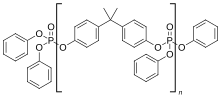
Bisphenol-A bis(diphenyl phosphate)
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C39H34O8P2 | |
| Molar mass | 692.641 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Bisphenol A diphenyl phosphate is a halogen-free flame retardant used plastics. It is used in polymer blends of engineering plastics, such as PPO/HIPS and PC/ABS,[1] which are commonly used to make casing for electrical items like TVs, computers and home appliances.
It is formed by the transesterification of bisphenol A with triphenyl phosphate. The commercial grade material can contain oligomers (CAS: 181028–79–5)
References
[edit]- ^ Pawlowski, Kristin H; Schartel, Bernhard (November 2007). "Flame retardancy mechanisms of triphenyl phosphate, resorcinol bis(diphenyl phosphate) and bisphenol A bis(diphenyl phosphate) in polycarbonate/acrylonitrile–butadiene–styrene blends". Polymer International. 56 (11): 1404–1414. doi:10.1002/pi.2290.


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch