Histopathologic diagnosis of prostate cancer
A histopathologic diagnosis of prostate cancer is the discernment of whether there is a cancer in the prostate, as well as specifying any subdiagnosis of prostate cancer if possible. The histopathologic subdiagnosis of prostate cancer has implications for the possibility and methodology of any subsequent Gleason scoring.[1] The most common histopathological subdiagnosis of prostate cancer is acinar adenocarcinoma, constituting 93% of prostate cancers.[2] The most common form of acinar adenocarcinoma, in turn, is "adenocarcinoma, not otherwise specified", also termed conventional, or usual acinar adenocarcinoma.[3]
Sampling
[edit]
The main sources of tissue sampling are prostatectomy and prostate biopsy.[citation needed]
Subdiagnoses - overview
[edit]
| Subdiagnosis | Relative incidence | Image | Microscopic characteristics | Immunohistochemistry | Gleason scoring | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Core biopsy | Radical prostatectomy | ||||||
| Acinar adenocarcinoma - 93%[2] | Adenocarcinoma (not otherwise specified/ conventional/ usual acinar)[3] | 77%[notes 2] | 54%[notes 2] | 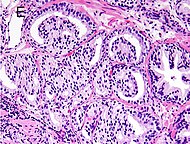 | Further information in section below
| Tumorous glands: | As usual |
| Foamy gland carcinoma | 17%[5][notes 1] | 13–23%[5][notes 1] | Based on architecture, discounting foamy cytoplasms[1] | ||||
| Atrophic carcinoma | 2%[5][notes 3] | 16%[5][notes 3] | Tumorous glands: | As usual[1] | |||
| Pseudohyperplastic carcinoma | 2%[5] | 11%[5] |
| Tumorous glands: | 3+3=6[1] | ||
| Microcystic carcinoma | 11%[5] | On (usually) adjacent acinar adeocarcinoma[6] | |||||
| PIN-like | 1.3%[7] |
| Tumorous glands:
| Not recommended[1] | |||
| Non acinar (or mixed acinar/ non-acinar) adenocarcinoma | Ductal adenocarcinoma | 3% to 12.7%[8][notes 1] |  | ||||
| Intraductal adenocarcinoma | 2.8%[10] | 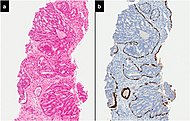 H&E and CK5/6 | |||||
| Urothelial carcinoma | 0.7 to 2.8%[12] |  |
| Not recommended[1] | |||
| Small-cell carcinoma | 0.3–2%[14][15][notes 1] | 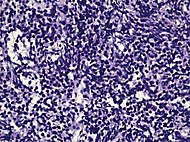 |
Half of cases have usual acinar components[1] | ||||
| Mucinous adenocarcinoma | 0.2%[12] | 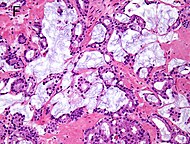 |
| Tumorous glands: | 4+4=8 for irregular cribriform glands floating in mucin.[1] | ||
| Signet-ring adenocarcinoma | 0.02%[16] | 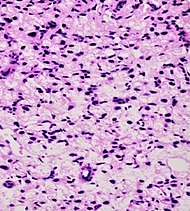 |
| Tumorous glands: | Not recommended[1] | ||
| Basal-cell carcinoma | 0.01%[17] | Basaloid tumor:
BCC-pattern:
| Not recommended.[1] | ||||

In uncertain cases, a diagnosis of malignancy can be excluded by immunohistochemical detection of basal cells (or confirmed by absence thereof),[4] such as using the PIN-4 cocktail of stains, which targets p63, CK-5, CK-14 and AMACR (latter also known as P504S).
Other prostate cancer tumor markers may be necessary in cases that remain uncertain after microscopy.
Acinar adenocarcinoma
[edit]These constitute 93% of prostate cancers.[2]
Microscopic characteristics
[edit]- Specific but relatively rare
- [notes 4]
- Collagenous micronodules[4]
- Glomerulations,[4] epithelial proliferations into one or more gland lumina, typically a cribriform tuft with a single attachment to the gland wall.[18]
- Perineural invasion.[4] It should be circumferential[18][notes 5]
- Angiolymphatic invasion[4]
- Extraprostatic extension [4]
- Glomerulation.
- Relatively common and highly specific
- [4]
- Multiple nucleoli
- Eccentric nucleoli[4]
- Acinar adenocarcinoma with multiple nucleoli.
- Acinar adenocarcinoma with double and eccentric nucleoli.
- Less specific findings.
- Mitoses (also seen in for example high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (HGPIN) and prostate inflammation).[4]
- Prominent nucleoli[4]
- Intraluminal eosinophilic secretion[4]
- Intraluminal blue mucin[4]
- Adenocarcinoma with two mitoses in reactive epithelium.
- Acinar adenocarcinoma with intraluminal blue mucin.
In uncertain cases, a diagnosis of malignancy can be discarded by immunohistochemical detection of basal cells.[4]
- Atrophy is a differential diagnosis to prostate cancer. This example shows gradually increasing simple atrophy from left to right, H&E stain. Crowding and angulation may mimic that of adenocarcinoma, but there is nuclear basophilia rather than atypia, and occasional basal cells can still be seen.
- Also, seminal vesicle glands may mimic prostatic adenocarcinoma by crowded glands with enlarged hyperchromatic and irregular nuclei, but will have inconspicuous nucleoli and coarse refractile golden brown lipofuscin granules.[19]
Intraductal carcinoma
[edit]
Intraductal carcinoma of the prostate gland (IDCP), which is now categorised as a distinct entity by WHO 2016, includes two biologically distinct diseases. IDCP associated with invasive carcinoma (IDCP-inv) generally represents a growth pattern of invasive prostatic adenocarcinoma while the rarely encountered pure IDCP is a precursor of prostate cancer.[20] The diagnostic criterion of nuclear size at least 6 times normal is ambiguous as size could refer to either nuclear area or diameter. If area, then this criterion could be re-defined as nuclear diameter at least three times normal as it is difficult to visually compare area of nuclei.[20] It is also unclear whether IDCP could also include tumors with ductal morphology.[20] There is no consensus whether pure IDCP in needle biopsies should be managed with re-biopsy or radical therapy. A pragmatic approach would be to recommend radical therapy only for extensive pure IDCP that is morphologically unequivocal for high-grade prostate cancer.[20] Active surveillance is not appropriate when low-grade invasive cancer is associated with IDCP, as such patients usually have unsampled high-grade prostatic adenocarcinoma.[20] It is generally recommended that IDCP component of IDCP-inv should be included in tumor extent but not grade.[20] However, there are good arguments in favor of grading IDCP associated with invasive cancer.[20] WHO 2016 recommends that IDCP should not be graded, but it is unclear whether this applies to both pure IDCP and IDCP-inv.[20]
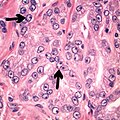
- Intraductal carcinoma of the prostate with an infiltrative growth pattern may be morphologically difficult to distinguish from invasive cancer. One focus shows comedonecrosis (arrow), morphologically suggesting Gleason pattern 5 invasive carcinoma (a haematoxylin and eosin, b CK5/6)[20]
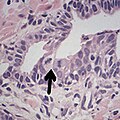
- Intraductal carcinoma of the prostate with very patchy basal cells identified by immunohistochemistry. At least some of the glands lacking basal cell immunoreactivity represent intraductal rather than invasive carcinoma (a haematoxylin and eosin, b CK 5/6)[20]
Ductal adenocarcinoma may have a prominent cribriforming architecture, with glands appearing relatively round, and may thereby mimic intraductal adenocarcinoma, but can be distinguished by the following features:[10]
| Feature | Ductal adenocarcinoma | Intraductal adenocarcinoma |
|---|---|---|
| True fibrovascular cores in micropapillary architecture | Present | Usually absent |
| Cribriform lumens | Lined by pseudostratified, columnar cells | Punched out lumens lined by cuboidal cells |
| Basal cell markers | Usually negative | Usually positive |
Further workup
[edit]Further workup of a diagnosis of prostate cancer includes mainly:[citation needed]
Notes
[edit]- ^ a b c d e At least where noted, the numbers include cases where the pattern is found admixed with usual acinar adenocarcinoma.
- ^ a b Numbers for usual acinar adenocarcinoma do not include mixed patterns with other types.
- ^ a b Number refers to sporadic atrophic pattern adenocarcinoma.
- ^ "Rare" here refers to prevalence at least in core biopsies.
-Cruz, Andrea O.; Santana, Amanda L. S.; Santos, Andréia C.; Athanazio, Daniel A. (2016). "Frequency of the morphological criteria of prostate adenocarcinoma in 387 consecutive prostate needle biopsies: emphasis on the location and number of nucleoli". Jornal Brasileiro de Patologia e Medicina Laboratorial. doi:10.5935/1676-2444.20160018. ISSN 1676-2444. - ^ Glands adjacent to and indenting nerves is not sufficient as a diagnostic criterion by itself. Glands partially surrounding a nerve is an indication of carcinoma.
- Robert V Rouse MD. "Prostatic Adenocarcinoma". Stanford Medical School. Archived from the original on 2019-09-11. Retrieved 2019-10-30. Last update 2/2/16
Reference list
[edit]- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag ah ai aj ak al am an ao ap aq ar as at au av aw ax ay az ba bb bc bd be bf bg bh bi Li J, Wang Z (February 2016). "The pathology of unusual subtypes of prostate cancer". Chin. J. Cancer Res. 28 (1): 130–43. doi:10.3978/j.issn.1000-9604.2016.01.06. PMC 4779761. PMID 27041935.
- ^ a b c d e f g Baig, Faraz A.; Hamid, Amna; Mirza, Talat; Syed, Serajuddaula (2015). "Ductal and Acinar Adenocarcinoma of Prostate: Morphological and Immunohistochemical Characterization". Oman Medical Journal. 30 (3): 162–166. doi:10.5001/omj.2015.36. ISSN 1999-768X. PMC 4459157. PMID 26171121.
- ^ a b "Prostatic Adenocarcinoma". Stanford University School of Medicine. Archived from the original on 2019-09-11. Retrieved 2019-10-30.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o Cruz, Andrea O.; Santana, Amanda L. S.; Santos, Andréia C.; Athanazio, Daniel A. (2016). "Frequency of the morphological criteria of prostate adenocarcinoma in 387 consecutive prostate needle biopsies: emphasis on the location and number of nucleoli". Jornal Brasileiro de Patologia e Medicina Laboratorial. doi:10.5935/1676-2444.20160018. ISSN 1676-2444.
- ^ a b c d e f g Humphrey, Peter A (2018). "Variants of acinar adenocarcinoma of the prostate mimicking benign conditions". Modern Pathology. 31 (S1): 64–70. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2017.137. ISSN 0893-3952. PMID 29297496.
- ^ a b c d e f Yaskiv, Oksana; Cao, Dengfeng; Humphrey, Peter A. (2010). "Microcystic Adenocarcinoma of the Prostate: A Variant of Pseudohyperplastic and Atrophic Patterns". The American Journal of Surgical Pathology. 34 (4): 556–561. doi:10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181d2a549. ISSN 0147-5185. PMID 20216381. S2CID 24149412.
- ^ Zhou, Ming (2018). "High-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia, PIN-like carcinoma, ductal carcinoma, and intraductal carcinoma of the prostate". Modern Pathology. 31 (S1): 71–79. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2017.138. ISSN 0893-3952. PMID 29297491.
- ^ Liu T, Wang Y, Zhou R, Li H, Cheng H, Zhang J (February 2016). "The update of prostatic ductal adenocarcinoma". Chin. J. Cancer Res. 28 (1): 50–7. doi:10.3978/j.issn.1000-9604.2016.02.02. PMC 4779765. PMID 27041926.
- ^ Robert V Rouse (2012-01-06). "Prostatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma". Stanford University School of Medicine.
- ^ a b c d e f Magers, Martin; Kunju, Lakshmi Priya; Wu, Angela (2015). "Intraductal Carcinoma of the Prostate: Morphologic Features, Differential Diagnoses, Significance, and Reporting Practices". Archives of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine. 139 (10): 1234–1241. doi:10.5858/arpa.2015-0206-RA. ISSN 0003-9985. PMID 26414467.
- ^ a b Roberts, Jordan A.; Zhou, Ming; Park, Yong Wok; Ro, Jae Y. (2013). "Intraductal Carcinoma of Prostate: A Comprehensive and Concise Review". Korean Journal of Pathology. 47 (4): 307–315. doi:10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2013.47.4.307. ISSN 1738-1843. PMC 3759629. PMID 24009625.
- ^ a b Grignon, David J (2004). "Unusual subtypes of prostate cancer". Modern Pathology. 17 (3): 316–327. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3800052. ISSN 0893-3952. PMID 14976541.
- ^ a b c Robert V Rouse. "Papillary Urothelial (Transitional Cell) Carcinoma". Stanford University School of Medicine. Original posting/updates: 10/20/12, 12/29/12
- ^ 0.3–1%: Page 77 in:Beltran, Antonio (2017). Pathology of the prostate : an algorithmic approach. Cambridge, United Kingdom New York, NY: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1-108-18565-3. OCLC 1011514854.
- ^ 0.5-2%: Kumar, Kishore; Ahmed, Rafeeq; Chukwunonso, Chime; Tariq, Hassan; Niazi, Masooma; Makker, Jasbir; Ihimoyan, Ariyo (2018). "Poorly Differentiated Small-Cell-Type Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the Prostate: A Case Report and Literature Review". Case Reports in Oncology. 11 (3): 676–681. doi:10.1159/000493255. ISSN 1662-6575. PMC 6243899. PMID 30483097.
- ^ Wang, Jue; Wang, Fen Wei; Hemstreet, George P. (2011). "Younger Age Is an Independent Predictor for Poor Survival in Patients with Signet Ring Prostate Carcinoma". Prostate Cancer. 2011: 1–8. doi:10.1155/2011/216169. ISSN 2090-3111. PMC 3216005. PMID 22110982.
- ^ Ninomiya, Sahoko; Kawahara, Takashi; Iwashita, Hiromichi; Iwamoto, Genta; Takamoto, Daiji; Mochizuki, Taku; Kuroda, Shinnosuke; Takeshima, Teppei; Izumi, Koji; Teranishi, Jun-ichi; Yumura, Yasushi; Miyoshi, Yasuhide; Asai, Takuo; Uemura, Hiroji (2018). "Prostate Basal Cell Carcinoma: A Case Report". Case Reports in Oncology. 11 (1): 138–142. doi:10.1159/000487389. ISSN 1662-6575.
- ^ a b Robert V Rouse MD. "Prostatic Adenocarcinoma". Stanford Medical School. Archived from the original on 2019-09-11. Retrieved 2019-10-30. Last update 2/2/16
- ^ Image by Mikael Häggström, MD. Reference for findings: Faryal Shoaib, M.D., Chinedum Okafor, M.D., Y. Albert Yeh, M.D., Ph.D. "Anatomy & histology-seminal vesicles / ejaculatory duct". Pathology Outlines.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) Last staff update: 20 November 2023 - ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Varma, Murali; Delahunt, Brett; Egevad, Lars; Samaratunga, Hemamali; Kristiansen, Glen (2019). "Intraductal carcinoma of the prostate: a critical re-appraisal". Virchows Archiv. 474 (5): 525–534. doi:10.1007/s00428-019-02544-6. ISSN 0945-6317. PMC 6505500. PMID 30825003.
- "This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/),"
Sources
[edit]![]() This article incorporates text from a free content work. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) license. (license statement/permission). Text taken from adenocarcinoma Prostate adenocarcinoma, Patholines.
This article incorporates text from a free content work. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) license. (license statement/permission). Text taken from adenocarcinoma Prostate adenocarcinoma, Patholines.


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch
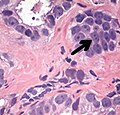


![Also, seminal vesicle glands may mimic prostatic adenocarcinoma by crowded glands with enlarged hyperchromatic and irregular nuclei, but will have inconspicuous nucleoli and coarse refractile golden brown lipofuscin granules.[19]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/d/d2/Histology_of_seminal_vesicle_glands_on_H%26E_stain.jpg/241px-Histology_of_seminal_vesicle_glands_on_H%26E_stain.jpg)
![Intraductal carcinoma of the prostate with an infiltrative growth pattern may be morphologically difficult to distinguish from invasive cancer. One focus shows comedonecrosis (arrow), morphologically suggesting Gleason pattern 5 invasive carcinoma (a haematoxylin and eosin, b CK5/6)[20]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/9/97/Micrograph_of_intraductal_carcinoma_of_the_prostate_with_an_infiltrative_growth_pattern%2C_with_comedonecrosis.jpg/517px-Micrograph_of_intraductal_carcinoma_of_the_prostate_with_an_infiltrative_growth_pattern%2C_with_comedonecrosis.jpg)
![Intraductal carcinoma of the prostate with very patchy basal cells identified by immunohistochemistry. At least some of the glands lacking basal cell immunoreactivity represent intraductal rather than invasive carcinoma (a haematoxylin and eosin, b CK 5/6)[20]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/4b/Micrograph_of_intraductal_carcinoma_of_the_prostate_with_very_patchy_basal_cells.jpg/520px-Micrograph_of_intraductal_carcinoma_of_the_prostate_with_very_patchy_basal_cells.jpg)