Shi (rank)
Shi (Chinese: 士; Korean: 사; Hanja: 士) is the rank usually held by Non-commissioned officers in some East Asian militaries. The ranks are used in both the People's Republic of China and Taiwan, and both North and South Korea. The rank name is based on the on one of the four ancient occupations.
China
[edit]The same rank names are used for all services, prefixed by haijun (simplified Chinese: 海军; traditional Chinese: 海軍; lit. 'naval force') or kongjun (simplified Chinese: 空军; traditional Chinese: 空軍; lit. 'air force').
| Rank group | Non-commissioned officers | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese | 一级军士长 | 二级军士长 | 三级军士长 | 四级军士长 | 上士 | 中士 | 下士 |
| Pinyin | Yījí jūnshìzhǎng | Èrjí jūnshìzhǎng | Sānjí jūnshìzhǎng | Sìjí jūnshìzhǎng | Shàngshì | Zhōngshì | Xiàshì |
| Literal translation | First-class soldier leader | Second-class soldier leader | Third-class soldier leader | Fourth-class soldier leader | Upper soldier | Middle soldier | Lower soldier |
 |  |  |  |  |  |  | |
 |  |  |  |  |  |  | |
 |  |  |  |  |  |  | |
| Rank group | Non-commissioned officers | ||||||
Taiwan
[edit]| Rank group | Non-commissioned officers | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chinese | 一等士官長 | 二等士官長 | 三等士官長 | 上士 | 中士 | 下士 |
| Pinyin | Yīděng shìguānzhǎng | Èrděng shìguānzhǎng | Sānděng shìguānzhǎng | Shàngshì | Zhōngshì | Xiàshì |
| Literal translation | First-class officer leader | Second-class officer leader | Third-class officer leader | Upper officer | Middle officer | Lower officer |
 |  |  |  |  |  | |
 |  |  |  |  |  | |
 |  |  |  |  |  | |
 |  |  |  |  |  | |
| 一等士官長 Yīděng shìguānzhǎng | 二等士官長 Èrděng shìguānzhǎng | 三等士官長 Sānděng shìguānzhǎng | 上士 Shàngshì | 中士 Zhōngshì | 下士 Xiàshì | |
| Rank group | Non-commissioned officers | |||||
Japan
[edit]| Rank group | Enlisted | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Japanese | 士長 | 1等士 | 2等士 |
| Romanization | Shichō | Ittō shi | Nitō shi |
| Literal translation | Officer leader | First-class officer | Second-class officer |
 |  | ||
 |  | ||
 |  | ||
| Rank group | Enlisted | ||
North Korea
[edit]| Sa | |
| Hangul | 사 |
|---|---|
| Hanja | |
| Revised Romanization | Sa |
| McCune–Reischauer | Sa |
| Rank group | Non-commissioned officers | Enlisted | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hangul | 특무상사 | 상사 | 중사 | 하사 | 상급병사 | 중급병사 | 하급병사 | 전사 |
| Hanja | 特務上士 | 上士 | 中士 | 下士 | 上級兵士 | 中級兵士 | 下級兵士 | 戰士 |
| Romanization | T'ŭkmu-sangsa | Sangsa | Chungsa | Hasa | Sanggŭp-pyŏngsa | Chungŭp-pyŏngsa | Hagŭp-pyŏngsa | Chŏnsa |
| Literal translation | Special duty upper officer | Upper officer | Middle officer | Lower officer | Upper-class soldier | Middle-class soldier | Lower-class soldier | Combat officer |
 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  | |
| U.S. equivalent[4] | Sergeant major | Master sergeant | Sergeant first class | Staff sergeant | Sergeant | Corporal | Private first class | Private |
 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  | |
| U.S. equivalent[4] | Master chief petty officer | Senior chief petty officer | Chief petty officer | Petty officer first class | Petty officer second class | Petty officer third class | Seaman | Seaman apprentice |
 |  |  |  |  |  |  |  | |
| U.S. equivalent[4] | Chief master sergeant | Senior master sergeant | Master sergeant | Technical sergeant | Staff sergeant | Sergeant | Airman first class | Airman |
| 특무상사 T'ŭkmu-sangsa | 상사 Sangsa | 중사 Chungsa | 하사 Hasa | 상급병사 Sanggŭp-pyŏngsa | 중급병사 Chungŭp-pyŏngsa | 하급병사 Hagŭp-pyŏngsa | 전사 Chŏnsa | |
| Rank group | Non-commissioned officers | Enlisted | ||||||
South Korea
[edit]| Rank group | Non-commissioned officer | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hangul | 원사 | 상사 | 중사 | 하사 |
| Hanja | 元士 | 上士 | 中士 | 下士 |
| Romanization | Wonsa | Sangsa | Jungsa | Hasa |
| Literal translation | Chief soldier | Upper soldier | Middle soldier | Lower soldier |
 |  |  |  | |
| U.S. equivalent (Army)[6] | Sergeant major | Master sergeant | Sergeant first class | Staff sergeant |
| U.S. equivalent (Navy)[6] | Master chief petty officer | Senior chief petty officer | Chief petty officer | Petty officer first class |
| U.S. equivalent (Air Force)[6] | Chief master sergeant | Senior master sergeant | Master sergeant | Technical sergeant |
| U.S. equivalent (Marine Corps) | Sergeant major | Master sergeant | Gunnery sergeant | Staff sergeant |
| Rank group | Non-commissioned officers | |||
Vietnamese variant
[edit]| Rank group | Non-commissioned officers | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Vietnamese | Thượng sĩ | Trung sĩ | Hạ sĩ |
| Chữ Hán | 上士 | 中士 | 下士 |
| Literal translation | Upper officer | Middle officer | Lower officer |
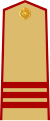 | 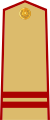 |  | |
 | 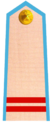 |  | |
| Rank group | Non-commissioned officers | ||
South Vietnamese variant
[edit]| Rank group | Senior NCOs | Junior NCOs | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Native name | Thượng sĩ nhất | Thượng sĩ | Trung sĩ nhất | Trung sĩ | Hạ sĩ nhất | Hạ sĩ |
| Chữ Hán | 上士一 | 上士 | 中士一 | 中士 | 下士一 | 下士 |
| Literal translation | First upper officer | Upper officer | First middle officer | Middle officer | First lower officer | Lower officer |
(1967-1975)[8] |  |  | ||||
| Translation[8] | Master sergeant, first class | Master sergeant | Sergeant first class | Sergeant | Corporal major | Corporal |
(1967-1975)[8] |  |  |  |  | ||
| Translation[8] | Officer | Chief petty officer | Petty officer first class | Petty officer second class | Leading seaman | Able seaman |
(1967-1975) |  |  |  |  | ||
| Translation | Master sergeant, first class | Master sergeant | Sergeant first class | Sergeant | Corporal major | Corporal |
(1967-1975)[8] |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Translation[8] | Master sergeant, first class | Master sergeant | Sergeant first class | Sergeant | Corporal major | Corporal |
| Rank group | Senior NCOs | Junior NCOs | ||||
See also
[edit]- Wei (rank)
- Jiang (rank)
- Xiao (rank)
- Ranks of the People's Liberation Army Ground Force
- Ranks of the People's Liberation Army Navy
- Ranks of the People's Liberation Army Air Force
- Republic of China Armed Forces rank insignia
References
[edit]- ^ a b c Ping, Xu (7 August 2017). "我军建军九十年军衔制度沿革" [The evolution of our military rank system over the ninety years of its establishment]. mod.gov.cn (in Chinese). Ministry of National Defense. Archived from the original on 28 December 2019. Retrieved 13 June 2021.
- ^ a b c d "Lùhǎikōng jūnfú zhì tiáolì fù tú" 陸海空軍服制條例附圖 [Drawings of the Uniform Regulations of the Army, Navy and Air Force] (PDF). Gazette of the Presidential Palace (6769): 65–67. 7 November 1996. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 March 2017. Retrieved 15 August 2022.
- ^ a b c "自衛官の階級" [Self-Defense Forces rank]. mod.go.jp (in Japanese). Japanese Ministry of Defense. Retrieved 7 June 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f Minnich, James M. (2008). "National Security". In Worden, Robert L. (ed.). North Korea: a country study. Area Handbook (5th ed.). Washington, D.C.: Library of Congress. pp. 266, 268. LCCN 2008028547. Retrieved 20 October 2021.
- ^ "gyegeubjang-ui jesig(je7joje2hang gwanlyeon)" 계급장의 제식(제7조제2항 관련) [Rank insignia (related to Article 7 (2))]. law.go.kr (in Korean). Retrieved 30 December 2021.
- ^ a b c Katz, Rodney P. (1992). "National Security". In Savada, Andrea Matles; Shaw, William (eds.). South Korea: a country study. Area Handbook (4th ed.). Washington, D.C.: Library of Congress. p. 292. LCCN 91039109. Retrieved 2 January 2022.
- ^ a b c "Quy định quân hiệu, cấp hiệu, phù hiệu và lễ phục của Quân đội nhân dân Việt Nam". mod.gov.vn (in Vietnamese). Ministry of Defence (Vietnam). 26 August 2009. Archived from the original on 2 December 2021. Retrieved 30 May 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f Armed Forces Information and Education (1968). Uniforms of Seven Allies (DOD GEN-30). Department of Defense. pp. 26–28. Retrieved 2 July 2022.


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch