Leptanilla
| Leptanilla | |
|---|---|
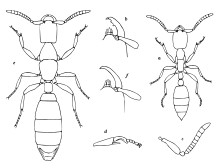 | |
| L. swani queen and worker | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Hymenoptera |
| Family: | Formicidae |
| Tribe: | Leptanillini |
| Genus: | Leptanilla Emery, 1870 |
| Diversity[1] | |
| 44 species | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Leptanilla is a genus of ant in the subfamily Leptanillinae. Like other genera in this subfamily, the queen is fed by the hemolymph of their own larvae, which have specialized processes for this purpose.[2]
Biology
[edit]Some species form colonies consisting of several hundred workers in the soil. They feed on small arthropods, including centipedes, and are rarely seen because they live underground and rarely come to the surface. In some species the queen is wingless, and new colonies form by budding from established colonies. Others have a nomadic life-style resembling that of army ants.[2]
Description
[edit]Leptanilla workers have no eyes, and are pale, yellow, and small.[2]
Distribution
[edit]Several species are found in North Africa, L. doderoi and L. revelierei in Corsica and Sardinia, L. havilandi and L. butteli in the Malay Peninsula, L. santschii in Java.[3] L. swani and L. voldemort are the only two Australian species that have been described.[2][4]
Species
[edit]- Leptanilla africana Baroni Urbani, 1977
- Leptanilla alexandri Dlussky, 1969
- Leptanilla astylina Petersen, 1968
- Leptanilla australis Baroni Urbani, 1977
- Leptanilla besucheti Baroni Urbani, 1977
- Leptanilla bifurcata Kugler, 1987
- Leptanilla boltoni Baroni Urbani, 1977
- Leptanilla buddhista Baroni Urbani, 1977
- Leptanilla butteli Forel, 1913 — Malay Peninsula
- Leptanilla charonea Barandica, López, Martínez & Ortuño, 1994
- Leptanilla clypeata Yamane & Ito, 2001
- Leptanilla doderoi Emery, 1915 — Corsica, Sardinia
- Leptanilla escheri (Kutter, 1948)
- Leptanilla exigua Santschi, 1908 — North Africa
- Leptanilla havilandi Forel, 1901 — Malay Peninsula
- Leptanilla hunanensis Tang, Li & Chen, 1992
- Leptanilla hypodracos Wong & Guénard, 2016[5]
- Leptanilla islamica Baroni Urbani, 1977
- Leptanilla israelis Kugler, 1987
- Leptanilla japonica Baroni Urbani, 1977
- Leptanilla judaica Kugler, 1987
- Leptanilla kebunraya Yamane & Ito, 2001
- Leptanilla kubotai Baroni Urbani, 1977
- Leptanilla kunmingensis Xu & Zhang, 2002
- Leptanilla lamellata Bharti & Kumar, 2012
- Leptanilla macauensis Leong, Yamane & Guénard, 2018 — Macau
- Leptanilla minuscula Santschi, 1907 — North Africa
- Leptanilla morimotoi Yasumatsu, 1960
- Leptanilla nana Santschi, 1915 — North Africa
- Leptanilla oceanica Baroni Urbani, 1977
- Leptanilla ortunoi López, Martínez & Barandica, 1994
- Leptanilla palauensis (Smith, 1953)
- Leptanilla plutonia López, Martínez & Barandica, 1994
- Leptanilla poggii Mei, 1995
- Leptanilla revelierii Emery, 1870 — Corsica, Sardinia, Morocco
- Leptanilla santschii Wheeler & Wheeler, 1930 — Java
- Leptanilla swani Wheeler, 1932 — Western Australia
- Leptanilla taiwanensis Ogata, Terayama & Masuko, 1995
- Leptanilla tanakai Baroni Urbani, 1977
- Leptanilla tanit Santschi, 1907
- Leptanilla tenuis Santschi, 1907 — North Africa
- Leptanilla thai Baroni Urbani, 1977
- Leptanilla theryi Forel, 1903 — North Africa
- Leptanilla vaucheri Emery, 1899 — North Africa
- Leptanilla voldemort Wong et al, 2024 — Western Australia
- Leptanilla yunnanensis Xu, 2002
- Leptanilla zaballosi Barandica, López, Martínez & Ortuño, 1994
References
[edit]- ^ Bolton, B. (2014). "Leptanilla". AntCat. Retrieved 20 July 2014.
- ^ a b c d Genus Leptanilla Australian Ants Online
- ^ Wheeler (1932): An Australian Leptanilla. Psyche 39: 53-58. PDF
- ^ Gartner, Annelies; Australia, University of Western. "New species of ant found pottering under the Pilbara named after Voldemort". phys.org. Retrieved 3 May 2024.
- ^ Zoo Bank
External links
[edit] Media related to Leptanilla at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Leptanilla at Wikimedia Commons


 French
French Deutsch
Deutsch