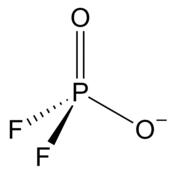
Difluorophosphate
 | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name Difluorophosphate[1] | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| PO2F−2 | |||
| Molar mass | 100.97 g mol−1 | ||
| Structure | |||
| Tetracoordinated at phosphorus atom | |||
| Tetrahedral at phosphorus atom | |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
Difluorophosphate or difluorodioxophosphate or phosphorodifluoridate is an anion with formula PO2F−2. It has a single negative charge and resembles perchlorate (ClO−4) and monofluorosulfonate (SO3F−) in shape and compounds.[2] These ions are isoelectronic, along with tetrafluoroaluminate, phosphate, orthosilicate, and sulfate.[2][3] It forms a series of compounds. The ion is toxic to mammals as it causes blockage to iodine uptake in the thyroid. However it is degraded in the body over several hours.[2]
Compounds containing difluorophosphate may have it as a simple uninegative ion, it may function as a difluorophosphato ligand where it is covalently bound to one or two metal atoms, or go on to form a networked solid.[4] It may be covalently bound to a non metal or an organic moiety to make an ester or an amide.
Formation
[edit]Ammonium difluorophosphate ([NH4]PO2F2) is formed from treating phosphorus pentoxide with ammonium fluoride.[2] This was how the ion was first made by its discoverer, Willy Lange, in 1929.[3][5]
Alkali metal chlorides can react with dry difluorophosphoric acid to form alkali metal salts.[6]
- NaCl + HPO2F2 → NaPO2F2 + HCl(g)
Fluorination of dichlorophosphates can produce difluorophosphates.[7] Another method is fluorination of phosphates or polyphosphates.[5]
Trimethylsilyl difluorophosphate ((CH3)3Si−O−P(=O)F2) reacts with metal chlorides to give difluorophosphates.[8]
The anhydride of difluorophosphoric acid (HPO2F2), phosphoryl difluoride oxide (P2O3F4) reacts with oxides such as UO3 to yield difuorophosphates.[9] Phosphoryl difluoride oxide also reacts with alkali metal fluorides to yield difluorophosphates.[10]
Properties
[edit]The difluorophosphate ion in ammonium difluorophosphate and potassium difluorophosphate has these interatomic dimensions:[11]
| Difluorophosphate salt | P–O length | P–F length | O–P–O angle | F–P–O angle | F–P–F angle |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ammonium difluorophosphate | 1.457 Å | 1.541 Å | 118.7° | 109.4° | 98.6° |
| Potassium difluorophosphate | 1.470 Å | 1.575 Å | 122.4° | 108.6° | 97.1° |
Hydrogen bonding from ammonium ion to oxygen atoms causes a change to the difluorophosphate ion in the ammonium salt.[11]
On heating the salts that are not of alkali metals or alkaline earth metals, difluorophosphates decompose firstly by giving off POF3 forming a monofluorophosphate (PO3F2−) compound, and then this in turn decomposes to an orthophosphate PO3−4 compound.[12][13]
Difluorophosphate salts are normally soluble and stable in water. However, in acidic or alkaline conditions they can be hydrolyzed to monofluorophosphates and hydrofluoric acid.[14] The caesium and potassium salts are the least soluble.[14]
Irradiating potassium difluorophosphate with gamma rays can make the free radicals •PO2F−, •PO3F− and •PO2F2.[15][16]
Compounds
[edit]| Formula | Name | Structure | Infrared spectrum | Melting point | Comments | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LiPO2F2 | Lithium difluorophosphate | 360 °C | [5][6] | |||
| Be(PO2F2)2 | Beryllium difluorophosphate | >400 °C d | prepared from BeCl2 and acid | [17] | ||
| CH3CH2−O−P(=O)F2 | Ethyl difluorophosphate | [18] | ||||
| [NH4]+PO2F−2 | Ammonium difluorophosphate | orthorhombic: a = 8.13 Å, b = 6.43 Å, c = 7·86 Å, Z = 4 space group Pnma | P–F stretching 842 and 860 cm−1; P–O stretching 1138 and 1292 cm−1 | 213 °C | ||
| [NO2]+PO2F−2 | Nitronium difluorophosphate | 515, 530, 550, 560, 575, 845, 880, 1145, 1300, 2390, 3760 cm−1 | nitronium formed from anhydride and N2O5 | [19] | ||
| [NO]+PO2F−2 | Nitrosonium difluorophosphate | 500, 840, 880, 1130, 1272, 1315, 2278 cm−1 | nitrosonium formed from anhydride and N2O3 | [19] | ||
| NaPO2F2 | Sodium difluorophosphate | 210 °C | [6] | |||
| Mg(PO2F2)2 | Magnesium difluorophosphate | 200 °C | [5] | |||
| [NH4]+Mg2+(PO2F−2)3 | Ammonium magnesium difluorophosphate | Cmcm a=5.411 b=15.20 c=12.68 | [20] | |||
| Al(PO2F2)3 | Aluminium difluorophosphate | polymeric[4] | 505, 541, 582, 642, 918, 971, 1200, 1290 cm−1 (with 355 cm−1 impurity) | formed from Al(CH2CH3)3 and acid; colourless insoluble powder[4] | [7][8] | |
| Si(−O−P(=O)F2)4 | Silicon(IV) difluorophosphate | formed from SiCl4 and anhydride | [18] | |||
| (CH3)3Si−O−P(=O)F2 | Trimethylsilyl difluorophosphate | formed from anhydride and [(CH3)3Si]2O | [4][18] | |||
| KPO2F2 | Potassium difluorophosphate | orthorhombic: a = 8.03 Å, b = 6.205 Å, c = 7.633 Å, Z = 4, V=380.9 Å3, density = 2.44 g/cm3 | 510, 525, 570, 835, 880, 1145, 1320, 1340 cm−1 | 263 °C | colourless elongated prisms | [6][11][19][21][22] |
| (K+)4(PO2F−2)2(S2O2−7) | Tetrapotassium difluorophosphate pyrosulfate | C2/c: a = 13.00 Å, b = 7.543 Å, c = 19.01 Å, β = 130.07°, Z = 4 | [23] | |||
| Ca(PO2F2)2·CH3COOCH2CH3 | Calcium difluorophosphate - ethyl acetate 1:1 solvate | [24] | ||||
| Ca(PO2F2)2 | Calcium difluorophosphate | >345 °C d | [5] | |||
| [VO2]+PO2F−2 | Pervanadyl difluorophosphate | [9] | ||||
| CrO2(PO2F2)2 | Chromyl difluorophosphate | formed from anhydride; red-brown | [25] | |||
| Cr(PO2F2)3 | Chromium(III) difluorophosphate | 320, 385, 490, 575, 905, 955, 1165, 1255 cm−1 | formed from excess anhydride, green | [25] | ||
| Mn(CO)5PO2F2[clarification needed] | 184 °C | [26] | ||||
| HMn(PO2F2)3[clarification needed] | dissolve manganese in acid; white | [27] | ||||
| [NH+4](Mn2+)3(PO2F−2)(PO3F2−)2(F−)2 | [28] | |||||
| Fe(PO2F2)2 | Iron(II) difluorophosphate | 463, 496, 668 (weak), 869 (double), 1139, 1290 cm−1 | 180 °C d | colour blue green, hygroscopic, melts 250 °C, above 300 °C starts decomposing to Fe3(PO4)2 | [12] | |
| Fe(PO2F2)3 | Iron(III) difluorophosphate | 262, 493, 528, 570, 914, 965, 1173, 1242 cm−1 | >400 °C | decomposes at 230 °C yielding FeF3; dissolve iron in acid in presence of oxygen | [7] | |
| K+(Fe2+)3(PO2F−2)(PO3F2−)2(F−)2 | [28] | |||||
| Co(PO2F2)2 | Cobalt(II) difluorophosphate | 173 °C | prepared from CoCl2 and acid; pink or blue; blue formed by heating pink to 140 °C | [17] | ||
| HCo(PO2F2)3[clarification needed] | dissolve cobalt in acid; red-purple | [27] | ||||
| Co(PO2F2)2·2CH3CN | Cobalt(II) difluorophosphate - methyl cyanide solvate 1:2 | orthorhombic: a = 9.227 Å, b = 13.871 Å, c = 9.471 Å, V = 1212 Å3, Z = 4, density = 1.88 g/cm3 | treat HCo(PO2F2)3 with CH3CN for a few weeks; red crystals | [29] | ||
| [NH+4](Co2+)3(PO2F−2)(PO3F2−)2(F−)2 | [28] | |||||
| Ni(PO2F2)2 | Nickel(II) difluorophosphate | 255 °C d | slowly prepared from NiCl2 and acid; yellow | [17] | ||
| HNi(PO2F2)3[clarification needed] | dissolve nickel in acid; yellow | [27] | ||||
| Cu(PO2F2)2 | Copper(II) difluorophosphate | orthorhombic Fddd: a = 10.134 Å, b = 24.49 Å, c = 34.06 Å, Z = 48, V = 8454.3 Å3, density = 2.50 g/cm3 | 265 °C d | pale blue needles | [5][29] | |
| CuI(xantphos)2(μ-PO2F2) | polymeric; monoclinic: a = 12.435 Å, b = 10.887 Å, c = 25.682 Å, β = 100.220°, V = 3421 Å3 | colourless | [30] | |||
| Zn(PO2F2)2 | Zinc(II) difluorophosphate | c. 25 °C? | glassy | [5] | ||
| H2[Zn(PO2F2)4] | Tetra(difluorophosphato)zincic(II) acid | |||||
| Ga(PO2F2)3 | Gallium(III) difluorophosphate | |||||
| [(CH3)2GaPO2F2]2 | Dimethylgallium(III) difluorophosphate | dimeric | 380, 492, 520, 551, 616, 709, 750, 899, 949, 1171, 1218, 1262, 1295, 1404, 2922, 2982 cm−1 | [4][31] | ||
| RbPO2F2 | Rubidium difluorophosphate | orthorhombic: a = 8.15 Å, b = 6.45 Å, c = 7.79 Å, Z = 4, V = 409.5 Å3 density = 3.02 g/cm3 | P–F stretching 827 and 946 cm−1; P–O stretching 1145 and 1320 cm−1 | 160 °C | white | [6][11][21] |
| Sr(PO2F2)2 | Strontium difluorophosphate | 250 °C d | prepared from SrCl2 and acid | [17] | ||
| [NH4]Sr(PO2F2)3 | Ammonium strontium difluorophosphate | Triclinic P1 a=7.370 b=11.054 c=13.645 α=88.861 β=87.435° γ=89.323° | [20] | |||
| AgPO2F2 | Silver(I) difluorophosphate | [32] | ||||
| Ag9(PO2F2)14[clarification needed] | [28] | |||||
| Ag(1-methyl-2-alkylthiomethyl-1H-benzimidazole)PO2F2 | [32] | |||||
| Ag(2,6-bis-[(2-methylthiophenyl)-2-azaethenyl]pyridine)PO2F2 | Triclinic P1: a = 7.687 Å, b = 10.740 Å, c = 13.568 Å, α = 99.52°, β = 96.83°, γ = 99.83°, Z = 2, V = 1076 Å3, density = 1.81 g/cm3 | [33] | ||||
| Ag(4,4′-dicyanodiphenylacetylene)PO2F2 | ||||||
| Cd(PO2F2)2 | Cadmium(II) difluorophosphate | 245 °C d | [5] | |||
| In(PO2F2)3 | Indium(III) difluorophosphate | 269, 492, 528, 567, 910, 962, 1179, 1269 cm−1 | white, decomposes at 260 °C yielding InF3 | [7] | ||
| [(CH3)2InPO2F2]2 | Dimethylindium(III) difluorophosphate | dimeric | 373, 490, 500, 535, 559, 735, 878, 925, 1128, 1179, 1275, 1435, 2928, 3000 cm−1 | [31] | ||
| SnCl2(PO2F2)2 | Tin(IV) dichloride difluorophosphate | [34] | ||||
| (CH3)2Sn(PO2F2)2 | Dimethyltin(IV) difluorophosphate | 204 °C d | prepared from (CH3)2SnCl2 and acid; yellow | [17] | ||
| (CH3CH2)2Sn(PO2F2)2 | Diethyltin(IV) difluorophosphate | 262 °C d | prepared from (CH3CH2)2SnCl2 and acid; yellow | [17] | ||
| (CH3CH2CH2)2Sn(PO2F2)2 | Dipropyltin(IV) difluorophosphate | 245 °C d | prepared from (CH3CH2CH2)2SnCl2 and acid; yellow | [17] | ||
| (CH3(CH2)3)2Sn(PO2F2)2 | Dibutyltin(IV) difluorophosphate | 235 °C d | prepared from (CH3(CH2)7)2SnCl2 and acid; yellow | [17] | ||
| (CH3(CH2)7)2Sn(PO2F2)2 | Dioctyltin(IV) difluorophosphate | 114 °C | prepared from (CH3(CH2)7)2SnCl2 and acid; yellow | [17] | ||
| SbCl4PO2F2 | Antimony(V) tetrachloride difluorophosphate | [34] | ||||
| SbF4PO2F2 | Antimony(V) tetrafluoride difluorophosphate | [34] | ||||
| (2,2-dipyradyl)2Re(CO)2PO2F2[clarification needed] | [35] | |||||
| Au[bis(triphenylphosphine sulfide-S)]PO2F2[clarification needed] | [36] | |||||
| IO2PO2F2[clarification needed] | Raman: 130, 163, 191, 219, 295, 323, 329, 378, 637, 713, 737, 781, 799, 839, 918, 1163 cm−1 | yellowish colour, produced from IO3, decomposed by water | [37] | |||
| IO3PO2F2[clarification needed] | Raman: 217, 247, 269, 305, 343, 367, 395, 473, 569, 643, 671, 717, 797, 891, 1123 cm−1 | yellowish colour, produced from H5IO6, decomposed by water | [37] | |||
| FXePO2F2 | Xenon(II) fluoride difluorophosphate | [38] | ||||
| Xe(PO2F2)2 | Xenon(II) difluorophosphate | [38] | ||||
| CsPO2F2 | Caesium difluorophosphate | orthorhombic: a = 8.437 Å, b = 6.796 Å, c = 8.06 Å, Z = 4, V = 462.1 Å3, density = 3.36 g/cm3 | 286 °C | [6][11][21] | ||
| (Cs+)2(Fe3+)2(PO2F−2)(PO3F2−)2(F−)3 | [28] | |||||
| Ba(PO2F2)2 | Barium difluorophosphate | orthorhombic I42d a =10.4935 b =10.4935 c =26.030 | >400 °C | [5][20] | ||
| [NH4]2Ba(PO2F2)4 | Diammonium barium difluorophosphate | P2/n a=14.285 b=5.472 c=19.474 β=97.607° | [20] | |||
| Re(CO)5PO2F2 | [35] | |||||
| Hg(PO2F2)2 | Mercury(II) difluorophosphate | [5] | ||||
| Hg2(PO2F2)2 | Mercury(I) difluorophosphate or di(difluorophosphato)dimercurane | Raman: 220 cm−1 | produced from anhydride | [5] | ||
| TlPO2F2 | Thallium(I) difluorophosphate | produced from anhydride, or acid on TlCl | [5] | |||
| [(CH3)2TlPO2F2]2 | Dimethylthallium(III) difluorophosphate | dimeric | 360, 374, 500, 505, 520, 559, 850, 880, 1120, 1140, 1195, 1250, 1285, 2932, 3020 cm−1 | [31] | ||
| Pb(PO2F2)2 | Lead(II) difluorophosphate | 189 °C d | [5] | |||
| UO2(PO2F2)2 | Uranyl difluorophosphate | 260, 498, 854, 924, 980, 1124 cm−1 | IR spectrum due to UO2+2 | [9] | ||
| [(CH3CH2)4N]+PO2F−2 | Tetraethylammonium difluorophosphate | [39] | ||||
| 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium difluorophosphate | ionic liquid | [40] | ||||
| 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium difluorophosphate | ionic liquid | [40] | ||||
| 1-butyl-1-methylpyrrolidinium difluorophosphate | ionic liquid | [40] | ||||
| 1-butyl-1-methylpiperidinium difluorophosphate | ionic liquid | [40] | ||||
| di(3,3′,4,4′-tetramethyl-2,2′,5,5′-tetraselenafulvalenium)difluorophosphate | Transitions to a metallic state below 137 K (−136 °C) | [41] | ||||
| 1,4-diphenyl-3,5-enanilo-4,5-dihydro-1,2,4-triazole (nitron) | monoclinic P21/n: a = 7.3811 Å, b = 14.9963 Å, c = 16.922 Å, β = 102.138°, V = 1361.2 Å3, Z = 4 | insoluble; yellow-brown | [2][28] | |||
| Strychnine PO2F2 | [3] | |||||
| Cocaine PO2F2 | [3] | |||||
| Brucine PO2F2 | [3] | |||||
| Morphine PO2F2 | [3] | |||||
| [N(CH3)4]+PO2F−2 | Tetramethylammonium difluorophosphate | [3] | ||||
| H[B(PO2F2)4] | Tetra(difluorophosphato)boric acid | 469, 502, 552, 647, 836, 940, 994, 1093, 1348, 1567 cm−1 | formed from BBr3 and acid; liquid | [4] | ||
| Li[B(PO2F2)4] | Lithium tetra(difluorophosphato)borate | monoclinic P21/c: a=7.9074 Å, b = 14.00602 Å, c = 13.7851 Å, β = 121.913°, Z = 4 | 479, 502, 568, 833, 945, 1002, 1080, 1334 cm−1 | formed from HB(PO2F2)4 and butyllithium; colourless | [4] | |
| [HS(CH3)2]+[B(PO2F2)4]− | Dimethylsulfonium tetra(difluorophosphato)borate | 472, 511, 555, 648, 832, 933, 993, 1082, 1337, 1436, 2851, 2921, 3042 cm−1 | formed from BH3·S(CH3)2 and acid; ionic liquid | [4] | ||
| [Li((CH3CH2)2O)+]3[Al(PO2F2)6]− | (Diethyl ether)lithium hexa(difluorophosphato)aluminate | trigonal R3: a = 17.4058 Å, b = 17.4058 Å, c = 21.4947 Å, γ = 120°, Z = 6 | 417, 503, 536, 624, 723, 891, 922, 964, 1174, 1204, 1283 cm−1 | formed from butyllithium and triethylaluminium and the acid; white | [4] | |
| K2CrO2(PO2F2)4 | 305, 370, 485, 550, 870, 920, 1050, 1130, 1250 cm−1 | 145 °C d | formed from anhydride and K2CrO4; brown | [25] | ||
| Na2MoO2(PO2F2)4 | amorphous | 280, 490, 620, 880, 915, 950, 1020, 1070, 1140, 1280 cm−1 | 125 °C d | formed from anhydride and K2MoO4; white | [25] | |
| Na2WO2(PO2F2)4 | amorphous | 280, 474, 620, 930, 1030, 1130, 1230 cm−1 | 109 °C d | formed from anhydride and K2WO4; white | [25] |
Related substances
[edit]Difluorphosphoric acid
[edit]Difluorophosphoric acid (HPO2F2) is one of the fluorophosphoric acids. It is produced when phosphoryl fluoride reacts with water:
- POF3 + H2O → HPO2F2 + HF
This in turn is hydrolysed more to give monofluorophosphoric acid (H2PO3F), and a trace of hexafluorophosphoric acid (HPF6). HPO2F2 also is produced when HF reacts with phosphorus pentoxide. Yet another method involves making difluorphosphoric acid as a side product of calcium fluoride being heated with damp phosphorus pentoxide. A method to make pure difluorphosphoric acid involves heating phosphoryl fluoride with monofluorophosphoric acid and separating the product by distillation:[42]
- POF3 + H2PO3F → 2 HPO2F2
Difluorophosphoric acid can also be produced by fluorinating phosphorus oxychlorides. P2O3Cl4 and POCl3 react with hydrogen fluoride solution to yield HPO2Cl2 and then HPO2F2.[43] Yet another way is to treat orthophosphate (PO3−4) with fluorosulfuric acid (HSO3F).[44]
Difluorphosphoric acid is a colorless liquid. It melts at −96.5 °C (−141.7 °F) and boils at 115.9 °C (240.6 °F). Its density at 25 °C is 1.583 g/cm3.[14]
Phosphoryl difluoride oxide
[edit]Difluorophosphoric acid anhydride also known as phosphoryl difluoride oxide or diphosphoryl tetrafluoride (F2(O=)P−O−P(=O)F2 or P2O3F4) is an anhydride of difluorphosphoric acid. It crystallises in the orthorhombic system, with space group Pcca and Z = 4.[45] P2O3F4 can be made by refluxing difluorophosphoric acid with phosphorus pentoxide. P2O3F4 boils at 71 °C.[46]
Substitution
[edit]In addition to the isoelectronic series, ions related by substituting fluorine or oxygen by other elements include monofluorophosphate, difluorothiophosphate, dichlorothiophosphate, dichlorophosphate, chlorofluorothiophosphate, chlorofluorophosphate, dibromophosphate, and bromofluorophosphate.[47]
Adducts
[edit]Difluorophosphate can form adducts with PF5 and AsF5. In these the oxygen atoms form a donor-acceptor link between the P and As (or P) atoms, linking the difluorides to the pentafluorides. Example salts include KPO2F2·2AsF5, KPO2F2·AsF5, KPO2F2·2PF5 and KPO2F2·PF5.[48]
Amines can react with phosphoryl fluoride to make substances with a formula RR′N−P(=O)F2. The amines shown to do this include ethylamine, isopropylamine, n-butylamine, t-butylamine, dimethylamine, and diethylamine. The monoamines can further react to yield an alkyliminophosphoric fluoride (R−N=P(=O)F).[49]
References
[edit]- ^ Toy, Arthur D. F. (22 Oct 2013). The Chemistry of Phosphorus. Pergamon Texts in Inorganic Chemistry. Vol. 3. Pergamon Press. pp. 536–537. ISBN 9781483147413. Retrieved 19 June 2015.
- ^ a b c d e Anbar, M.; Guttmann, S.; Lewitus, Z. (30 May 1959). "Effect of Monofluorosulphonate, Difluorophosphate and Fluoroborate Ions on the Iodine Uptake of the Thyroid Gland". Nature. 183 (4674): 1517–1518. Bibcode:1959Natur.183.1517A. doi:10.1038/1831517a0. PMID 13666792. S2CID 4291858.
- ^ a b c d e f g Lange, Willy (3 April 1929). "Über die Difluorphosphorsäure und ihre der Perchlorsäure ähnliche Salzbildung" [On difluorophosphoric acid and its perchlorate-like salt formation]. Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft (A and B Series). 62 (4): 786–792. doi:10.1002/cber.19290620408.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Schulz, Christoph; Eiden, Philipp; Klose, Petra; Ermantraut, Andreas; Schmidt, Michael; Garsuch, Arnd; Krossing, Ingo (2015). "Homoleptic borates and aluminates containing the difluorophosphato ligand – [M(O2PF2)x]y− – synthesis and characterization". Dalton Trans. 44 (15): 7048–7057. doi:10.1039/c5dt00469a. PMID 25785817.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m Vast, P.; Semmoud, A.; Addou, A.; Palavit, G. (March 1988). "Étude méthodologique de la synthèse des difluorodioxophosphates métalliques à partir de l'oxyde difluorure de phosphoryle" [Methodical study of the synthesis of metal difluorodioxophosphates from phosphoryl difluoride oxide]. Journal of Fluorine Chemistry. 38 (3): 297–302. doi:10.1016/S0022-1139(00)81065-9.
- ^ a b c d e f Thompson, R.C.; Reed, W. (July 1969). "Preparation and infrared spectra of alkali metal difluorophosphates". Inorganic and Nuclear Chemistry Letters. 5 (7): 581–585. doi:10.1016/0020-1650(69)80034-6.
- ^ a b c d Weidlein, J. (April 1968). "Darstellung, Eigenschaften und IR-Spektren von OTi(O2PCl2)2, Fe(O2PF2)3 und In(O2PF2)3" [Description, properties and IR spectra of...]. Zeitschrift für anorganische und allgemeine Chemie. 358 (1–2): 13–20. doi:10.1002/zaac.19683580103.
- ^ a b Shihada, Abdel-Fattah; Mohammed, Abdulalah T. (1 January 1980). "Zur Reaktion von Trimethylsilyl-difluorophosphat, Trimethylsilyl-dimethylphosphinat und Difluorophosphorsäureanhydrid mit TiCl4 bzw. SbCl5" [On the Reactions of Trimethylsilyl Difluorophosphate, Trimethylsilyl Dimethylphosphinate and Difluorophosphoric Acid Anhydride with TiCl4 and SbCl5]. Zeitschrift für Naturforschung B. 35 (1): 60–63. doi:10.1515/znb-1980-0114. S2CID 96302051.
- ^ a b c Vast, P.; Semmoud, A. (January 1985). "Préparation de nouveaux difluorodioxophosphates à partir de l'oxyde de difluorure de phosphoryle. Partie V. Réactions sur le trioxyde d'uranium" [Preparation of new difluorodioxophosphates from phosphoryl difluorideoxide. Part V. Reactions with uranium dioxide]. Journal of Fluorine Chemistry. 27 (1): 47–52. doi:10.1016/S0022-1139(00)80896-9.
- ^ Addou, A.; Vast, P.; Legrand, P. (January 1982). "Champ de forces de symetrie locale des composés oxyfluorés du phosphore(V). I. Les difluorodioxophosphates (DFP) alcalins" [Local symmetry force-field of oxyfluorine compounds of phosphorus(V). I. Alkali difluorodioxophosphates (DFP)]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular Spectroscopy. 38 (7): 785–790. Bibcode:1982AcSpA..38..785A. doi:10.1016/0584-8539(82)80068-8.
- ^ a b c d e Harrison, R. W.; Trotter, James (1969). "Structure of ammonium difluorophosphate". Journal of the Chemical Society A: Inorganic, Physical, Theoretical: 1783. doi:10.1039/J19690001783.
- ^ a b Vast, P.; Semmoud, A. (June 1994). "Comportement thermique du difluorodioxophosphate ferreux" [Thermal behaviour of ferrous difluorodioxophosphate]. Journal of Thermal Analysis. 41 (6): 1489–1493. doi:10.1007/bf02549945. S2CID 95079191.
- ^ Vast, P.; Semmoud, A.; Palavit, G. (December 1986). "Préparation de l'acide monofluorotrioxophosphorique H2PO3F à partir de l'acide difluorodioxophosphorique HPO2F2" [Preparation of monofluorotrioxophosphoricacid H2PO3F from difluorodioxophosphoric acid HPO2F2]. Journal of Fluorine Chemistry. 34 (2): 229–232. doi:10.1016/s0022-1139(00)85072-1.
- ^ a b c Reed, William (September 1965). Studies of Difluorophosphoric Acid and its Alkali Metal Salts (Thesis). Retrieved 23 April 2023.
- ^ Begum, Afrozi; Subramanian, S.; Symons, M. C. R. (1970). "Unstable intermediates. Part LXVIII. Electron spin resonance studies of the radicals O3PF− and O2PF2". Journal of the Chemical Society A: Inorganic, Physical, Theoretical: 1323. doi:10.1039/J19700001323.
- ^ Begum, A.; Subramanian, S.; Symons, M. C. R. (1971). "Unstable intermediates. Part LXXXVI. Electron spin resonance studies of the effect of γ-rays on potassium difluorophosphate: the radical PO2F?". Journal of the Chemical Society A: Inorganic, Physical, Theoretical: 700–702. doi:10.1039/J19710000700.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Tan, Thiam Hock (August 1970). Preparation and Properties of Metal Difluorophosphates (Thesis). University of British Columbia. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2016-03-04.
- ^ a b c Roesky, Herbert W. (July 1967). "Über Reaktionen mit Pyrophosphoryltetrafluorid" [On Reactions with pyrophosphoryl tetrafluoride]. Chemische Berichte. 100 (7): 2147–2150. doi:10.1002/cber.19671000706.
- ^ a b c Addou, A.; Vast, P. (August 1979). "Préparation de nouveaux difluorodioxophosphates à partir de l'oxyde de difluororure de phosphoryle. Partie I. Réactions sur les oxydes d'azote" [Preparation of new difluorodioxophosphates from phosphoryl difluoride oxide. Part I. Reactions with nitrogen oxides]. Journal of Fluorine Chemistry. 14 (2): 163–169. doi:10.1016/S0022-1139(00)82884-5.
- ^ a b c d Zhang, Wenyao; Jin, Wenqi; Cheng, Meng; Zhang, Ruonan; Yang, Zhihua; Pan, Shilie (2021). "From centrosymmetric to noncentrosymmetric: effect of the cation on the crystal structures and birefringence values of (NH 4 ) n−2 AE(PO 2 F 2 ) n (AE = Mg, Sr and Ba; n = 2, 3 and 4)". Dalton Transactions. 50 (29): 10206–10213. doi:10.1039/D1DT00698C. ISSN 1477-9226. PMID 34231608. S2CID 235758275.
- ^ a b c Trotter, James; Whitlow, S. H. (1967). "The structures of caesium and rubidium difluorophosphates". Journal of the Chemical Society A: Inorganic, Physical, Theoretical: 1383–1386. doi:10.1039/J19670001383.
- ^ Harrison, R. W.; Thompson, R. C.; Trotter, James (1966). "The structure of potassium difluorophosphate". Journal of the Chemical Society A: Inorganic, Physical, Theoretical: 1775. doi:10.1039/J19660001775.
- ^ Zhang, Wenyao; Jin, Wenqi; Yang, Zhihua; Pan, Shilie (2020). "K4(PO2F2)2(S2O7): first fluorooxophosphorsulfate with mixed-anion [S2O7]2− and [PO2F2]− groups". Dalton Transactions. 49 (48): 17658–17664. doi:10.1039/D0DT03307C. ISSN 1477-9226. PMID 33231582. S2CID 227157666.
- ^ Grunze, H.; Jost, K.-H.; Wolf, G.-U. (April 1969). "Salze von Halogenophosphorsäuren. V. Darstellung und Struktur des Bis(äthylacetat)-calcium-difluorophosphates Ca[PO2F2]2 · 2 CH3COOC2H5" [Salts of halophosphoric acids. V. Description and structure of bis(ethylacetate)calcium difluorophosphate...]. Zeitschrift für anorganische und allgemeine Chemie. 365 (5–6): 294–300. doi:10.1002/zaac.19693650509.
- ^ a b c d e Brown, S.D.; Emme, L.M.; Gard, G.L. (December 1975). "The reaction of chromium trioxide and metal oxide salts with P2O3F4". Journal of Inorganic and Nuclear Chemistry. 37 (12): 2557–2558. doi:10.1016/0022-1902(75)80891-8.
- ^ Wimmer, F.L.; Snow, M.R. (1978). "Perchlorate and difluorophosphate coordination derivatives of manganese carbonyl". Australian Journal of Chemistry. 31 (2): 267. doi:10.1071/CH9780267.
- ^ a b c Dove, Michael F. A.; Hibbert, Richard C.; Logan, Norman (1985). "Difluorophosphate complexes of chromium, manganese, iron, cobalt, and nickel". Journal of the Chemical Society, Dalton Transactions (4): 707. doi:10.1039/DT9850000707.
- ^ a b c d e f Weil, Matthias; Fürst, Markus (2020-07-01). "Crystal structure of (1,4-diphenyl-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)phenylamine difluorophosphate, and a survey of the difluorophosphate anion (PO2F2−)". Acta Crystallographica Section E. 76 (7): 1003–1006. doi:10.1107/S2056989020006933. ISSN 2056-9890. PMC 7336792. PMID 32695441.
- ^ a b Begley, Michael J.; Dove, Michael F. A.; Hibbert, Richard C.; Logan, Norman; Nunn, Michael; Sowerby, D. Bryan (1985). "Crystal structures of the difluorophosphate complexes, Co(O2PF2)2 · 2MeCN and Cu(O2PF2)2". Journal of the Chemical Society, Dalton Transactions (11): 2433–2436. doi:10.1039/DT9850002433.
- ^ Keller, Sarah; Brunner, Fabian; Prescimone, Alessandro; Constable, Edwin C.; Housecroft, Catherine E. (August 2015). "Hexafluoridophosphate partial hydrolysis leading to the one-dimensional coordination polymer [{Cu(xantphos)(μ-PO2F2)}n]". Inorganic Chemistry Communications. 58: 64–66. doi:10.1016/j.inoche.2015.06.002.
- ^ a b c Schaible, B.; Weidlein, J. (February 1974). "Untersuchungen an Dialkylmetallphosphor- und -phosphinsäurederivaten der Elemente Aluminium, Gallium, Indium und Thallium. II. Die Schwingungsspektren der Difluoro- und Dichlorophosphate" [Investigations upon dialkylmetal phosphate and phosphite derivatives of the elements aluminium, gallium, indium and thallium. II. The vibrational spectroscopy of difluoro- and dichlorophosphates]. Zeitschrift für anorganische und allgemeine Chemie. 403 (3): 301–309. doi:10.1002/zaac.19744030309.
- ^ a b Albrecht, Markus; Hübler, Klaus; Kaim, Wolfgang (May 2000). "Syntheses, Structures, and Properties of the Complexes [Ag(N∧S)n](X), N∧S = 1-Methyl-2-(alkylthiomethyl)-1H-benzimidazoles, X = PF6 (n = 2) or PO2F2 (n = 1)". Zeitschrift für anorganische und allgemeine Chemie. 626 (5): 1033–1037. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1521-3749(200005)626:5<1033::AID-ZAAC1033>3.0.CO;2-A.
- ^ Fessler, Th. U.; Hübener, R.; Strähle, J. (September 1997). "Synthese von Kupfer- und Silberkomplexen mit fünfzähnigen N,S- und sechszähnigen N,O-Chelatliganden – Charakterisierung und Kristallstrukturen von {Cu2[C6H4(SO2)NC(O)]2(C5H5N)4}, {Cu2[C5H3N(CHNC6H4SCH3)2]2}(PF6)2 und {Ag[C5H3N(CHNC6H4SCH3)2]}PO2F2" [Synthesis of copper und silver complexes with pentadentate N,S- und hexadentate N,O-chelation ligands – characterization und crystal structures of...]. Zeitschrift für anorganische und allgemeine Chemie. 623 (9): 1367–1374. doi:10.1002/zaac.19976230908.
- ^ a b c Krüger, N.; Dehnicke, K.; Shihada, A.-F. (February 1978). "Difluorophosphate von Zinn(IV) und Antimon(V)" [Difluorophosphates of tin(IV) and antimony(V)]. Zeitschrift für anorganische und allgemeine Chemie. 438 (1): 169–175. doi:10.1002/zaac.19784380118.
- ^ a b Horn, E.; Snow, M.R. (1980). "Perchlorate and difluorophosphate coordination derivatives of rhenium carbonyl". Australian Journal of Chemistry. 33 (11): 2369. doi:10.1071/CH9802369.
- ^ LeBlanc, D. J.; Britten, J. F.; Lock, C. J. L. (15 September 1997). "Bis(triphenylphosphine sulfide-)gold(I) Difluorophosphate(V)". Acta Crystallographica Section C. 53 (9): 1204–1206. doi:10.1107/S0108270197005209.
- ^ a b Addou, A.; Vast, P. (July 1980). "Préparation de nouveaux difluorodioxophosphates à partir de l'oxyde de difluorure de phosphoryle. Partie II. Réactions sur les acides iodique et periodique" [Preparation of new difluorodioxophosphates from phosphoryl difluoride oxide. Part II. Reactions with iodic and periodic acids]. Journal of Fluorine Chemistry. 16 (1): 89–96. doi:10.1016/s0022-1139(00)85151-9.
- ^ a b Eisenberg, Max; Desmarteau, Darryl D. (August 1972). "Xenon(II) difluorophosphates. Preparations, properties, and evidence for the difluorophosphate free radical". Inorganic Chemistry. 11 (8): 1901–1904. doi:10.1021/ic50114a033.
- ^ Matsumoto, Kazuhiko; Okawa, Takeshi; Hagiwara, Rika (2012). "The Crystal to Plastic Crystal Phase Transition of Tetraethylammonium Difluorophosphate and Tetrafluoroborate". Chemistry Letters. 41 (4): 394–396. doi:10.1246/cl.2012.394. hdl:2433/259816. S2CID 97011854.
- ^ a b c d Matsumoto, Kazuhiko; Hagiwara, Rika (3 August 2009). "A New Series of Ionic Liquids Based on the Difluorophosphate Anion". Inorganic Chemistry. 48 (15): 7350–7358. doi:10.1021/ic9008009. PMID 19580312.
- ^ Eriks, K.; Wang, H. H.; Reed, P. E.; Beno, M. A.; Appelman, E. H.; Williams, J. M. (15 February 1985). "Di(3,3′,4,4′-tetramethyl-2,2′,5,5′-tetraselenafulvalenium)difluorophosphate, (C10H12Se4)2PO2F2, at 293 and 125 K". Acta Crystallographica Section C. 41 (2): 257–260. doi:10.1107/S0108270185003535.
- ^ Lange, Willy; Livingston, Ralph (March 1950). "Studies of Fluorophosphoric Acids and their Derivatives. XIV. Preparation of Anhydrous Difluorophosphoric Acid". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 72 (3): 1280–1281. doi:10.1021/ja01159a057.
- ^ Semmoud, A.; Benghalem, A.; Addou, A. (January 1990). "Acide difluorophosphorique: nouvelle préparation" [Difluorophosphoric acid: new preparation]. Journal of Fluorine Chemistry. 46 (1): 1–6. doi:10.1016/S0022-1139(00)81555-9.
- ^ Vast, P.; Semmoud, A.; Addou, A.; Palavit, G. (March 1985). "Nouvelle méthode de preparation de l'acide difluorophosphorique" [New preparation method of difluorophosphoric acid]. Journal of Fluorine Chemistry. 27 (3): 319–325. doi:10.1016/S0022-1139(00)81312-3.
- ^ Zeng, Xiaoqing; Gerken, Michael; Beckers, Helmut; Willner, Helge (17 June 2010). "ChemInform Abstract: Spectroscopic and Structural Studies of Difluorophosphoryl Azide F2P(O)N3, Difluorophosphoryl Isocyanate F2P(O)NCO, and Difluorophosphoric Acid Anhydride, F2(O)POP(O)F2". ChemInform. 41 (28): no. doi:10.1002/chin.201028001. Originally in Inorg. Chem. 49 (2010) 6, 3002–3010
- ^ Robinson, E. A. (September 1962). "The Preparation and Raman Spectrum of Diphosphoryl Tetrafluoride: Comparison with the Spectrum of Diphosphoryl Tetrachloride". Canadian Journal of Chemistry. 40 (9): 1725–1729. doi:10.1139/v62-264.
- ^ Dehnicke, Kurt; Shihada, Abdel-Fattah (1976). "Structural and bonding aspects in phosphorus chemistry—inorganic derivatives of oxohalogeno phosphoric acids". Electrons in Oxygen- and Sulphur-Containing Ligands Structure and Bonding. Structure and Bonding. 28: 51–82. doi:10.1007/3-540-07753-7_2. ISBN 978-3-540-07753-4.
- ^ Christe, K. O.; GNANN, R.; WAGNER, R. I.; WILSON, W. W. (4 August 2010). "ChemInform Abstract: The (PO2F2×2 AsF5)− Anion, an Example of a Stable, Oxygen- Bridged, 1:2 Donor-Acceptor Polynuclear Anion". ChemInform. 28 (2): no. doi:10.1002/chin.199702025. Full article at Eur. J. Solid State Inorg. Chem. 33 (1996) 9, 865–877
- ^ Olah, Georg; Oswald, Alexius; Kuhn, Stephan (4 August 1959). "Untersuchung organischer Phosphorverbindungen. III. Darstellung von Difluorphosphorsäure- und von Difluorthiophosphorsäure-alkylamiden" [Investigations of organic phosphorus compounds. III. description of difluorophosphoric and difluorothiophosphoric alkylamides]. Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie. 625 (1): 88–91. doi:10.1002/jlac.19596250111.


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch
