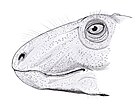
Ennatosaurus
| Ennatosaurus Temporal range: | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Synapsida |
| Clade: | †Caseasauria |
| Family: | †Caseidae |
| Genus: | †Ennatosaurus Efremov, 1956 |
| Type species | |
| Ennatosaurus tecton Efremov, 1956 | |
Ennatosaurus is an extinct genus of caseid synapsid that lived during the Middle Permian (late Roadian - early Wordian) in northern European Russia.[1] The genus is only represented by its type species, Ennatosaurus tecton, which was named in 1956 by Ivan Antonovich Efremov.[2] The species is known from at least six skulls associated with their lower jaws (two of them preserved with the hyoid apparatus), as well as from the postcranial bones of several juvenile individuals.[3][4][5] Ennatosaurus has the typical caseid skull with a short snout tilted forward and very large external nares. However, it differs from other derived caseids by its postcranial skeleton with smaller proportions compared to the size of the skull.[3][5] As with other advanced caseids, the teeth of Ennatosaurus were well suited for slicing and cutting vegetation.[3] The presence of a highly developed hyoid apparatus indicates the presence of a massive and mobile tongue, which had to work in collaboration with the palatal teeth during swallowing.[3][6] With a late Roadian - early Wordian age, Ennatosaurus is one of the last known caseids[1] (with Lalieudorhynchus from southern France).
Etymology
[edit]Ennatosaurus tecton means "ninth carpenter lizard". The strangeness of the name of this synapsid is related to its very unusual origin since the genus and species names correspond to the translation into Greek of the meaning of the Russian names of the discoverers of the first fossils of this animal. The genus name is dedicated to Tatyana A. Devyataya (the feminine form of Devyatyi whose name means ‘ninth’ = "ennatos" in Greek) and of "saurus" meaning lizard. The species honors Mikhail Alekseevich Plotnikov (after the Russian plotnik, meaning "carpenter" = "tecton" in Greek).[7]
Description
[edit]
Ennatosaurus is known by several adult skulls (PIN 1580/14, 17 (holotype), 122, 4543/1), as well as by a juvenile skull (PIN 1580/24) associated with many postcranial elements from several individuals.[3][4] All these elements allowed the reconstruction of a composite skeleton. Unlike all other derived caseids that have a tiny skull relative to the body size, Ennatosaurus is peculiar by the small size of its postcranial skeleton compared to that of its skull. However, almost all of the postcranial material in Ennatosaurus belongs to juvenile individuals, and the unusual proportions of this composite skeleton could be explained by the mounting of an adult skull on a juvenile skeleton. However, the existence of some bones of subadult and adult individuals suggests that Ennatosaurus did indeed have a proportionally smaller body than that of other derived caseids.[3][5] The largest adult skull of Ennatosaurus (the holotype PIN 1580/17) is approximately 17 cm long, a size similar to the skull of Cotylorhynchus romeri, while the few adult bones of Ennatosaurus are half the size of the corresponding adult elements in C. romeri.[3]
As in other caseids, Ennatosaurus has a very short skull with a snout sharply sloping forward and very large external nares. Ennatosaurus is distinguished, however, by its proportionally longer facial region than in Casea and Euromycter. The dorsal ramus of each premaxilla contributes to a narrow intranarial bar, narrower than that of Euromycter, but of width similar to that of Cotylorhynchus romeri. The skull roof is distinguished by the very large contribution of the frontal to the dorsal margin of the orbit. It occupies about 50% of the length of the latter while in Euromycter and C. romeri the frontal represents less than 10% of the margin of the orbit. The jugal is very characteristic in having a thick and very elongated anterior ramus creating an area of extended contact with the lacrimal. In other caseids, the anterior ramus is very thin and ends in narrow vertical contact with the lacrimal. Ennatosaurus also differs from all other caseid in its temporal fenestrae significantly larger than the nostrils and orbits, its palate with a narrower parasphenoid, and its upper dentition more reduced in number. In Ennatosaurus, each premaxilla and maxilla only have two and eight teeth respectively against 4 and 11 teeth respectively in Euromycter and 3 and 15 or 16 teeth in C. romeri.[3][4] The premaxillary teeth are conical in shape, the following teeth are spatulate with five to seven cuspules arranged longitudinally.[4]

The postcranial skeleton also shows many original characters. The vertebral centra of all regions of the body are characterized by the presence of two well-developed ventrolateral pits, deep and elongated anteroposteriorly. The neural spines of the vertebrae show a diamond-shaped section along its entire length, a condition similar to that observed in Ruthenosaurus. The vertebrae of the "lumbar region" are characterized by the absence of fused or co-ossified ribs (a characteristic to be taken with caution given the juvenile condition of the specimens). The humerus has a robust ectepicondyle and a not completely closed ectepicondylar foramen. A deep and well marked fossa is present immediately behind the acetabular buttress of the ilium. The femur is very characteristic, its proximal articular surface is much wider dorsoventrally than anteroposteriorly and an elevated and robust bony crest extends from the narrowest part of the shaft to the top of the posterior condyle with which it merges to form a single support structure. The intertrochanteric fossa is much more developed mediolaterally than anteroposteriorly in relation with the conformation of the proximal articular surface. The tibia is distinguished by its flattened shaft with a subelliptic and non-circular cross section, as is the case in most caseids which have not undergone diagenetic deformation. The manus is not fully known and the preserved elements indicate a phalangeal formula 2-2-3-?-2. It was probably similar to that of the foot, more complete, whose formula is 2-2-3-3-2. The toes are short and terminated by small unguals similar to blunt claws.[3][5]
Geographic and stratigraphic range
[edit]All the fossils of Ennatosaurus tecton are from Arkhangelsk Oblast in northern European Russia. The holotype and the majority of the referred specimens were discovered in 1955 in the Nijneoustinskaia Formation (Karpogorskaia Member), on the banks of the Pinega River, and come from the locality of Moroznitsa near the town of Karpoga in the Pinezhsky District.[3][8][4] A nearly complete skull with lower jaw, a fragment of the cheek region of a second skull, and an incomplete dentary were also discovered in the Krasnoshelskaia Formation, near the village of Nisogora (Leshukonsky District), on the banks of the Mezen River, more than 100 km east of the first site.[8][4] Ennatosaurus has long been known as one of the last caseids with a middle Permian age. But a more precise age was difficult to assess because Ennatosaurus is the only known vertebrate at the Moroznitsa locality.[9][3] A Capitanian age was sometimes mentioned.[4] However, the Nisogora locality, which has yielded Ennatosaurus remains, contains a more diverse fauna containing the parareptiles Nyctiphruretus acudens, Macroleter poezicus and Lanthaniscus efremovi, the Varanopidae Mesenosaurus romeri, and the juvenile therapsid of uncertain affinity Niaftasuchus zekkeli.[10] All these species (except Ennatosaurus) are also known in at least eight other localities of the Arkhangelsk Oblast which have yielded additionally the parareptiles Lanthanolania ivachnenkoi, Bashkyroleter mesensis and Nycteroleter ineptus, the Varanopidae Pyozia mesensis, and several basal therapsids : the Nikkasauridae Nikkasaurus tatarinovi, Reiszia gubini and R. tippula, the biarmosuchian Alrausuchus tagax,[10] and a yet undescribed basal anteosaurid dinocephalian.[11][12] This fauna constitutes the Mezen assemblage which is more or less contemporary with the Ochyor (or Ocher) assemblage. Magnetostratigraphic data suggests that these two faunal assemblages are late Roadian to early Wordian in age.[13][1] Compared to the Ochyor assemblage largely dominated by therapids (Estemmenosuchus, the anteosaur Archaeosyodon, Biarmosuchus, and the anomodont Otsheria), the Mezen assemblage, characterized by the presence of pelycosaurs, the great diversity of small terrestrial parareptiles, and more primitive therapsids, seems more archaic. These two faunal assemblages were geographically separated from each other by a marine area. It is possible that the Mezen assemblage is a relict fauna which lived in the regions of marshy plains west of the Kazanian Sea, while the Ochyor fauna lived east of this sea, along the Paleo-Urals mountains.[1][10]
In 2016, Mujal and colleagues attributed to cf. Ennatosaurus tecton, an incomplete posterior dorsal vertebra (including the dorsal half of the centrum and the base of the neural arch) found in deposits possibly dating from the Middle Permian of La Vansa i Fórnols in northern Spain (Province of Lleida).[14] This tentative determination was based on the presence of a small pit on the lateral surface of the centrum. However, Romano and colleagues have shown that the very small size and location of the pit of the Spanish vertebra does not correspond to the large elongated pits clearly visible in lateral and ventral views on all vertebrae of Ennatosaurus tecton[5] (as Olson had already figured in 1968[3]). The small pit of the Spanish vertebra probably represents a perforation for the blood vessels, and its owner currently remains unidentified.[5]
Phylogeny
[edit]In the first phylogenetic analysis of Caseidae published in 2008, Ennatosaurus was identified as the sister group of a clade containing Cotylorhynchus romeri and Angelosaurus dolani. The Wordian age of Ennatosaurus compared to the two American species dated to the Lower Permian indicates that the Russian species is the product of a ghost lineage of several million years.[4]
Below the first phylogenetic analysis of Caseidae published by Maddin et al. in 2008.[4]
| Caseasauria |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In 2015, Romano and Nicosia published the first cladistic study including almost all the Caseidae (with the exception of Alierasaurus ronchii of Sardinia, considered too fragmentary). In their most parsimonious analysis, Ennatosaurus is more closely related to the genus Angelosaurus . However, the close relationship between Angelosaurus dolani and Ennatosaurus tecton may be distorted by the extreme incompleteness of the material of the North American species.[15]
Below the most pasimonious phylogenetic analysis published by Romano & Nicosia in 2015.[15]
Two other cladogams published in 2020 by Berman and colleagues recover Ennatosaurus as the sister xaxon of a clade containing the taxa Angelosaurus romeri, Alierasaurus ronchii, and the three species of Cotylorhynchus.[16]
Below are the two Caseidae cladograms published by Berman and colleagues in 2020.[16]
In the cladogram published by Werneburg and colleagues in 2022, Ennatosaurus occupies a similar position between Euromycter and all more derived caseids.[17]
Below is the cladogram published by Werneburg and colleagues in 2022.[17]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d Golubev, V.K. (2015). "Dinocephalian Stage in the History of the Permian Tetrapod Fauna of Eastern Europe". Paleontological Journal. 49 (12): 1346–1352. doi:10.1134/S0031030115120059. S2CID 130694755.
- ^ Efremov, I.A. (1956). "[American elements in the fauna of Permian reptiles of the U.S.S.R.]". Doklady Akademii Nauk SSSR. 111 (5): 1091-1094 [in Russian].
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Olson, E.C. (1968). "The family Caseidae". Fieldiana: Geology. 17: 225–349.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Maddin, H.C.; Sidor, C.A.; Reisz, R.R. (2008). "Cranial anatomy of Ennatosaurus tecton (Synapsida: Caseidae) from the Middle Permian of Russia and the evolutionary relationships of Caseidae". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 28 (1): 160–180. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2008)28[160:CAOETS]2.0.CO;2. S2CID 44064927.
- ^ a b c d e f Romano, M.; Brocklehurst, N.; Fröbisch, J. (2017). "The postcranial skeleton of Ennatosaurus tecton (Synapsida, Caseidae)". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 16 (13): 1097–1122. doi:10.1080/14772019.2017.1367729. S2CID 89922565.
- ^ Kemp, T.S. (2005). The Origin & Evolution of Mammals. Oxford University Press. p. 22. ISBN 978-0198507611.
- ^ "The Gift of Names: Tuditanus, Ennatosaurus, Bottosaurus, and more". Archives of the Dinosaur Mailing List. Ben Creisler. Retrieved 22 December 2014.
- ^ a b Ivakhnenko, M.F. (2008). "[Subclass Ophiacomorpha]". In Ivakhnenko, M.F.; Kurochkin, E.N. (eds.). [Fossil Vertebrates from Russia and Adjacent Countries. Fossil reptiles and birds. Part 1] (in Russian). Moscow: GEOS. pp. 95–100.
- ^ Olson, E.C. (1962). "Late Permian terrestrial vertebrates, U.S.A. and U.S.S.R.". Transactions of the American Philosophical Society. New Series. 52 (52): 1–224. doi:10.2307/1005904. JSTOR 1005904.
- ^ a b c Ivakhnenko, M.F. (2008). "Cranial morphology and evolution of Permian Dinomorpha (Eotherapsida) of Eastern Europe". Paleontological Journal. 42 (42, 859–995): 859–995. doi:10.1134/S0031030108090013. S2CID 85114195.
- ^ Jansen, M.; Reisz, R.R.; Fröbisch, J. (2012). "A new basal dinocephalian from the Middle Permian Mezen fauna (Russia) and its implications for the evolution of basal therapsids". Conference Proceedings of the Centenary Meeting of the Paläontologische Gesellschaft, Terra Nostra 2013(3): 85–86.
- ^ Jansen, M.; Reisz, R.R.; Kammerer, C.F.; Fröbisch, J. (2013). "3D reconstruction of a basal therapsid skull – combining modern and conventional methods for 3D retro-deformation". Palaeontology & Geobiology of Fossil Lagerstätten through Earth History.Abstract Volume, Göttingen, Universitätsdrucke: 93: 77–78.
- ^ Gorsky, V.P.; Gusseva, E.A.; Crasquin-Soleau, S.; Broutin, J. (2003). "Stratigraphic data of the Middle – Late Permian on Russian Platform". Geobios. 36 (5): 533–558. doi:10.1016/S0016-6995(03)00057-3.
- ^ Mujal, E.; Gretter, N.; Ronchi, A.; López-Gómez, J.; Falconnet, J.; Diez, J.B.; De la Horra, R.; Bolet, A.; Oms, O.; Arche, A.; Barrenechea, J.F.; Steyer, J.S.; Fortuny, J. (2016). "Constraining the Permian/Triassic transition in continental environments : Stratigraphic and paleontological record from the Catalan Pyrenees (NE Iberian Peninsula)". Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology. 445: 18–37. Bibcode:2016PPP...445...18M. doi:10.1016/j.palaeo.2015.12.008.
- ^ a b Romano, M.; Nicosia, U. (2015). "Cladistic analysis of Caseidae (Caseasauria, Synapsida): using the gap-weighting method to include taxa based on incomplete specimens". Palaeontology. 58 (6): 1109–1130. doi:10.1111/pala.12197. S2CID 86489484.
- ^ a b Berman, D.S.; Maddin, H.C.; Henrici, A.C.; Sumida, S.S.; Scott, D.; Reisz, R.R. (2020). "New primitive Caseid (Synapsida, Caseasauria) from the Early Permian of Germany". Annals of Carnegie Museum. 86 (1): 43–75. doi:10.2992/007.086.0103. S2CID 216027787.
- ^ a b Werneburg, R.; Spindler, F.; Falconnet, J.; Steyer, J.-S.; Vianey-Liaud, M.; Schneider, J.W. (2022). "A new caseid synapsid from the Permian (Guadalupian) of the Lodève basin (Occitanie, France)" (PDF). Palaeovertebrata. 45 (45(2)-e2): e2. doi:10.18563/pv.45.2.e2. S2CID 253542331.


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch