ε0 (ΔT = T – 25 °C) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bond energy | ? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bond length | 1.39 Å C-C[1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular geometry | 120 °C–C–C 120° H–C–C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Magnetic susceptibility | ? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surface tension | 28.88 dyn/cm at 25 °C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Viscosity[2] |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Thermodynamic properties
[edit]| Phase behavior | |
|---|---|
| Triple point | 278.5 K (5.4 °C), 4.83 kPa |
| Critical point | 562 K (289 °C), 4.89 MPa |
| Std enthalpy change of fusion, ΔfusH | 9.9 kJ/mol at 5.42 °C |
| Std entropy change of fusion, ΔfusS | 35.5 J/(mol·K) at 5.42 °C |
| Std enthalpy change of vaporization, ΔvapH | 33.9 kJ/mol at 25 °C 30.77 kJ/mol at 80.1 °C |
| Std entropy change of vaporization, ΔvapS | 113.6 J/(mol·K) at 25 °C 87.1 J/(mol·K) at 80.1 °C |
| Solid properties | |
| Std enthalpy change of formation, ΔfH | ? kJ/mol |
| Standard molar entropy, S | 45.56 J/(mol K) |
| Heat capacity, cp | 118.4 J/(mol K) at 0 °C |
| Liquid properties | |
| Std enthalpy change of formation, ΔfH | +48.7 kJ/mol |
| Standard molar entropy, S | 173.26 J/(mol K) |
| Enthalpy of combustion, ΔcH | –3273 kJ/mol |
| Heat capacity,[2] cp | 134.8 J/(mol K) |
| Gas properties | |
| Std enthalpy change of formation, ΔfH | +82.93 kJ/mol |
| Standard molar entropy,[3] S | 269.01 J/(mol K) |
| Heat capacity,[2] cp | 82.44 J/(mol K) at 25 °C |
| van der Waals' constants[4] | a = 1823.9 L2 kPa/mol2 b = 0.1154 liter per mole |
Vapor pressure of liquid
[edit]| P in mm Hg | 1 | 10 | 40 | 100 | 400 | 760 | 1520 | 3800 | 7600 | 15200 | 30400 | 45600 | |
| T in °C | –36.7(s) | –11.5(s) | 7.6 | 26.1 | 60.6 | 80.1 | 103.8 | 142.5 | 178.8 | 221.5 | 272.3 | — | |
Table data obtained from CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics 44th ed. Note: (s) notation indicates equilibrium temperature of vapor over solid, otherwise value is equilibrium temperature of vapor over liquid.

Distillation data
[edit]
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Spectral data
[edit]| UV-Vis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ionization potential | 9.24 eV (74525.6 cm−1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| S1 | 4.75 eV (38311.3 cm−1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| S2 | 6.05 eV (48796.5 cm−1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| λmax | 255 nm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Extinction coefficient, ε | ? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IR | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Major absorption bands[6] |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
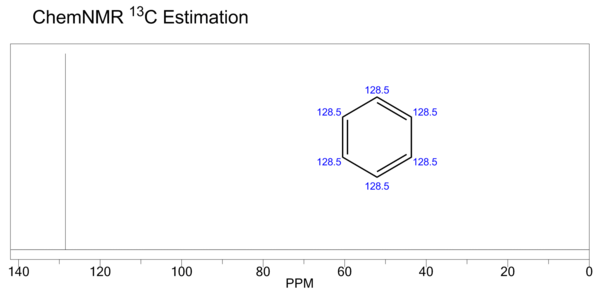
| NMR | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Proton NMR | (CDCl3, 300 MHz) δ 7.34 (s, 6H) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carbon-13 NMR | (CDCl3, 25 MHz) δ 128.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other NMR data | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Masses of main fragments | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Safety data
[edit]Material Safety Data Sheet for benzene:
| Common synonyms | None |
| Physical properties | Form: colorless liquid |
| Stability: Stable, but very flammable | |
| Melting point: 5.5 C | |
| Water solubility: negligible | |
| Specific gravity: 0.87 | |
| Principal hazards | *** Benzene is a carcinogen (cancer-causing agent). |
| *** Very flammable. The pure material, and any solutions containing it, constitute a fire risk. | |
| Safe handling | Benzene should NOT be used at all unless no safer alternatives are available. |
| If benzene must be used in an experiment, it should be handled at all stages in a fume cupboard. | |
| Wear safety glasses and use protective gloves. | |
| Emergency | Eye contact: Immediately flush the eye with plenty of water. Continue for at least ten minutes |
| and call for immediate medical help. | |
| Skin contact: Wash off with soap and water. Remove any contaminated clothing. If the skin | |
| reddens or appears damaged, call for medical aid. | |
| If swallowed: Call for immediate medical help. | |
| Disposal | It is dangerous to try to dispose of benzene by washing it down a sink, since it is toxic, will cause environmental damage |
| and presents a fire risk. It is probable that trying to dispose of benzene in this way will also break local | |
| environmental rules. Instead, retain in a safe place in the laboratory (well away from any source of ignition) | |
| for disposal with other flammable, non-chlorinated solvents. | |
| Protective equipment | Safety glasses. If gloves are worn, PVA, butyl rubber and viton are suitable materials. |
References
[edit]- ^ Brown; LeMay; Bursten (2006). Chemistry: The Central Science. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education. pp. 1067. ISBN 0-13-109686-9.
- ^ a b c d "Pure Component Properties" (Queriable database). Chemical Engineering Research Information Center. Retrieved 12 May 2007.
- ^ "ETP Entropy of Benzene" (Queriable database). Dortmund Data Bank. Retrieved 7 October 2011.
- ^ Lange's Handbook of Chemistry 10th ed, pp. 1522–1524
- ^ a b c d "Binary Vapor-Liquid Equilibrium Data" (Queriable database). Chemical Engineering Research Information Center. Retrieved 12 May 2007.
- ^ "Spectral Database for Organic Compounds". Advanced Industrial Science and Technology. Archived from the original (Queriable database) on 5 May 2006. Retrieved 10 June 2007.
This box:
- Except where noted otherwise, data relate to Standard temperature and pressure.
- Reliability of data general note.


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch