Tourism in Africa


Tourism is an important economic sector for many countries in Africa. There are many countries that benefit heavily from tourism like Kenya, Uganda, Algeria, Egypt, South Africa, Morocco, Tunisia, Ghana and Tanzania.[1] The touristic particularity of Africa lies in the wide variety of points of interest, diversity and multitudes of landscapes as well as the rich cultural heritage. Also, an ecotourist industry is present in some African countries (e.g., South Africa, Kenya, Namibia, Rwanda, Zambia, Uganda, Mozambique, etc.).[2]
Overview
[edit]Countries in Africa started investing in their tourism markets since the late 1960s and 1970s and are at different levels of tourism development. Countries in the continent of Africa are typically categorized using Butler's 1980 Tourist Area Life Cycle (TALC) model which is a common model that describes six specific stages of tourism development for all countries worldwide: exploration, involvement, development, consolidation and stagnation.[3]
However, a World Bank study in 2011 classified also African countries in to 4 categories based on performance. These performance groupings were based on indicators such business environment; tourism regulation, infrastructure, resources, tourism income, number of visitors and the potential growth of the market.
- “pre-emergent”: Somalia, Sudan, Eritrea, Comoros, Togo, Guinea, Chad, Guinea Bissau, Niger, Central African Rep., Congo D.R., Liberia, Congo Rep., Equatorial Guinea
- “potential”: Madagascar, Ethiopia, Mauritania, Mali, Benin, São Tomé and Príncipe, Sierra Leone, Burundi, Côte d’Ivoire, Nigeria, Lesotho, Angola, Swaziland, Cameroon, and Gabon
- “emerging”: Seychelles, Zambia, Uganda, Rwanda, The Gambia, Senegal, Zimbabwe, Burkina Faso, Malawi, and Mozambique
- “consolidating”: Morocco, South Africa, Mauritius, Tanzania, Kenya, Cape Verde, Ghana, Namibia, Botswana.[4][5]
Tourism sectors
[edit]Ecotourism
[edit]
Ecotourism is the concept of responsible trips and travel to areas that might be protected and especially fragile. The intent is to create as little detrimental impact on the environment as possible. In some locations (such as Gorongosa National Park) where the wildlife has previously been decimated, rewilding has been done and much of the wildlife has been brought back (along with vegetation, thus allowing the environment to sequester more carbon then what was previously the case). This return of wildlife has created tourism opportunities (wildlife viewing, safari trips) allowing to bring in financial revenue. It also requires personnel such as park rangers, to be present, thus creating local employment opportunities.
Historical sites and monuments
[edit]Africa has many historic structures that have survived from ancient civilizations as well as more recent structures of interest to tourists. Ancient historical sites include the Pyramids and temples in both Egypt and Sudan; The Obelisk of Axum from Ethiopia; the ruins of ancient Zimbabwe's trading city, Great Zimbabwe; and the Palace of Emperor Fasilides in Ethiopia.[6][7][8][9][10][11] More recent structures that attract tourism includes the old slave castles in Ghana, Elmina Castle and Cape Coast Castle, which are also sited for heritage tourism. It also includes the highest monument in the world, the African Renaissance Monument in Senegal.[12][13]
Medical tourism
[edit]Due to advance in technologies, techniques and practices and lower costs, Africa has experienced a surge in medical tourism and health tourism. Countries that are destinations for medical and health tourism packages include Algeria, Ghana, Ivory Coast, Kenya, Mauritius, Morocco, Nigeria, Rwanda, South Africa, Tanzania and Tunisia. The top destinations for European visitors include Egypt, Tunisia, and South Africa. South Africa is the top destination for both international tourists and regional tourists from other African countries.[14][15]
Tea tourism
[edit]Africa has a rich history of tea cultivation which has given rise to several countries becoming growing tea tourism destinations. Malawi was the first country to grow tea in Africa, and has many tea estates that are decades old. Countries like Morocco, Kenya, Malawi, South Africa are large tea-producing countries which are frequented by tea tourists. South Africa's tea tourism market is focused on rooibos tea.[16][17]
Tourism by arrivals
[edit]All of the data presented here is from the World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) and from "Reviewing Africa in the Global Tourism Economy."[18] The following table shows the number of arrivals in each country:
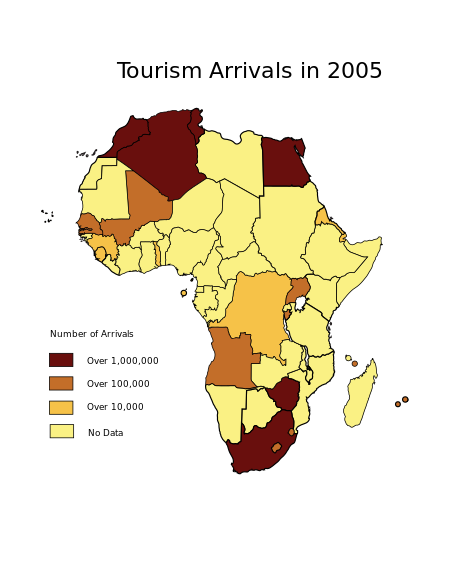
| Country[a] | Arrivals (2015) |
|---|---|
| 17,443,000 | |
| 210,000 | |
| 1,559,000 | |
| 148,000 | |
| 210,000 | |
| 198,000 | |
| 61,000 | |
| 30,000 | |
| 4,244,000 | |
| 83,000 | |
| 111,000 | |
| 45,000 | |
| 304,000 | |
| 143,000 | |
| 934,827 (2020)[19] | |
| 9,409,000 | |
| 11,000 | |
| 769,000 | |
| 129,000 | |
| 40,000 | |
| 7,518,000 | |
| 839,000 | |
| 81,000 | |
| 6,378,000 | |
| 1,468,000 (2017) | |
| 1,559,000 |
Tourism by receipts
[edit]The following map and data depict the income from tourism in US dollar equivalent:
| Country[b] | Receipts (2020) in US$ |
|---|---|
| $562,000,000 | |
| $2,000,000 | |
| $123,000,000 | |
| $16,851,000,000 | |
| $66,000,000 | |
| $879,000,000 | |
| $30,000,000 | |
| $26,000,000 | |
| $4,617,000,000 | |
| $130,000,000 | |
| $348,000,000 | |
| $384,000,000 | |
| $192,000,000 | |
| $83,000,000 | |
| $7,327,000,000 | |
| $89,000,000 | |
| $1,400,000,000 | |
| $2,063,000,000 | |
| $4,468,000,000 | |
| $1,559,000 |
Notes
[edit]- ^ No data is available for Benin, Burkina Faso, Central African Republic, Chad, Comoros, Republic of the Congo, Côte d'Ivoire, Equatorial Guinea, Ethiopia, Gabon, Ghana, Guinea-Bissau, Kenya, Libya, Madagascar, Malawi, Mauritania, Mozambique, Namibia, Niger, Nigeria, Rwanda, Sudan, Tanzania and Zambia.
- ^ No data is available for Algeria, Angola, Benin, Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Comoros, Republic of the Congo, Côte d'Ivoire, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Djibouti, Equatorial Guinea, Ethiopia, Gabon, Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Libya, Madagascar, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, Nigeria, Rwanda, Sao Tome and Principe, Senegal, Togo, Swaziland and Zambia.
Visa policies to visit
[edit]- Algeria
- Angola
- Benin
- Botswana
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Cameroon
- Cape Verde
- Central African Republic
- Chad
- Comoros
- Democratic Republic of the Congo
- Republic of the Congo
- Djibouti
- Egypt
- Equatorial Guinea
- Eritrea
- Eswatini
- Ethiopia
- Gabon
- The Gambia
- Ghana
- Guinea
- Guinea-Bissau
- Ivory Coast
- Kenya
- Lesotho
- Liberia
- Libya
- Madagascar
- Malawi
- Mali
- Mauritania
- Mauritius
- Morocco
- Mozambique
- Namibia
- Niger
- Nigeria
- Rwanda
- São Tomé and Príncipe
- Senegal
- Seychelles
- Sierra Leone
- Somalia
- South Africa
- South Sudan
- Sudan
- Tanzania
- Togo
- Tunisia
- Uganda
- Zambia
- Zimbabwe
See also
[edit]- Economy of Africa
- ECOWAS ECOTOUR
- Africa Travel Association
- African Continental Free Trade Area
- Rail transport in Africa
- Single African Air Transport Market
- CARICOM passport (Caribbean Community)
- UN Decade on Ecosystem Restoration
- Safari lodge
- UN Tourism
References
[edit]- ^ WhiteOrange. "Homepage". Ghana Tourism Authourity. Retrieved 2020-09-03.
- ^ Africa can Benefit from Nature-based Tourism in a Sustainable Manner
- ^ "Butler's Tourism Area Life Cycle Model: A simple explanation | Tourism Teacher".
- ^ Signé, Landry (2019-03-05). "Africa's tourism: A global destination for investment and entrepreneurship". Brookings. Retrieved 2023-05-09.
- ^ World Bank, 2011, The Africa Region Tourism Strategy: Transformation through Tourism, https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/server/api/core/bitstreams/883cf00a-5c7d-5d41-b91a-ddaa24e050ea/content
- ^ "The pyramids few tourists have seen".
- ^ "These mighty pyramids were built by one of Africa's earliest civilizations". National Geographic Society. 28 December 2022. Archived from the original on December 28, 2022.
- ^ "Obelisk returned to Ethiopia after 68 years". The Guardian. 20 April 2005.
- ^ https://whc.unesco.org/en/news/116 https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/364/
- ^ "Zimbabwe Travel Guide - A Travel Guide to Great Zimbabwe".
- ^ "15 famous buildings in Africa that showcase continent's iconic architecture". 27 August 2022.
- ^ Underwood, Joseph L. (2022-09-26). "Authorship & Authority: The Contested Origins of Dakar's African Renaissance Monument". ARTnews.com. Retrieved 2023-05-09.
- ^ "Ghana cashes in on slave heritage tourism". Reuters. 2019-08-20. Retrieved 2023-05-09.
- ^ "Medical tourism in Africa: Sun, sea, scalpel and safari".
- ^ Mogaka JJ, Tsoka-Gwegweni JM, Mupara LM, Mashamba-Thompson T. Role, structure and effects of medical tourism in Africa: a systematic scoping review protocol. BMJ Open. 2017 Jun 23;7(6):e013021. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-013021. PMID 28645947; PMCID: PMC5541447.
- ^ "20+ Best Destinations for Tea Tourism Around the World".
- ^ Phori, Madiseng & Mathole, Lebo & Henama, Unathi & Mokoena, Lehlohonolo. (2022). Tea tourism in the global south: An African perspective.
- ^ Rogerson, Christian (2017). "Reviewing Africa in the global tourism economy", Vol. 24 No. 3 United Nations World Tourism Organization. September 2017.
- ^ "Tourist arrival 2020 (mauritius)" (PDF). Retrieved 7 January 2012.
External links
[edit]![]() Media related to Tourism in Africa at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Tourism in Africa at Wikimedia Commons


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch