Kentucky General Assembly
Kentucky General Assembly | |
|---|---|
| 2025 session (adjourned) | |
 | |
| Type | |
| Type | |
| Houses | Senate House of Representatives |
Term limits | None |
| History | |
| Founded | May 26, 1845 |
| Leadership | |
| Structure | |
| Seats | 138 voting members
|
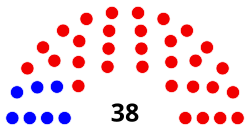 | |
Senate political groups |
|
 | |
House political groups |
|
Length of term | Senate 4 years House of Representatives 2 years |
| Salary | $188.22/day + per diem (elected before January 1, 2023) $203.28/day + per diem (elected after January 1, 2023)[1] |
| Elections | |
Last Senate election | November 5, 2024 (19 seats) |
Last House election | November 5, 2024 |
Next Senate election | November 3, 2026 (19 seats) |
Next House election | November 3, 2026 |
| Redistricting | Legislative control |
| Motto | |
| United we stand, divided we fall | |
| Meeting place | |
 | |
| Kentucky State Capitol Frankfort | |
| Website | |
| https://legislature.ky.gov/Pages/index.aspx | |
The Kentucky General Assembly, also called the Kentucky Legislature, is the state legislature of the U.S. state of Kentucky. It comprises the Kentucky Senate and the Kentucky House of Representatives.
The General Assembly meets annually in the state capitol building in Frankfort, convening on the first Tuesday after the first Monday in January. In even-numbered years, sessions may not last more than 60 legislative days, and cannot extend beyond April 15. In odd-numbered years, sessions may not last more than 30 legislative days, and cannot extend beyond March 30. Special sessions may be called by the Governor of Kentucky at any time and for any duration.
History
[edit]The first meeting of the General Assembly occurred in 1792, shortly after Kentucky was granted statehood. Legislators convened in Lexington, the state's temporary capital. Among the first orders of business was choosing a permanent state capital. In the end, the small town of Frankfort, with their offer to provide a temporary structure to house the legislature and a cache of materials for constructing a permanent edifice, was chosen, and the state's capital has remained there ever since.[2]
After women gained suffrage in Kentucky, Mary Elliott Flanery was elected to the Kentucky House of Representative from the 89th District, representing Boyd County, Kentucky. When Flanery took her seat in January 1922, she was the first female state legislator elected in Kentucky and the first female legislator elected south of the Mason–Dixon line.[3]
Operation Boptrot led to the conviction of more than a dozen legislators between 1992 and 1995. The investigation also led to reform legislation being passed in 1993.[4]
The Civil War
[edit]Due to the strong Southern Unionist sympathies of a large portion of the Commonwealth's citizens and elected officials, Kentucky remained officially neutral during the Civil War. Even so, a group of Confederate sympathizers met in Russellville representing 68 Kentucky counties in the western and central parts of the state in November 1861, to establish a Confederate government for the state. The group established a Confederate state capital in Bowling Green controlling half the state early in the war, but never successfully displaced the elected General Assembly in Frankfort.[5]
Assassination of Governor Goebel
[edit]The General Assembly played a decisive role in the disputed gubernatorial election of 1899. Initial vote tallies had Republican William S. Taylor leading Democrat William Goebel by a scant 2,383 votes.[6] The General Assembly, however, wielded the final authority in election disputes. With a majority in both houses, the Democrats attempted to invalidate enough votes to give the election to Goebel. During the contentious days that followed, an unidentified assassin shot Goebel as he approached the state capitol.[7]
As Goebel hovered on the brink of death, chaos ensued in Frankfort, and further violence threatened. Taylor, serving as governor pending a final decision on the election, called out the militia and ordered the General Assembly into a special session, not in Frankfort, but in London, Kentucky, a Republican area of the state.[6] The Republican minority naturally heeded the call and headed to London. Democrats predictably resisted the call, many retiring to Louisville instead. Both factions claimed authority, but the Republicans were too few in number to muster a quorum.[7]
Goebel died four days after receiving the fatal shot, and the election was eventually contested to the U.S. Supreme Court, who ruled the General Assembly's actions legal and made Goebel's lieutenant governor, J. C. W. Beckham, governor of the state.[8]
Houses
[edit]The General Assembly is bicameral, consisting of a Senate and a House of Representatives.[9] The House and Senate chambers are on opposite ends of the third floor of the capitol building, and legislators have offices in the nearby Capitol Annex building.
Section 33 of the Kentucky Constitution requires that the General Assembly divide the state into 38 Senate and 100 House districts. Districts are required to be as nearly equal in population as possible. Districts can be formed by joining more than one county, but the counties forming a district must be contiguous. Districts must be reviewed every 10 years and be re-divided if necessary.
Under the state constitution, only three counties may be divided to form a Senate district—Jefferson (Louisville), Fayette (Lexington) and Kenton (Covington).
Senate
[edit]The Senate is the upper house of the General Assembly.
Terms and qualifications
[edit]According to Section 32 of the Kentucky Constitution, a senator must:
- be at least 30 years old;
- be a citizen of Kentucky;
- have resided in the state at least 6 years and the district at least 1 year prior to election.
Under section 30 of the Kentucky Constitution, senators are elected to four year staggered terms, with half the Senate elected every two years.
Leadership
[edit]Prior to a 1992 constitutional amendment, the Lieutenant Governor of Kentucky presided over the Senate; the 1992 amendment created a new office of President of the Senate to be held by one of the 38 senators.
- President (elected by full body): Robert Stivers (R-25)
- President Pro-Tempore (elected by full body): David P. Givens (R-9)
Additionally, each party elects a floor leader, whip, and caucus chair.
| Republican Party | Democratic Party | |
|---|---|---|
| Floor Leader | Max Wise (R-16) | Gerald Neal (D-33) |
| Whip | Mike Wilson (R-32) | David Yates (D-37) |
| Caucus chair | Robby Mills (R-4) | Reggie Thomas (D-13) |
House of Representatives
[edit]The House of Representatives is the lower house of the General Assembly. Section 47 of the Kentucky Constitution stipulates that all bills for raising revenue must originate in the House of Representatives.
Terms and qualifications
[edit]According to Section 32 of the Kentucky Constitution, a representative must:
- be at least 24 years old;
- be a citizen of Kentucky
- have resided in the state at least 2 years and the district at least 1 year prior to election.
Per section 30 of the Kentucky Constitution, representatives are elected every two years in the November following a regular session of the General Assembly.
Leadership
[edit]- Speaker (elected by full body): David Osborne (R-59)
- Speaker Pro Tempore (elected by full body): David Meade (R-80)
Additionally, each party elects a floor leader, whip, and caucus chair.
| Republican Party | Democratic Party | |
|---|---|---|
| Leader | Steven Rudy (R-1) | Pamela Stevenson (D-43) |
| Whip | Jason Nemes (R-33) | Lindsey Burke (D-75) |
| Caucus chair | Suzanne Miles (R-7) | Al Gentry (D-46) |
Committees
[edit]Senate committees
[edit]| Committee | Chair | Vice Chair |
|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Jason Howell | Gary Boswell |
| Appropriations and Revenue | Christian McDaniel | Amanda Mays Bledsoe |
| Banking and Insurance | Jared Carpenter | Rick Girdler |
| Committee on Committees | Robert Stivers | none |
| Economic Development, Tourism, and Labor | Phillip Wheeler | Shelley Funke Frommeyer |
| Education | Stephen West | Lindsey Tichenor |
| Enrollment | Matt Nunn | none |
| Families and Children | Danny Carroll | Amanda Mays Bledsoe |
| Health and Services | Stephen Meredith | Craig Richardson |
| Judiciary | Brandon J. Storm | Phillip Wheeler |
| Licensing and Occupations | Julie Raque Adams | Jason Howell |
| Natural Resources and Energy | Brandon Smith | Gex Williams |
| Rules | Robert Stivers | none |
| State and Local Government | Michael J. Nemes | Greg Elkins |
| Transportation | Jimmy Higdon | Donald Douglas |
| Veterans, Military Affairs, and Public Protection | Matthew Deneen | Aaron Reed |
House of Representatives committees
[edit]| Committee | Chair | Vice Chair(s) |
|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Myron Dossett | Daniel Fister |
| Appropriations and Revenue | Jason Petrie | Adam Bowling and Josh Bray |
| Banking and Insurance | Michael Meredith | Matt Lockett and Michael Pollock |
| Committee on Committees | David W. Osborne | David Meade |
| Economic Development and Workforce Investment | Josh Branscum | Thomas Huff |
| Elections, Const. Amendments, and Intergovermental Affairs | DJ Johnson | John Hodgson |
| Enrollment | Thomas Huff | none |
| Families and Children | Samara Heavrin | Nick Wilson |
| Health Services | Kimberly Poore Moser | Robert Duvall |
| Judiciary | Daniel Elliott | Jennifer Decker |
| Licensing, Occupations, and Administrative Regulations | Matthew Koch | Tom Smith |
| Local Government | Patrick Flannery | Amy Neighbors |
| Natural Resources and Energy | Jim Gooch Jr. | Jared Bauman and Richard White |
| Postsecondary Education | James Tipton | Shane Baker |
| Primary and Secondary Education | Scott Lewis | Mike Clines |
| Rules | David W. Osborne | David Meade |
| Small Business and Information Technology | Deanna Frazier Gordon | William Lawrence |
| State Government | David Hale | Rebecca Raymer |
| Tourism and Outdoor Recreation | Kim King | Susan Witten |
| Transportation | John Blanton | Mary Beth Imes |
| Veterans, Military Affairs, and Public Protection | Bobby McCool | Billy Wesley |
Legislative Research Commission
[edit]The Kentucky General Assembly is served by a 16-member nonpartisan agency called the Legislative Research Commission (LRC). Created in 1948, the LRC provides the General Assembly with staff and research support including committee staffing, bill drafting, oversight of the state budget and educational reform, production of educational materials, maintenance of a reference library and Internet site, and the preparation and printing of research reports, informational bulletins and a legislative newspaper. It is led by the elected leadership of the Democratic and Republican parties in both the Kentucky House of Representatives and the Kentucky Senate, while the agency is run on a day-to-day basis by a Director.[12]
See also
[edit]- Kentucky Senate
- Kentucky House of Representatives
- List of Kentucky General Assemblies
- Government of Kentucky
References
[edit]- ^ "How much do Kentucky's governor and other elected officials make? Here's a list". Louisville Courier-Journal. Retrieved January 17, 2024.
- ^ Klotter, James. "The General Assembly: Its History, Its Homes, Its Functions". Kentucky Legislative Research Commission. Archived from the original on March 3, 2016. Retrieved December 26, 2013.
- ^ Powers, James C. (1992). John E. Kleber (ed.). The Kentucky Encyclopedia. Lexington, Kentucky: The University Press of Kentucky. pp. 323–324. ISBN 0-8131-1772-0. Retrieved March 11, 2010.
- ^ Lowell Hayes Harrison, James C. Klotter (1997). A New History of Kentucky. University Press of Kentucky. p. 422. ISBN 978-0-8131-2008-9.
- ^ Talbott, Tim (July 31, 2013). "Kentucky's Neutrality during the Civil War". history.ky.gov. By Laura Forde, Bismarck High School, Bismarck, ND. National Endowment for the Humanities, Kentucky Historical Society. Archived from the original on June 8, 2016. Retrieved September 10, 2019.
- ^ a b McQueen, Keven (2001). "William Goebel: Assassinated Governor". Offbeat Kentuckians: Legends to Lunatics. Ill. by Kyle McQueen. Kuttawa, Kentucky: McClanahan Publishing House. ISBN 0-913383-80-5.
- ^ a b Woodson, Urey (1939). The First New Dealer. Louisville, Kentucky: The Standard Press.
- ^ Klotter, James C. (1977). William Goebel: The Politics of Wrath. Lexington, Kentucky: The University Press of Kentucky. ISBN 0-8131-0240-5.
- ^ "The Constitution of the Commonwealth of Kentucky: Informational Bulletin No. 59" (PDF). Kentucky Legislative Research Commission. October 2005. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 2, 2014. Retrieved October 9, 2007.
- ^ "Legislators - Legislative Research Commission". Kentucky Legislative Research Commission. Retrieved January 16, 2024.
- ^ "Legislators - Legislative Research Commission". Kentucky Legislative Research Commission. Retrieved January 16, 2024.
- ^ "About the Legislative Research Commission". Kentucky Legislative Research Commission. Archived from the original on December 10, 2006. Retrieved January 9, 2007.


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch