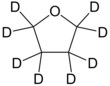
Deuterated THF
| |||
 | |||
| Identifiers | |||
|---|---|---|---|
3D model (JSmol) | |||
| 111854 | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.015.363 | ||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID | |||
| UN number | 2056 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C 4D 8O | |||
| Molar mass | 80.1550 g mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colourless liquid | ||
| Density | 985 mg cm−3 | ||
| Melting point | −106 °C (−159 °F; 167 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 65 to 66 °C (149 to 151 °F; 338 to 339 K) | ||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
  | |||
| Danger | |||
| H225, H319, H335 | |||
| P210, P261, P305+P351+P338 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | −17 °C (1 °F; 256 K) | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
Deuterated tetrahydrofuran (d8-THF) is a colourless, organic liquid at standard temperature and pressure.[1] This heterocyclic compound has the chemical formula C4D8O, and is an isotopologue of tetrahydrofuran.[2] Deuterated THF is used as a solvent in NMR spectroscopy, though its expense can often be prohibitive.[citation needed]
References
[edit]- ^ Andersson, O.; Suga, H. (1996-01-01). "Thermal conductivity of normal and deuterated tetrahydrofuran clathrate hydrates". Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids. 57 (1): 125–132. doi:10.1016/0022-3697(95)00157-3. ISSN 0022-3697.
- ^ David, W. I. F.; Ibberson, R. M. (1992-02-15). "A reinvestigation of the structure of tetrahydrofuran by high-resolution neutron powder diffraction". Acta Crystallographica Section C: Crystal Structure Communications. 48 (2): 301–303. doi:10.1107/S0108270191008582. ISSN 0108-2701.


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch