Renal capsule
| Renal capsule | |
|---|---|
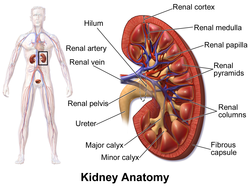 The kidney capsule surrounds both kidneys, and is labelled at the bottom right. | |
 Cross-section, showing the positioning of the kidney capsule | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | capsula fibrosa renis |
| FMA | 66610 |
| Anatomical terminology | |

The renal capsule is a tough fibrous layer surrounding the kidney and covered in a layer of perirenal fat known as the adipose capsule of kidney. The adipose capsule is sometimes included in the structure of the renal capsule. It provides some protection from trauma and damage. The renal capsule is surrounded by the renal fascia. Overlying the renal fascia and between this and the transverse fascia is a region of pararenal fat.[1]
The renal capsule resists stretching, limiting renal swelling, with important implications for renal circulation.[2] Stretching of the renal capsule due to swelling of the kidney causes flank pain.[3]
Structure
[edit]The renal capsule surrounds the functional tissue of the kidney, and is itself surrounded by a fatty adipose capsule, fascia, and fat. From the inner part of the kidney to outside the kidney, the positioning of the capsule is:
- renal medulla
- renal cortex
- renal capsule
- adipose capsule of kidney (or perirenal fat, or perinephric fat)
- renal fascia
- pararenal fat
- peritoneum (anteriorly), and transverse fascia (posteriorly).
Sometimes the adipose capsule of the kidney also known as the perirenal fat, is regarded as a part of the renal capsule.[4]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Squire L (2013). Fundamental neuroscience (4th ed.). Amsterdam: Elsevier/Academic Press. p. 315. ISBN 978-0-12-385870-2.
- ^ Davies, Andrew; Blakeley, Asa G. H.; Kidd, Cecil, eds. (2001). Human physiology. Edinburgh [u.a.]: Churchill Livingstone. p. 717. ISBN 978-0-443-04559-2.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ "Flank Pain - Kidney and Urinary Tract Disorders". MSD Manual Consumer Version. Retrieved 2024-02-29.
- ^ Favre G, Grangeon-Chapon C, Raffaelli C, François-Chalmin F, Iannelli A, Esnault V (2017-04-19). "Perirenal fat thickness measured with computed tomography is a reliable estimate of perirenal fat mass". PLOS ONE. 12 (4): e0175561. Bibcode:2017PLoSO..1275561F. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0175561. PMC 5396915. PMID 28423008.
External links
[edit]- Anatomy image: urogen/dissectkidney2 at Human Anatomy Lecture (Biology 129), Pennsylvania State University
- figures/chapter_29/29-5.HTM: Basic Human Anatomy at Dartmouth Medical School


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch